User:Lynmarie K Thompson/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
| (101 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | <applet load=' | + | [[Image:intactModelLargeText.jpg|frame|Bacterial chemotaxis receptor]] |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | Many bacteria can "smell" their surroundings and "choose" where to go. They detect molecules such as amino acids or sugars using receptors that bind these molecules and transmit a signal into the cell. This signal controls several proteins which ultimately control the motors that rotate the flagella to cause the cell to either continue swimming or to tumble. When an attractant molecule binds, it signals: "Things look good, keep swimming!" The opposite signal occurs when bacteria sense decreasing concentrations of attractant molecules: "Time to tumble and try a new swimming direction." | |
| + | |||
| + | |||
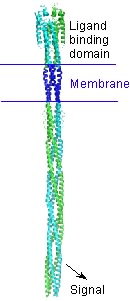
| + | A bacterial chemotaxis receptor is an unusually long alpha-helical structure. The attractant molecule (the ligand) binds near the top of this picture and sends a signal across the membrane into the cell to control proteins that bind near the bottom. This is a model of the structure of the receptor based on experimental structures of pieces of related proteins. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <applet load='1wat' size='[450,338]' frame='true' align='left' | ||
| + | caption='Aspartate receptor ligand binding domain (1wat)' scene='User:Lynmarie_K_Thompson/Sandbox_1/Loadedfrompdb/4'/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | === Ligand-binding domain === | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | The spinning protein (<scene name='User:Lynmarie_K_Thompson/Sandbox_1/Loadedfrompdb/4'>Initial view</scene>) ) is the ligand binding domain of the aspartate receptor with the aspartate ligand bound (LKT). | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Molecular Playground banner: A receptor protein used by bacteria to "smell" their environment. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{Clear}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==Using the new scrollable sections==<StructureSection load='1acj' size='500' side='right' caption='Crystal Structure of tacrine bound to acetylcholinesterase [[1acj]] ' scene=>Anything in this section will appear adjacent to the 3D structure and will be scrollable. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Use the 4 green squares button (top right in edit mode) to insert a structure window with a companion scrolling text section. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Here is a <scene name='User:Lynmarie_K_Thompson/Sandbox_1/Tacrine/1'>green scene</scene> made following the DIY instructions: [[Proteopedia:DIY:Scenes]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | </StructureSection> | ||
Current revision
Many bacteria can "smell" their surroundings and "choose" where to go. They detect molecules such as amino acids or sugars using receptors that bind these molecules and transmit a signal into the cell. This signal controls several proteins which ultimately control the motors that rotate the flagella to cause the cell to either continue swimming or to tumble. When an attractant molecule binds, it signals: "Things look good, keep swimming!" The opposite signal occurs when bacteria sense decreasing concentrations of attractant molecules: "Time to tumble and try a new swimming direction."
A bacterial chemotaxis receptor is an unusually long alpha-helical structure. The attractant molecule (the ligand) binds near the top of this picture and sends a signal across the membrane into the cell to control proteins that bind near the bottom. This is a model of the structure of the receptor based on experimental structures of pieces of related proteins.
|
Ligand-binding domain
The spinning protein () ) is the ligand binding domain of the aspartate receptor with the aspartate ligand bound (LKT).
Molecular Playground banner: A receptor protein used by bacteria to "smell" their environment.
| |||||||||||