Proteopedia:Featured EDU/9
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (One intermediate revision not shown.) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
<imagemap> | <imagemap> | ||
Image:2vv5-2oau-morf-mechanosensitive-channel.gif|center | Image:2vv5-2oau-morf-mechanosensitive-channel.gif|center | ||
| - | default [[ | + | default [[Mechanosensitive channels: opening and closing]] |
</imagemap> | </imagemap> | ||
</td></tr> | </td></tr> | ||
<tr><td><div class="scrolling">'''Touch-Sensitive Channel'''<br> | <tr><td><div class="scrolling">'''Touch-Sensitive Channel'''<br> | ||
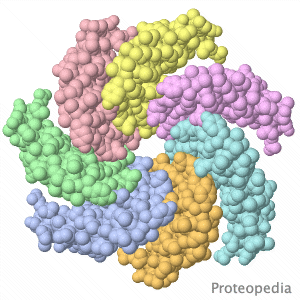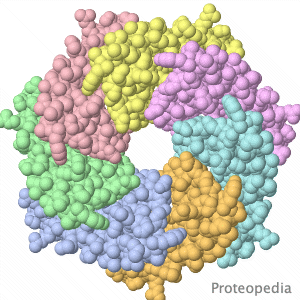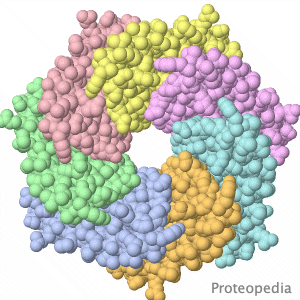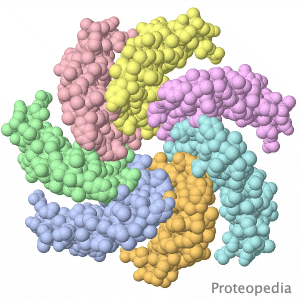
| - | Touching stretches cell membranes, opening mechanosensitive ion channels, leading to sensation. | + | Touching stretches cell membranes, opening mechanosensitive ion channels, leading to sensation by the nervous system. |
Pictured is the transmembrane region of a similar channel in bacteria. When closed, the narrow opening is lined by hydrophobic | Pictured is the transmembrane region of a similar channel in bacteria. When closed, the narrow opening is lined by hydrophobic | ||
amino acid sidechains, making it non-conductive to ions. | amino acid sidechains, making it non-conductive to ions. | ||
Current revision
Touch-Sensitive Channel
Touching stretches cell membranes, opening mechanosensitive ion channels, leading to sensation by the nervous system. Pictured is the transmembrane region of a similar channel in bacteria. When closed, the narrow opening is lined by hydrophobic amino acid sidechains, making it non-conductive to ions. |