We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox 1b41
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
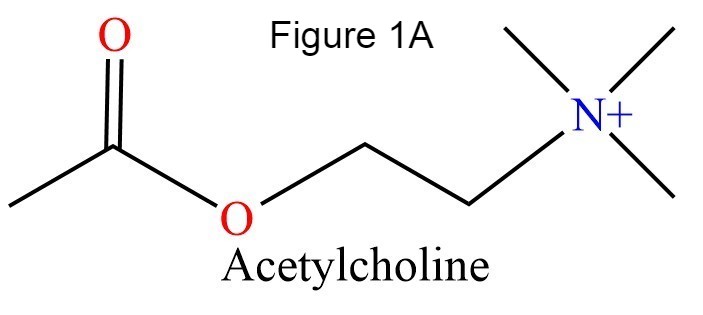
The human acetylcholinesterase (AChE) is an enzyme which hydrolyses the neurotransmitter Acethylcholin (ACh) in the neuromuscular junctions and in other cholinergic synapses to terminate the neuronal signal. | The human acetylcholinesterase (AChE) is an enzyme which hydrolyses the neurotransmitter Acethylcholin (ACh) in the neuromuscular junctions and in other cholinergic synapses to terminate the neuronal signal. | ||
In the physiological conditions, AChE exists as tetramers associated with either collagen-like Q subunit (ColQ) or proline-rich membrane-anchoring protein (PRiMA). There is also a monomeric form which is soluble in the blood. | In the physiological conditions, AChE exists as tetramers associated with either collagen-like Q subunit (ColQ) or proline-rich membrane-anchoring protein (PRiMA). There is also a monomeric form which is soluble in the blood. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Acetylcholine.jpg]] | ||
Revision as of 10:21, 5 November 2009
Human Acetylcholinesterase (1b41)
| |||||||||
| 1b41, resolution 2.76Å () | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligands: | , , | ||||||||
| Gene: | ACHE (Homo sapiens) | ||||||||
| Activity: | Acetylcholinesterase, with EC number 3.1.1.7 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Resources: | FirstGlance, OCA, RCSB, PDBsum | ||||||||
| Coordinates: | save as pdb, mmCIF, xml | ||||||||
The human acetylcholinesterase (AChE) is an enzyme which hydrolyses the neurotransmitter Acethylcholin (ACh) in the neuromuscular junctions and in other cholinergic synapses to terminate the neuronal signal. In the physiological conditions, AChE exists as tetramers associated with either collagen-like Q subunit (ColQ) or proline-rich membrane-anchoring protein (PRiMA). There is also a monomeric form which is soluble in the blood.