Classification: MEMBRANE PROTEIN
Organism(s): Homo sapiens
Expression System: Homo sapiens
Mutation(s): No
Deposited: 2024-11-13 Released: 2025-11-05
Deposition Author(s): Jeon, H.M., Eun, J., Kim, Y.
Funding Organization(s): National Research Foundation (NRF, Korea)
Experimental Data Snapshot
Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY
Resolution: 3.85 Å
Aggregation State: PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method: SINGLE PARTICLE
Introduction
Members of the organic anion transporter (OAT) family, including
OAT1, are expressed on the epithelial membrane of the kidney,
liver, brain, intestine, and placenta.[2][3] OAT1 regulates the transport
of organic anion drugs from the blood into kidney epithelial
cells by utilizing the α-ketoglutarate (α-KG) gradient across the
membrane established by the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle.[4] [5]OAT1 also plays a key role in excreting waste from organic drug metabolism and
contributes significantly to drug-drug interactions and drug disposition. However, the structural basis of specific
substrate and inhibitor transport by human OAT1 (hOAT1) has remained elusive. Here are four
cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structures of hOAT1 in its inward-facing conformation: the apo
form, the substrate (olmesartan)-bound form with different anions, and the inhibitor (probenecid)-bound
form.
Cryo-EM structure of hOAT1
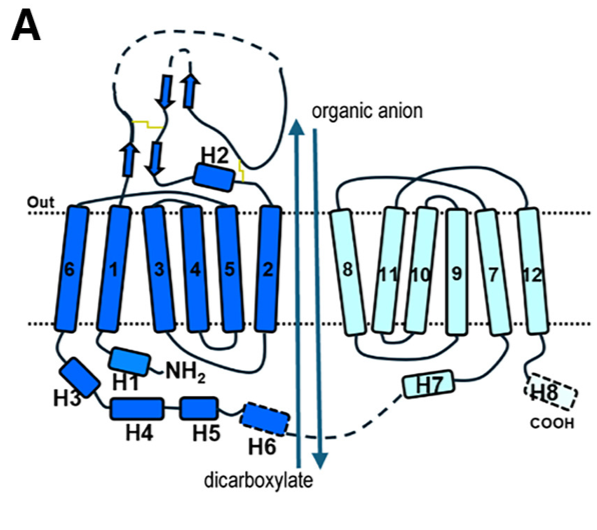
Fig 1. (A) Schematic diagram of human OAT1 topology and the overall transport process.
The apo state structure of human Organic Anion Transporter 1 (hOAT1), determined by cryo-EM, reveals the transporter in an inward-facing conformation. This means the central substrate-binding cavity is open toward the intracellular side of the membrane, ready to release a substrate or accept one from the cytoplasm.
Key Structural Characteristics:
- Adopts the classic Major Facilitator Superfamily (MFS) fold.
- Comprises 12 transmembrane helices (TMs 1-12).
- Exhibits pseudo-two-fold symmetry, divided into an N-lobe (TMs 1-6) and a C-lobe (TMs 7-12).
- The cavity is located between the N-lobe (formed by TM1, TM2, TM4, TM5) and the C-lobe (formed by TM7, TM8, TM10, TM11).
- It possesses a positively charged electrostatic environment, which explains its strong preference for transporting anionic substrates.
- The cavity is lined by 29 residues, forming a hydrophobic and aromatic-rich environment.
- Cavity Borders and Cytosolic Gate:
- The top border (extracellular side) of the cavity is formed by residues including N35, Y230, Y353, and Y354 and are involved in substrate recognition
- The bottom border (cytosolic side) features a narrow "thin bottom gate" formed by residues M207 and F442. The interaction between these two residues splits the cytosolic entrance into two distinct pathways:
- Path A: Located between TM2 and TM11.
- Path B: Located between TM5 and TM8.
- This suggests that aromatic residues located at the top border are important for extracellular anion binding, while residues at the bottom play a role in exporting extracellular anions to the cytoplasmic side.
- In the apo state, the transporter is in a relaxed, inward-open conformation, providing access for substrates from the cytoplasm.
Olmesartan recognition by hOAT1
The structural and functional analysis of provides a detailed blueprint for substrate specificity and binding.
- Olmesartan binds within the central cavity of hOAT1 in an inward-facing conformation where it occupies Site 3 of the binding pocket. The drug adopts a diagonal orientation relative to the membrane plane, a pose that requires more space than the smaller inhibitor probenecid.
- Olmesartan occupies Site 3 of the binding pocket and is located within 5A˚ distance of residues of TM1, TM4, TM5, TM7, TM10, and TM11, namely N35, M207, G227, Y230, W346, Y353, Y354, F438, F442, S462, and R466.
Mechanism of OAT1 inhibition by probenecid
The cryo-EM structure of reveals a dual-mechanism of action that goes beyond simple competition, effectively arresting the transporter in a restricted state.
1. Binding Mode and Direct Competition
- Probenecid binds at the top of the central cavity, parallel to the membrane plane. Its binding site overlaps with both Site 1 (partially) and Site 3.
- In the binding pocket of Site 1, surrounded by 16 residues located within a 5 A ˚ (M31, N35, M142, V145, G227, Y230, W346, Y353, Y354, K382, D378, F438, S462, A465, R466, and S469).
2. Conformational Arrest and Cytoplasmic Path Blockage
The primary inhibitory mechanism is a probenecid-induced conformational change that physically blocks substrate access and exit. Compared to the apo state, the cytoplasmic opening of the binding pocket narrows from ~15 Å to ~12 Å in the probenecid-bound state. Probenecid binding narrows Path A and completely blocks Path B. Restriction of the access route to path B likely limits the entry of substrates to Site 1 and the exit of substrates from the binding pocket.
This structural rearrangement is caused by a slight inward movement of the cytoplasmic ends of TM5, TM8, TM10, and TM11 toward the binding pocket.
3. Locked Conformation
By constricting the cytoplasmic access routes, probenecid does not just compete for the substrate-binding site; it stabilizes the transporter in an apo-like, inward-facing conformation that is inaccessible to cytosolic substrates. This prevents the entry of new substrates and likely traps the transporter in this non-functional state, effectively "locking" it and preventing the conformational changes necessary for the transport cycle.
Mechanistic Insights into hOAT1 Function and Inhibition
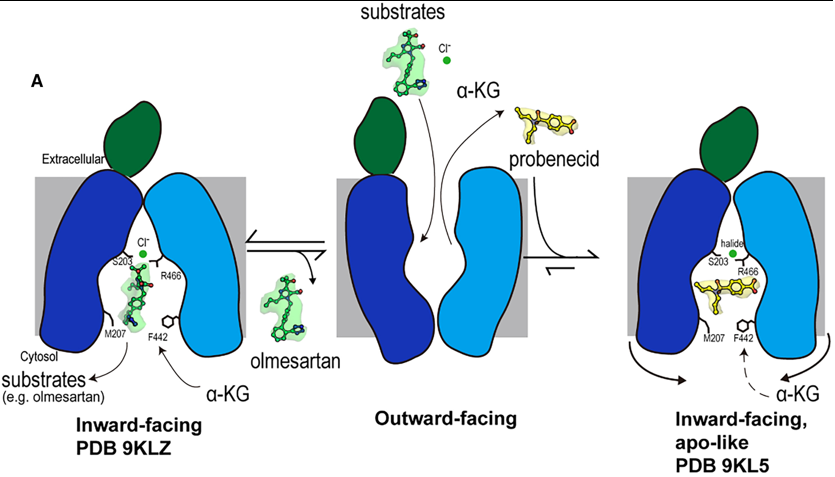
Fig 2. Mechanism of olmesartan binding and conformational inhibition by probenecid. A) When the transporter is in its outward-facing conformation, substrates or inhibitors enter the central binding pocket and undergo structural rearrangement to the inward-facing conformation. When olmesartan interacts with the bottom gating residues M207 and F442, the side chains S203, Y230 (not shown here), and R466 appear to rearrange to coordinate with a chloride ion and drug compared to the apo structure. Whereas probenecid binding induces an additional conformation change for inhibition (apo-like conformation).
A Dual-Mechanism for Potent Inhibition by Probenecid
The study reveals that the classic inhibitor probenecid employs a sophisticated, dual-mechanism to arrest OAT1 function, moving beyond simple competition.
Direct Competition: Probenecid occupies the central binding pocket, and its interaction with K382 in Site 1 directly competes with the binding of the counter-substrate α-ketoglutarate (α-KG). This disrupts the exchange cycle that drives substrate transport.
Conformational Arrest: More significantly, probenecid binding induces subtle conformational changes in the cytoplasmic ends of transmembrane helices (TM5, TM8, TM10, TM11). This leads to a constriction of the cytosolic opening, completely blocking one access path (Path B) and narrowing the other (Path A). This physically prevents substrates from entering or exiting the binding site from the cytoplasm, effectively "locking" the transporter in an inactive, inward-facing state. This mechanism is reminiscent of inhibition seen in other transporters like hURAT1, suggesting it may be a general strategy for effective transport arrest.
Conclusion
rOAT1 structures with probenecid have been reported previously, [6] and our hOAT1 structures align with findings for rOAT1 and provide new insights into the mechanism by which probenecid inhibits transport activity. Additionally, this study reveals the structure of hOAT1 with olmesartan, offering mechanistic insights into species-specific differences in OAT1 transport of specific substrates.
This web page was created for an assignment in Course BI3323-Aug2025 (Structural Biology), IISER, Pune
References
- ↑ Cryo-EM structures of human OAT1 reveal drug
binding and inhibition mechanisms https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2025.07.019
- ↑ Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel liver-specific transport protein https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.107.4.1065
- ↑ Molecular Cloning and Characterization of NKT, a Gene Product Related to the Organic Cation Transporter Family That Is Almost Exclusively Expressed in the Kidney https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.272.10.6471
- ↑ Ingraham, L., Li, M., Renfro, J.L., Parker, S., Vapurcuyan, A., Hanna, I., and
Pelis, R.M. (2014). A plasma concentration of α-ketoglutarate influences
the kinetic interaction of ligands with organic anion transporter 1. Mol.
Pharmacol. 86, 86–95. https://doi.org/10.1124/mol.114.091777.
- ↑ Uwai, Y., Kawasaki, T., and Nabekura, T. (2017). D-Malate decreases renal
content of α-ketoglutarate, a driving force of organic anion transporters
OAT1 and OAT3, resulting in inhibited tubular secretion of phenolsulfonphthalein,
in rats. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 38, 479–485. https://doi.org/10.
1002/bdd.2089.
- ↑ Parker, J.L., Kato, T., Kuteyi, G., Sitsel, O., and Newstead, S. (2023).
Molecular basis for selective uptake and elimination of organic anions in
the kidney by OAT1. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 30, 1786–1793. https://doi.
org/10.1038/s41594-023-01039-y.




