Chad Sorenson sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
Retinoblastoma protein has two main domains (<scene name='Chad_Sorenson_sandbox_1/Domain_a/2'>Domain A</scene> and | Retinoblastoma protein has two main domains (<scene name='Chad_Sorenson_sandbox_1/Domain_a/2'>Domain A</scene> and | ||
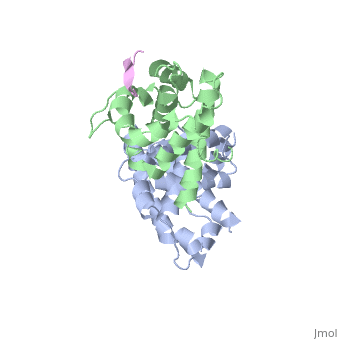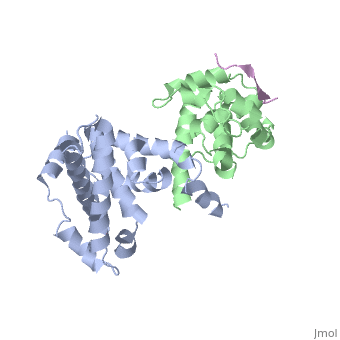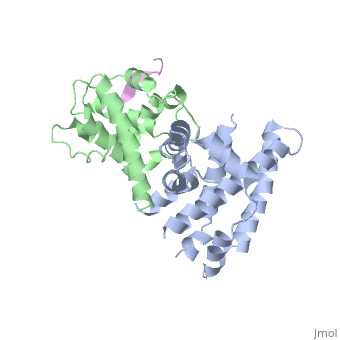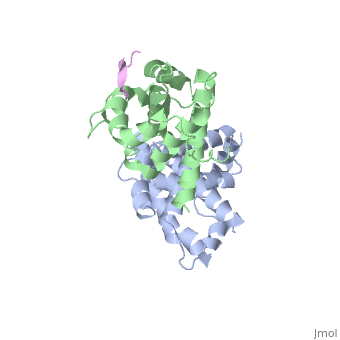
| - | <scene name='Chad_Sorenson_sandbox_1/Domain_b/1'>Domain B</scene>). At the interface of these two domains, there is a pocket that is able to bind and inhibit E2F (transcription factor). You can see pRb bound to E2F <scene name='Chad_Sorenson_sandbox_1/ | + | <scene name='Chad_Sorenson_sandbox_1/Domain_b/1'>Domain B</scene>). At the interface of these two domains, there is a pocket that is able to bind and inhibit E2F (transcription factor). You can see pRb bound to E2F <scene name='Chad_Sorenson_sandbox_1/E2f_and_prb/1'>here</scene>. The role of E2F is to promote the cell into the S phase. Since pRb binds E2F, then it inhibits the cell from entering the S phase. pRb is active when it is not phosphorylated, however when cyclin-dependent kinases (CDK) and cyclins phosphorylate pRb it inactivates the protein. Once it becomes phosphorylated, it releases E2F and then the cell can enter the S phase. |
'''Experimental Observations in Tumors''' | '''Experimental Observations in Tumors''' | ||
Revision as of 14:58, 29 October 2009
Contents |
RETINOBLASTOMA PROTEIN
BACKGROUND
Retinoblastoma protein (pRb)is a regulatory protein that prevents the cell from replicating damaged DNA. It thus keeps the cell in the G1 phase and does not allow the cell to enter the S phase with damaged DNA. This protein is one that is commonly mutated in cancer. The retinoblastoma gene that codes for the protein is a tumor suppressor gene, or a gene that protects a cell from one step on the path to cancer. One can tell early in one's life if they possess mutations in this gene because often mutations in this gene cause the person to develop retinoblastoma cancer, hence the name retinoblastoma. While retinoblastoma cancer is located in the eye, the protein is found in all cells in the human body. It is currently unknown why early mutations in this gene cause retinoblastoma cancer.
Retinoblastoma protein has two main domains ( and ). At the interface of these two domains, there is a pocket that is able to bind and inhibit E2F (transcription factor). You can see pRb bound to E2F . The role of E2F is to promote the cell into the S phase. Since pRb binds E2F, then it inhibits the cell from entering the S phase. pRb is active when it is not phosphorylated, however when cyclin-dependent kinases (CDK) and cyclins phosphorylate pRb it inactivates the protein. Once it becomes phosphorylated, it releases E2F and then the cell can enter the S phase.
Experimental Observations in Tumors
RB POCKET BOUND TO E7 LXCXE MOTIF
Template:ABSTRACT PUBMED 9495340
About this Structure
1GUX is a 3 chains structure of sequences from Homo sapiens and Human papillomavirus. Full crystallographic information is available from OCA.
Reference
- Lee JO, Russo AA, Pavletich NP. Structure of the retinoblastoma tumour-suppressor pocket domain bound to a peptide from HPV E7. Nature. 1998 Feb 26;391(6670):859-65. PMID:9495340 doi:10.1038/36038
Page seeded by OCA on Mon Feb 16 14:09:11 2009