Chymotrypsin
From Proteopedia
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
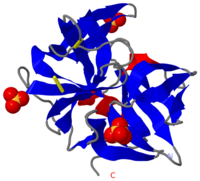
| + | [[Image:2ea3.png|left|200px|thumb|Crystal Structure of ''Cellulomonas Bogoriensis'' Chymotrypsin [[2ea3]]]] | ||
| + | {{STRUCTURE_2ea3| PDB=2ea3 | SIZE=300| SCENE=Chymotrypsin/Cv/1 |right|CAPTION=''Cellulomonas Bogoriensis'' Chymotrypsin [[2ea3]] }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Chymotrypsin]] (Chy or alpha Chy) is a digestive enzyme containing an active serine residue. It cleaves peptide bonds of proteins where the amide side of the bond is an aromatic amino acid like tyrosine, phenylalanine or tryptophane. The Chy precursor is the inactive chymotrypsinogen (Chygen) which gets cleaved 4 times by trypsine losing a 6 amino | ||
| + | acid long peptide to become the active Chy. Gamma Chy is a covalent acyl adduct of alpha Chy . Delta Chy results when Chygen is cleaved only twice by trypsin. The images at the left and at the right correspond to one representative Chymotrypsin, ''i.e.'' the crystal structure of ''Cellulomonas Bogoriensis'' Chymotrypsin ([[2ea3]]). | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{TOC limit|limit=2}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
{{STRUCTURE_1gl0 | PDB=1glo | SCENE='Chymotrypsin/Chymotrypsin_triad/2' }} | {{STRUCTURE_1gl0 | PDB=1glo | SCENE='Chymotrypsin/Chymotrypsin_triad/2' }} | ||
| - | Please click on the <scene name='Chymotrypsin/Chymotrypsin_triad/2'>green links</scene> as you read through the text and watch how the 3D picture on the right changes. | ||
| - | ==Overview== | ||
| + | == Overview == | ||
| + | Please click on the <scene name='Chymotrypsin/Chymotrypsin_triad/2'>green links</scene> as you read through the text and watch how the 3D picture on the right changes. | ||
Chymotrypsin is a protease, an enzyme catalyzing the hydrolysis of peptide bonds of proteins. Chymotrypsin helps to digest proteins in our food. Other proteases are crucial for blood clotting ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bookshelf/br.fcgi?book=stryer&part=A1378&rendertype=figure&id=A1401 thrombin and other proteases]), for the AIDS virus metabolism ([http://www.proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/Hiv_protease HIV protease]) and for many other processes relevant to human health and agriculture. | Chymotrypsin is a protease, an enzyme catalyzing the hydrolysis of peptide bonds of proteins. Chymotrypsin helps to digest proteins in our food. Other proteases are crucial for blood clotting ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bookshelf/br.fcgi?book=stryer&part=A1378&rendertype=figure&id=A1401 thrombin and other proteases]), for the AIDS virus metabolism ([http://www.proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/Hiv_protease HIV protease]) and for many other processes relevant to human health and agriculture. | ||
While chymotrypsin occurs in many organisms, the most-studied chymotrypsin is that from cows (bovine chymotrypsin). In its mature form, bovine chymotrypsin is a protein consisting of 245 amino acids. This string of amino acids folds into a | While chymotrypsin occurs in many organisms, the most-studied chymotrypsin is that from cows (bovine chymotrypsin). In its mature form, bovine chymotrypsin is a protein consisting of 245 amino acids. This string of amino acids folds into a | ||
| - | <scene name='Chymotrypsin/Cpk_oriented/1'>compact structure</scene>. (Can you guess where the substrate might bind? Try spinning around the molecule by dragging it with the mouse cursor. There should be a pocket somewhere on the surface of the enzyme. The active site is colored in this <scene name='Chymotrypsin/Chymotrypsin_spacefill_active/2'>hint</scene>). The path of the backbone is easier to see in this <scene name='Chymotrypsin/Chymotrypsin_fold_rainbow/1'>backbone cartoon</scene>, which shows that chymotrypsin folds into two large beta sheets. | + | <scene name='Chymotrypsin/Cpk_oriented/1'>compact structure</scene>. (Can you guess where the substrate might bind? Try spinning around the molecule by dragging it with the mouse cursor. There should be a pocket somewhere on the surface of the enzyme. The active site is colored in this <scene name='Chymotrypsin/Chymotrypsin_spacefill_active/2'>hint</scene>). The path of the backbone is easier to see in this <scene name='Chymotrypsin/Chymotrypsin_fold_rainbow/1'>backbone cartoon</scene>, which shows that chymotrypsin folds into two large beta sheets. The Chy precursor is the inactive chymotrypsinogen (Chygen) which gets cleaved 4 times by trypsine losing a 6 amino |
| + | acid long peptide to become the active Chy. Gamma Chy is a covalent acyl adduct of alpha Chy . Delta Chy results when Chygen is cleaved only twice by trypsin. | ||
| + | |||
==Active site residues== | ==Active site residues== | ||
The active site of an enzyme is the location where the substrate binds and where the chemical reaction occurs. Active site residues are those amino acid residues demonstrated to have importance for catalysis or substrate binding. Chymotrypsin contains three residues, Ser 195, His 57 and Asp 102, which are known as its <scene name='Chymotrypsin/Chymotrypsin_triad/2'>catalytic triad</scene>. Similar three-dimensional arrangements of a serine, a histidine and an aspartate are observed in many other proteases, and the role of these three residues in catalysis has been studied extensively. Serine acts as a nucleophile (contributing the electron pair for a new bond) attacking the carbonyl carbon of the peptide bond to be hydrolyzed. Histidine and aspartate turn serine into a better nucleophile by assisting in removing a hydrogen ion from serine. | The active site of an enzyme is the location where the substrate binds and where the chemical reaction occurs. Active site residues are those amino acid residues demonstrated to have importance for catalysis or substrate binding. Chymotrypsin contains three residues, Ser 195, His 57 and Asp 102, which are known as its <scene name='Chymotrypsin/Chymotrypsin_triad/2'>catalytic triad</scene>. Similar three-dimensional arrangements of a serine, a histidine and an aspartate are observed in many other proteases, and the role of these three residues in catalysis has been studied extensively. Serine acts as a nucleophile (contributing the electron pair for a new bond) attacking the carbonyl carbon of the peptide bond to be hydrolyzed. Histidine and aspartate turn serine into a better nucleophile by assisting in removing a hydrogen ion from serine. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == 3D Structures of Chymotrypsin == | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Native Chymotrypsin === | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[1yph]] – BtChyA chain A - ''Bos taurus''<br /> | ||
| + | [[4cha]], [[5cha]] – BtChy<br /> | ||
| + | [[2jet]] – RnChygen B chain A,B - ''Rattus norvegicus''<br /> | ||
| + | [[1kdq]] – RnChyB, chain B (mutant)<br /> | ||
| + | [[2ea3]] – Chy – ''Cellulomonas bogoriensis''<br /> | ||
| + | [[1ab9]], [[8gch]], [[1gct]], [[2gct]], [[3gct]], [[2gch]] - gamma BtChy<br /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | === Native Chymotrypsinogen === | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[2cga]], [[1chg]] – BtChygen A | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | === Chymotrypsin + polypeptide inhibitors === | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[1cbw]], [[1mtn]] - BtChy+BPTI <br /> | ||
| + | [[1t7c]], [[1t8l]], [[1t8m]], [[1t8n]], [[1t8o]] – BtChyA+P1 BPTI variants<br /> | ||
| + | [[1oxg]] – BtChyA+autolysis peptide<br /> | ||
| + | [[1p2m]], [[1p2n]], [[1p2o]], [[1p2q]] – BtChyA+ 4 amino acids in S1 pocket<br /> | ||
| + | [[1n8o]] – BtChyA+ecotin<br /> | ||
| + | [[1ca0]] – BtChy+APPI <br /> | ||
| + | [[1acb]] – BtChy+Elgin C <br /> | ||
| + | [[2cho]] – BtChy+turkey ovomucoid third domain | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | === Chymotrypsin + inhibitors === | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[3bg4]] – ChyA chain A+guamerin <br /> | ||
| + | [[2p8o]] - BtChyA chain A+benzohydroxamic acid/vanadate <br /> | ||
| + | [[1eq9]] – Chy+PMSF – fire ant <br /> | ||
| + | [[2cha]] –BtChy+p-sulfinotoluene | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | === Gamma Chymotrypsin + inhibitors === | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[1gg6]] – gamma BtChy+N-acetyl-phenylalanine trifluoromethyl ketone <br /> | ||
| + | [[1ggd]] – gamma BtChy+N-acetyl-phenylalanine trifluoromethyl aldehyde <br /> | ||
| + | [[1afq]] - gamma BtChy+synthetic inhibitor<br /> | ||
| + | [[3gch]], [[4gch]], [[5gch]] - gamma BtChy+cinnamate <br /> | ||
| + | [[6gch]], [[7gch]] - gamma BtChy+trifluoromethy ketone <br /> | ||
| + | [[6cha]] – gamma BtChy+phenylethane boronic acid – transition state inhibitor<br /> | ||
| + | [[1gmc]], [[1gmd]] – gamma BtChy+hexane – transition state inhibitor<br /> | ||
| + | [[2gmt]] - gamma BtChy+N-acetyl-alanyl-phenylalanyl-chloroethyl ketone 1gmh, 1gcd - gamma BtChy+organophosphoryl <br /> | ||
| + | [[1gha]], [[1ghb]] - gamma BtChy+ N-acetyl-tryptophan<br /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | === Gamma Chymotrypsin + reaction transition state inhibitors === | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[6cha]] – gamma BtChy+phenylethane boronic acid <br /> | ||
| + | [[1gmc]], [[1gmd]] – gamma BtChy+hexane | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | === Delta Chymotrypsin + inhibitors === | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[1dlk]] – delta BtChy+peptidyl chloromethyl ketone | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | === Chymotrypsinogen + inhibitors === | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[1gl0]], [[1gli]] – ChygenA+PMP_D2v – ''Locusta migratoria''<br /> | ||
| + | [[1k2i]] - BtChygen+7-hydroxycoumarin | ||
==Further reading== | ==Further reading== | ||
You can learn more about chymotrypsin structure, function and regulation in this publicly available [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bookshelf/br.fcgi?book=stryer&part=A1170#A1171 chapter] of the Biochemistry textbook by Berg, Tymoczka and Stryer. | You can learn more about chymotrypsin structure, function and regulation in this publicly available [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bookshelf/br.fcgi?book=stryer&part=A1170#A1171 chapter] of the Biochemistry textbook by Berg, Tymoczka and Stryer. | ||
Revision as of 13:26, 9 December 2010
Chymotrypsin (Chy or alpha Chy) is a digestive enzyme containing an active serine residue. It cleaves peptide bonds of proteins where the amide side of the bond is an aromatic amino acid like tyrosine, phenylalanine or tryptophane. The Chy precursor is the inactive chymotrypsinogen (Chygen) which gets cleaved 4 times by trypsine losing a 6 amino acid long peptide to become the active Chy. Gamma Chy is a covalent acyl adduct of alpha Chy . Delta Chy results when Chygen is cleaved only twice by trypsin. The images at the left and at the right correspond to one representative Chymotrypsin, i.e. the crystal structure of Cellulomonas Bogoriensis Chymotrypsin (2ea3).
| |||||||||||
Overview
Please click on the as you read through the text and watch how the 3D picture on the right changes. Chymotrypsin is a protease, an enzyme catalyzing the hydrolysis of peptide bonds of proteins. Chymotrypsin helps to digest proteins in our food. Other proteases are crucial for blood clotting (thrombin and other proteases), for the AIDS virus metabolism (HIV protease) and for many other processes relevant to human health and agriculture.
While chymotrypsin occurs in many organisms, the most-studied chymotrypsin is that from cows (bovine chymotrypsin). In its mature form, bovine chymotrypsin is a protein consisting of 245 amino acids. This string of amino acids folds into a . (Can you guess where the substrate might bind? Try spinning around the molecule by dragging it with the mouse cursor. There should be a pocket somewhere on the surface of the enzyme. The active site is colored in this ). The path of the backbone is easier to see in this , which shows that chymotrypsin folds into two large beta sheets. The Chy precursor is the inactive chymotrypsinogen (Chygen) which gets cleaved 4 times by trypsine losing a 6 amino acid long peptide to become the active Chy. Gamma Chy is a covalent acyl adduct of alpha Chy . Delta Chy results when Chygen is cleaved only twice by trypsin.
Active site residues
The active site of an enzyme is the location where the substrate binds and where the chemical reaction occurs. Active site residues are those amino acid residues demonstrated to have importance for catalysis or substrate binding. Chymotrypsin contains three residues, Ser 195, His 57 and Asp 102, which are known as its . Similar three-dimensional arrangements of a serine, a histidine and an aspartate are observed in many other proteases, and the role of these three residues in catalysis has been studied extensively. Serine acts as a nucleophile (contributing the electron pair for a new bond) attacking the carbonyl carbon of the peptide bond to be hydrolyzed. Histidine and aspartate turn serine into a better nucleophile by assisting in removing a hydrogen ion from serine.
3D Structures of Chymotrypsin
Native Chymotrypsin
1yph – BtChyA chain A - Bos taurus
4cha, 5cha – BtChy
2jet – RnChygen B chain A,B - Rattus norvegicus
1kdq – RnChyB, chain B (mutant)
2ea3 – Chy – Cellulomonas bogoriensis
1ab9, 8gch, 1gct, 2gct, 3gct, 2gch - gamma BtChy
Native Chymotrypsinogen
Chymotrypsin + polypeptide inhibitors
1cbw, 1mtn - BtChy+BPTI
1t7c, 1t8l, 1t8m, 1t8n, 1t8o – BtChyA+P1 BPTI variants
1oxg – BtChyA+autolysis peptide
1p2m, 1p2n, 1p2o, 1p2q – BtChyA+ 4 amino acids in S1 pocket
1n8o – BtChyA+ecotin
1ca0 – BtChy+APPI
1acb – BtChy+Elgin C
2cho – BtChy+turkey ovomucoid third domain
Chymotrypsin + inhibitors
3bg4 – ChyA chain A+guamerin
2p8o - BtChyA chain A+benzohydroxamic acid/vanadate
1eq9 – Chy+PMSF – fire ant
2cha –BtChy+p-sulfinotoluene
Gamma Chymotrypsin + inhibitors
1gg6 – gamma BtChy+N-acetyl-phenylalanine trifluoromethyl ketone
1ggd – gamma BtChy+N-acetyl-phenylalanine trifluoromethyl aldehyde
1afq - gamma BtChy+synthetic inhibitor
3gch, 4gch, 5gch - gamma BtChy+cinnamate
6gch, 7gch - gamma BtChy+trifluoromethy ketone
6cha – gamma BtChy+phenylethane boronic acid – transition state inhibitor
1gmc, 1gmd – gamma BtChy+hexane – transition state inhibitor
2gmt - gamma BtChy+N-acetyl-alanyl-phenylalanyl-chloroethyl ketone 1gmh, 1gcd - gamma BtChy+organophosphoryl
1gha, 1ghb - gamma BtChy+ N-acetyl-tryptophan
Gamma Chymotrypsin + reaction transition state inhibitors
6cha – gamma BtChy+phenylethane boronic acid
1gmc, 1gmd – gamma BtChy+hexane
Delta Chymotrypsin + inhibitors
1dlk – delta BtChy+peptidyl chloromethyl ketone
Chymotrypsinogen + inhibitors
1gl0, 1gli – ChygenA+PMP_D2v – Locusta migratoria
1k2i - BtChygen+7-hydroxycoumarin
Further reading
You can learn more about chymotrypsin structure, function and regulation in this publicly available chapter of the Biochemistry textbook by Berg, Tymoczka and Stryer.
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Karsten Theis, Alice Harmon, Alexander Berchansky
