We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
A1YIY3 9GAMM
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (3 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | <Structure load='3p4g' size='350' frame='true' align='right' caption=' | + | <Structure load='3p4g' size='350' frame='true' align='right' caption='Fragment of beta-helical antifreeze protein complex with Ca+2 ions (green) and acetate (PDB code [[3p4g]])' scene='Insert optional scene name here' /> |
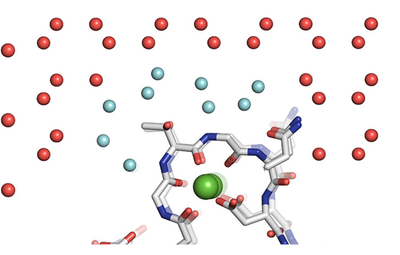
[[Image:IceBind 1.png |thumb|400px| The ice formation of water (red spheres) being scrambled (blue spheres) by the protein]] | [[Image:IceBind 1.png |thumb|400px| The ice formation of water (red spheres) being scrambled (blue spheres) by the protein]] | ||
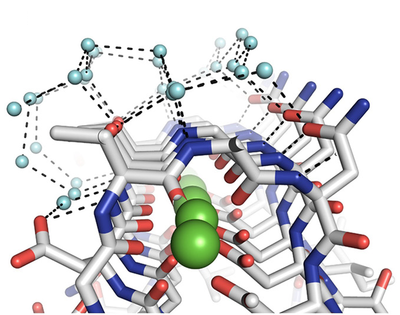
[[Image:IceBind 2.png |thumb|400px| Threonines and Aspartates are lined up in a manner that binds nearby water molecules in a manner that is off-set from the ice crystal lattice]] | [[Image:IceBind 2.png |thumb|400px| Threonines and Aspartates are lined up in a manner that binds nearby water molecules in a manner that is off-set from the ice crystal lattice]] | ||
== Marinomonas primoryensis == | == Marinomonas primoryensis == | ||
| + | |||
| + | Isolated from marine coastal sea-ice. Marinomonas primoryensis is aerobic, Gram-negative, psychrophilic, halophilic and motile by means of a single polar flagellum. This bacteria survives in extreme cold and high salinity environments. | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
| - | <scene name='10/1080038/Calcium_ions/2'>Calcium</scene> | + | |
| + | The distinct beta-sheet roll in this ice binding protein is stabilized by a series of <scene name='10/1080038/Calcium_ions/2'>Calcium ions</scene>. This beta sheet roll sets up in a row several amino acids capable of forming a hydrogen bond with water creating a | ||
<scene name='10/1080038/Ice-binding_site/1'>Ice-Binding Site</scene> | <scene name='10/1080038/Ice-binding_site/1'>Ice-Binding Site</scene> | ||
Current revision
|
Marinomonas primoryensis
Isolated from marine coastal sea-ice. Marinomonas primoryensis is aerobic, Gram-negative, psychrophilic, halophilic and motile by means of a single polar flagellum. This bacteria survives in extreme cold and high salinity environments.
Structural highlights
The distinct beta-sheet roll in this ice binding protein is stabilized by a series of . This beta sheet roll sets up in a row several amino acids capable of forming a hydrogen bond with water creating a
References
Garnham, Christopher P., Robert L. Campbell, and Peter L. Davies. "Anchored clathrate waters bind antifreeze proteins to ice." Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 108.18 (2011): 7363-7367.