Journal:Acta Cryst D:S2059798325007089
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)

| (One intermediate revision not shown.) | |||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
Cells rely on finely tuned machinery to build and maintain their membranes, balancing the insertion, folding, and removal of proteins. In ''E. coli'', this process is thought to involve the protease FtsH, the insertase YidC, and the regulatory HflKC complex. But their partnership had never been seen directly. To investigate, researchers turned to single-particle cryo-electron microscopy on detergent-solubilized samples enriched in these proteins. | Cells rely on finely tuned machinery to build and maintain their membranes, balancing the insertion, folding, and removal of proteins. In ''E. coli'', this process is thought to involve the protease FtsH, the insertase YidC, and the regulatory HflKC complex. But their partnership had never been seen directly. To investigate, researchers turned to single-particle cryo-electron microscopy on detergent-solubilized samples enriched in these proteins. | ||
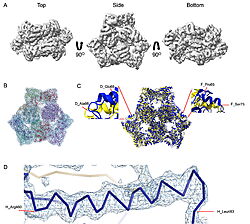
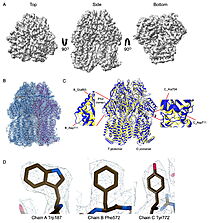
| - | What they found was surprising. Instead of the expected three-part assembly, the cryo-EM maps revealed exquisite structures of two other players: <scene name='10/1089031/022_fig_arna_hexamer/1'>high-resolution structures of ArnA</scene>, an enzyme tied to polymyxin resistance, and <scene name='10/1089031/022_fig_arcb_trimer/1'>AcrB</scene>, the major drug efflux transporter. Structural alignment of the final cryo-EM model (PDB ID [[9v5r]] (blue)) with the reference crystal structure (PDB ID [[7rr7]], (yellow)) shows that they are remarkably similar, with an | + | What they found was surprising. Instead of the expected three-part assembly, the cryo-EM maps revealed exquisite structures of two other players: <scene name='10/1089031/022_fig_arna_hexamer/1'>high-resolution structures of ArnA</scene>, an enzyme tied to polymyxin resistance, and <scene name='10/1089031/022_fig_arcb_trimer/1'>AcrB</scene>, the major drug efflux transporter. <scene name='10/1089031/022_aligned_9v5r_on_7rr7/1'>Structural alignment</scene> of the final cryo-EM model (PDB ID [[9v5r]] (blue)) with the reference crystal structure (PDB ID [[7rr7]], (yellow)) shows that they are remarkably similar, with an superposion of Cryo-EM vs crystal structure for AcrB with an RMSD between them, for CA atoms, of 2.0Å and <scene name='10/1089031/022_aligned_9v5r_on_7rr7/3'>animation</scene> <jmol> |
<jmolButton> | <jmolButton> | ||
<script>animation off</script> | <script>animation off</script> | ||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
</jmol> | </jmol> | ||
| - | Both proteins are known to appear during affinity purification, but their repeated presence across different methods and even in membrane fractions suggests that their recovery was not purely accidental. ArnA, usually described as cytoplasmic, was consistently found in membrane-enriched samples, while AcrB is a well-established membrane protein. | + | Both proteins are known to appear during affinity purification, but their repeated presence across different methods and even in membrane fractions suggests that their recovery was not purely accidental. ArnA, usually described as cytoplasmic, was consistently found in membrane-enriched samples, while AcrB is a well-established membrane protein. It was also observed that the class averages resembled GroEL and cytochrome bo3 oxidase. |
These findings show that cryo-EM can capture not only the intended targets but also unexpected complexes that are well resolved and may have physiological importance. While only partial densities of the FtsH AAA+ domain were visible and no stable FtsH–YidC–HflKC complex could be reconstructed, the high-quality ArnA and AcrB structures provide fresh insights into bacterial survival strategies, from antibiotic resistance to drug efflux. More broadly, this study illustrates how structural biology can reveal unplanned discoveries that enrich our understanding of cell biology and the challenges of protein purification. | These findings show that cryo-EM can capture not only the intended targets but also unexpected complexes that are well resolved and may have physiological importance. While only partial densities of the FtsH AAA+ domain were visible and no stable FtsH–YidC–HflKC complex could be reconstructed, the high-quality ArnA and AcrB structures provide fresh insights into bacterial survival strategies, from antibiotic resistance to drug efflux. More broadly, this study illustrates how structural biology can reveal unplanned discoveries that enrich our understanding of cell biology and the challenges of protein purification. | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
This page complements a publication in scientific journals and is one of the Proteopedia's Interactive 3D Complement pages. For aditional details please see I3DC.