Succinyl-CoA synthetase
From Proteopedia
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<applet load='1cqj' size='300' frame='true' align='right' caption='Structure of succinyl-CoA synthetase' /> | <applet load='1cqj' size='300' frame='true' align='right' caption='Structure of succinyl-CoA synthetase' /> | ||
| - | '''Succinyl-Coa synthetase''' catalyzes the reversible reaction of succinyl-CoA + NDP + Pi <-> succinate + CoA + NTP (where N is either adenosine or guanosine. | + | '''Succinyl-Coa synthetase''' catalyzes the reversible reaction of succinyl-CoA + NDP + Pi <-> succinate + CoA + NTP (where N is either adenosine or guanosine. It can be found in Escherichia coli. |
==Structure== | ==Structure== | ||
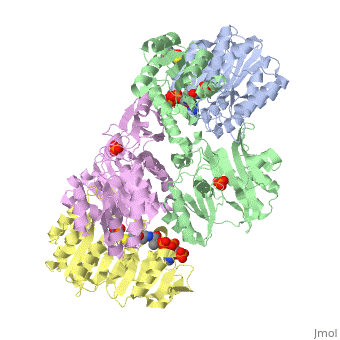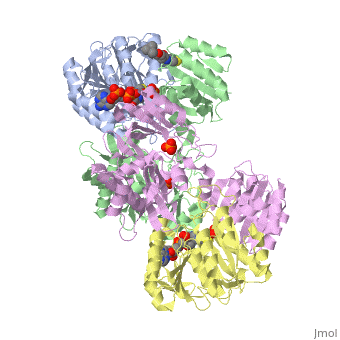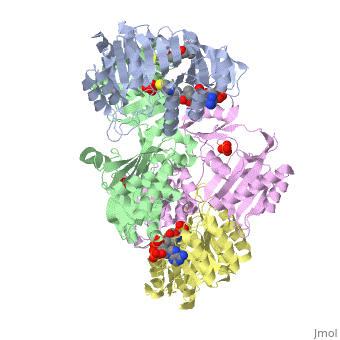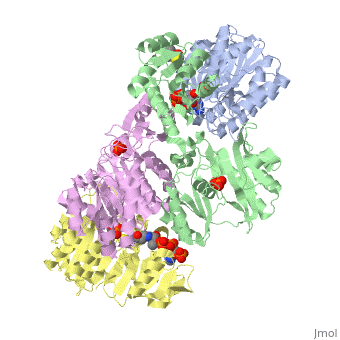
| - | '''Succinyl-CoA synthetase''' is a tetramer with an active site on each dimer. This can be seen in the Jmol representation (the PDB code is 1CQJ). The two dimers are denoted alpha and beta | + | '''Succinyl-CoA synthetase''' is a tetramer with an active site on each dimer. This can be seen in the Jmol representation (the PDB code is 1CQJ). The two dimers are denoted alpha and beta. A phosphorylated histidine intermediate <scene name='Lucas_Hamlow_sandbox_1/Active_histidine_residue/1'>(HIS 246)</scene> is responsible for the dephosphorylation of ATP and it is suspected that there are other active sites on the beta dimer that are responsible for the continued catalysis of the reaction. |
| + | |||
| - | <scene name='Lucas_Hamlow_sandbox_1/Active_sites/1'>The Histidine 246 Residues active in catalysis.</scene> | ||
Revision as of 20:09, 28 February 2010
|
Succinyl-Coa synthetase catalyzes the reversible reaction of succinyl-CoA + NDP + Pi <-> succinate + CoA + NTP (where N is either adenosine or guanosine. It can be found in Escherichia coli.
Structure
Succinyl-CoA synthetase is a tetramer with an active site on each dimer. This can be seen in the Jmol representation (the PDB code is 1CQJ). The two dimers are denoted alpha and beta. A phosphorylated histidine intermediate is responsible for the dephosphorylation of ATP and it is suspected that there are other active sites on the beta dimer that are responsible for the continued catalysis of the reaction.
Trypsin-BPTI complex
The trypsin backbone is shown in pink and the trypsin inhibitor, BPTI, in yellow (PDB code 2ptc). The residues [Ser195-His57-Asp102-Ser214] are shown in green, the disulfide bond between residues 14-38 is shown in yellow and the Lys 15 sidechain at the specificity site in pink.
Content Donators
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Lucas Hamlow, J.D. McClintic, Wayne Decatur, David Canner, Alexander Berchansky