TRPC1 TRPC4 8WPL BI3323 Aug2025
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
(new codes for the images, manual) |
(final changes) |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
2. The structure shows how the antagonist Pico145 binds to the channel, creating a stronger hydrophobic interaction than TRPC4-only channels.<ref>Won, J., Kim, J., Kim, J. et al. (2025). Cryo-EM structure of the heteromeric TRPC1/TRPC4 channel. ''Nature Structural & Molecular Biology'', 32(2):326–338. DOI: 10.1038/s41594-024-01408-1</ref>. This can explain why Pico145 is more potent against TRPC1-containing channels or how drug binding is influenced by heteromer composition. This information can improve selectivity and reduce side effects. | 2. The structure shows how the antagonist Pico145 binds to the channel, creating a stronger hydrophobic interaction than TRPC4-only channels.<ref>Won, J., Kim, J., Kim, J. et al. (2025). Cryo-EM structure of the heteromeric TRPC1/TRPC4 channel. ''Nature Structural & Molecular Biology'', 32(2):326–338. DOI: 10.1038/s41594-024-01408-1</ref>. This can explain why Pico145 is more potent against TRPC1-containing channels or how drug binding is influenced by heteromer composition. This information can improve selectivity and reduce side effects. | ||
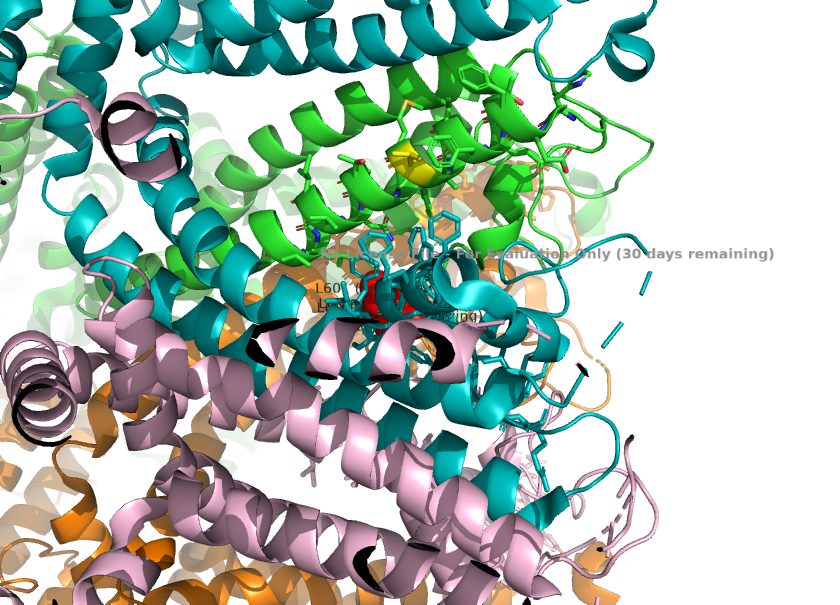
3. Residues in TRPC1, such as L601(selectivity filter) and K639(in the central cavity), explains how TRPC1 alters TRPC4's functions.<ref>Won, J., Kim, J., Kim, J. et al. (2025). Cryo-EM structure of the heteromeric TRPC1/TRPC4 channel. ''Nature Structural & Molecular Biology'', 32(2):326–338. DOI: 10.1038/s41594-024-01408-1</ref>. This helps us understand how ion permeability leads to diseases. | 3. Residues in TRPC1, such as L601(selectivity filter) and K639(in the central cavity), explains how TRPC1 alters TRPC4's functions.<ref>Won, J., Kim, J., Kim, J. et al. (2025). Cryo-EM structure of the heteromeric TRPC1/TRPC4 channel. ''Nature Structural & Molecular Biology'', 32(2):326–338. DOI: 10.1038/s41594-024-01408-1</ref>. This helps us understand how ion permeability leads to diseases. | ||
| - | |||
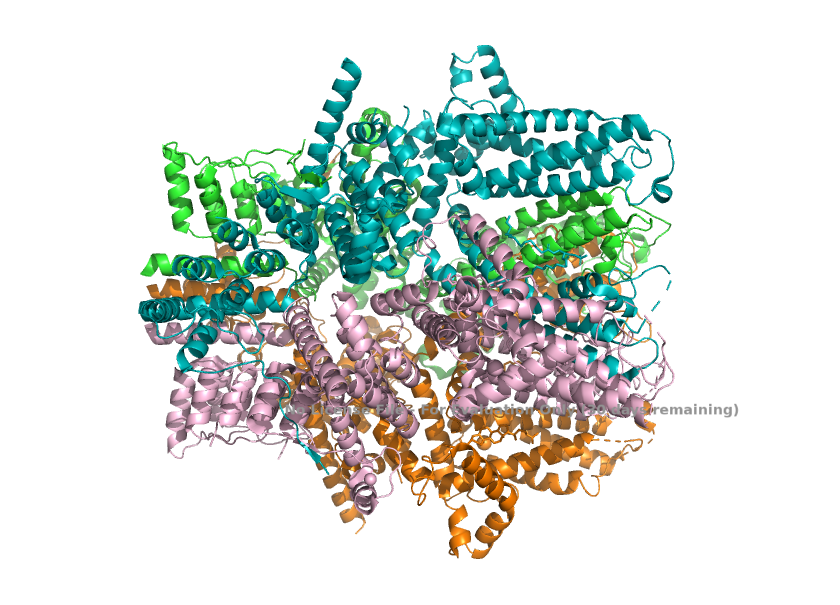
== Structural highlights ==1. The channel, when TRPC1 is incorporated, loses the 4-fold symmetry with one TRPC1 and three TRPC4. This change in arrangement breaks the symmetry of the pore and creates a different, asymmetric ion-conduction pathway. <ref>Won, J., Kim, J., Kim, J. et al. (2025). Cryo-EM structure of the heteromeric TRPC1/TRPC4 channel. ''Nature Structural & Molecular Biology'', 32(2):326–338. DOI: 10.1038/s41594-024-01408-1</ref> | == Structural highlights ==1. The channel, when TRPC1 is incorporated, loses the 4-fold symmetry with one TRPC1 and three TRPC4. This change in arrangement breaks the symmetry of the pore and creates a different, asymmetric ion-conduction pathway. <ref>Won, J., Kim, J., Kim, J. et al. (2025). Cryo-EM structure of the heteromeric TRPC1/TRPC4 channel. ''Nature Structural & Molecular Biology'', 32(2):326–338. DOI: 10.1038/s41594-024-01408-1</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Asymmetry_(TRPC1_TRPC4_Stoichiometry)_.png]] | ||
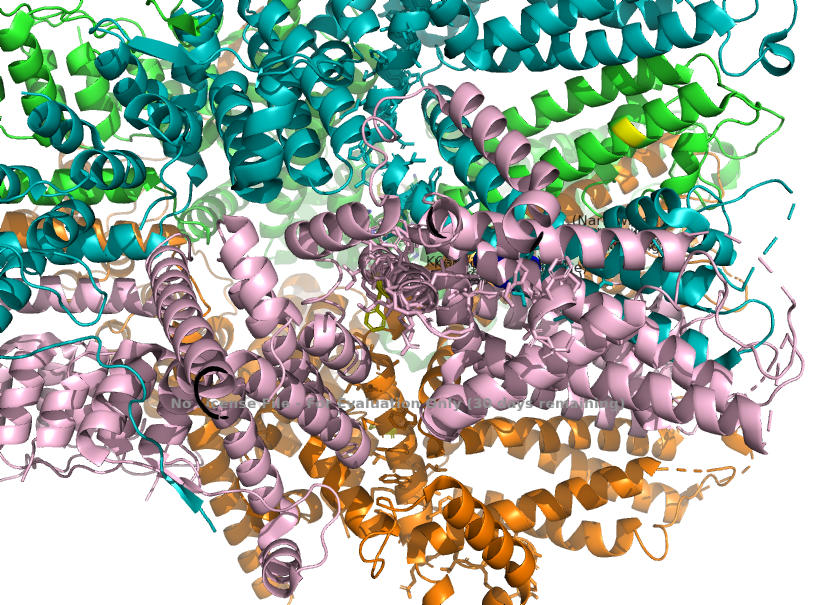
2. The selectivity filter loop(two maino acids longer than the corresponding loop in TRPC4) causes the loop to protrude further into the pore. L601 from TRPC1 is the key residue responsible for this, as it physically projects into the ion pathway, narrowing the pore radius. These change the channels' preference for monovalent channels. | 2. The selectivity filter loop(two maino acids longer than the corresponding loop in TRPC4) causes the loop to protrude further into the pore. L601 from TRPC1 is the key residue responsible for this, as it physically projects into the ion pathway, narrowing the pore radius. These change the channels' preference for monovalent channels. | ||
<ref>Won, J., Kim, J., Kim, J. et al. (2025). Cryo-EM structure of the heteromeric TRPC1/TRPC4 channel. ''Nature Structural & Molecular Biology'', 32(2):326–338. DOI: 10.1038/s41594-024-01408-1</ref> | <ref>Won, J., Kim, J., Kim, J. et al. (2025). Cryo-EM structure of the heteromeric TRPC1/TRPC4 channel. ''Nature Structural & Molecular Biology'', 32(2):326–338. DOI: 10.1038/s41594-024-01408-1</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Selectivity_Filter_Narrowing_(L601)_.png]] | ||
| + | |||
3. Calcium permeability is determined by the S6 helix present depeer in the pore. The TRPC1 subunit provides K639 here, which carries a positive charge in the central cavity of the pore. This creates an electropositive environment repelling calcium, which is also positively charged. <ref>Won, J., Kim, J., Kim, J. et al. (2025). Cryo-EM structure of the heteromeric TRPC1/TRPC4 channel. ''Nature Structural & Molecular Biology'', 32(2):326–338. DOI: 10.1038/s41594-024-01408-1</ref> | 3. Calcium permeability is determined by the S6 helix present depeer in the pore. The TRPC1 subunit provides K639 here, which carries a positive charge in the central cavity of the pore. This creates an electropositive environment repelling calcium, which is also positively charged. <ref>Won, J., Kim, J., Kim, J. et al. (2025). Cryo-EM structure of the heteromeric TRPC1/TRPC4 channel. ''Nature Structural & Molecular Biology'', 32(2):326–338. DOI: 10.1038/s41594-024-01408-1</ref> | ||
| + | [[Image:Calcium_Permeability_(K639_in_S6)_.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| - | === Figure 1: Asymmetric Tetramer Assembly (1:3 Stoichiometry) === | ||
| - | The TRPC1/TRPC4 channel structure (PDB 8WPL) displays an overall asymmetric tetrameric assembly, consisting of one TRPC1 subunit (Chain D) and three TRPC4 subunits (Chains A, B, C). This configuration breaks the expected C4 symmetry. | ||
| - | <StructureSection load='8WPL' size='340' side='right' caption='Figure 1: Overall Asymmetric Assembly of TRPC1/TRPC4 (1:3)' Commands='select all; cartoon; color chain; zoom 100; orient 0 0 0 1 0;'> | ||
| - | </StructureSection> | ||
| - | === Figure 2: The K639 Calcium Gate === | ||
| - | Calcium permeability is dictated by the **K639 residue** on the TRPC1 subunit. This residue protrudes into the central cavity, where its positive charge repels positively charged calcium ions, providing the mechanism for reduced calcium influx. | ||
| - | <StructureSection load='8WPL' size='340' side='right' caption='Figure 2: K639 residue (red) controlling the central cavity' Commands='select all; cartoon; color cartoon chain; select :639.D; wireframe off; spacefill 0.6; color red, :639.D; zoom 150;'> | ||
| - | </StructureSection> | ||
| - | === Figure 3: The L601 Selectivity Filter === | ||
| - | The channel's selectivity for monovalent ions is determined by the **L601 residue** on TRPC1. This residue causes a physical constriction at the selectivity filter, narrowing the pore radius and affecting ion preference. | ||
| - | <StructureSection load='8WPL' size='340' side='right' caption='Figure 3: L601 residue (magenta) constricting the selectivity filter' Commands='select all; cartoon; color cartoon chain; select :601.D; wireframe 0.2; color magenta, :601.D; zoom 200; orient 0 0 0 1 0;'> | ||
| - | </StructureSection> | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Current revision
Overview of the TRPC1/TRPC4 Channel
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Won, J., Kim, J., Kim, J. et al. (2025). Cryo-EM structure of the heteromeric TRPC1/TRPC4 channel. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, 32(2):326–338. DOI: 10.1038/s41594-024-01408-1
- ↑ Won, J., Kim, J., Kim, J. et al. (2025). Cryo-EM structure of the heteromeric TRPC1/TRPC4 channel. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, 32(2):326–338. DOI: 10.1038/s41594-024-01408-1
- ↑ Won, J., Kim, J., Kim, J. et al. (2025). Cryo-EM structure of the heteromeric TRPC1/TRPC4 channel. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, 32(2):326–338. DOI: 10.1038/s41594-024-01408-1
- ↑ Pani, B., Cornatzer, E. et al. (2006). Up-Regulation of Transient Receptor Potential Canonical 1 (TRPC1) following Sarco(endo)plasmic Reticulum Ca²⁺ ATPase 2 Gene Silencing Promotes Cell Survival: A Potential Role for TRPC1 in Darier's Disease. Molecular Biology of the Cell, 17(10):4446–4458.
- ↑ Won, J., Kim, J., Kim, J. et al. (2025). Cryo-EM structure of the heteromeric TRPC1/TRPC4 channel. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, 32(2):326–338. DOI: 10.1038/s41594-024-01408-1
- ↑ Jeon, J., Moore, T. I., Sob, I. et al. (2025). TRPC4 regulates limbic behavior and neuronal development by stabilizing dendrite branches through actomyosin-driven integrin activation. PNAS, 122(33):e2511037ca122.
- ↑ Pani, B., Cornatzer, E. et al. (2006). Up-Regulation of Transient Receptor Potential Canonical 1 (TRPC1) following Sarco(endo)plasmic Reticulum Ca²⁺ ATPase 2 Gene Silencing Promotes Cell Survival: A Potential Role for TRPC1 in Darier's Disease. Molecular Biology of the Cell, 17(10):4446–4458.
- ↑ Jeon, J., Moore, T. I., Sob, I. et al. (2025). TRPC4 regulates limbic behavior and neuronal development by stabilizing dendrite branches through actomyosin-driven integrin activation. PNAS, 122(33):e2511037122.
- ↑ Won, J., Kim, J., Kim, J. et al. (2025). Cryo-EM structure of the heteromeric TRPC1/TRPC4 channel. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, 32(2):326–338. DOI: 10.1038/s41594-024-01408-1
- ↑ Won, J., Kim, J., Kim, J. et al. (2025). Cryo-EM structure of the heteromeric TRPC1/TRPC4 channel. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, 32(2):326–338. DOI: 10.1038/s41594-024-01408-1
- ↑ Won, J., Kim, J., Kim, J. et al. (2025). Cryo-EM structure of the heteromeric TRPC1/TRPC4 channel. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, 32(2):326–338. DOI: 10.1038/s41594-024-01408-1
- ↑ Won, J., Kim, J., Kim, J. et al. (2025). Cryo-EM structure of the heteromeric TRPC1/TRPC4 channel. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, 32(2):326–338. DOI: 10.1038/s41594-024-01408-1
- ↑ Won, J., Kim, J., Kim, J. et al. (2025). Cryo-EM structure of the heteromeric TRPC1/TRPC4 channel. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, 32(2):326–338. DOI: 10.1038/s41594-024-01408-1
- ↑ Won, J., Kim, J., Kim, J. et al. (2025). Cryo-EM structure of the heteromeric TRPC1/TRPC4 channel. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, 32(2):326–338. DOI: 10.1038/s41594-024-01408-1