This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
User:Liz Thomas/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
| + | FoxP2 is a transcription factor containing a winged-helix DNA binding domain, and is necessary for proper development of the lungs and brain. It is located on human chromosome 7 (7q31), and comprises 715 amino acids in its major splice form. FoxP2 is a member of the FOX (forkhead box) family and foxP subfamily of proteins, all of which contain a 90 amino acid winged-helix DNA binding motif. The foxP subfamily contains motifs like a glutamine-rich region, a leucine zipper, a zinc finger, and a forkhead domain, and is notable for conducting domain swapping. | ||
==Evolutionary Conservation== | ==Evolutionary Conservation== | ||
| - | + | Because foxP2 is the first protein to be solidly linked to a human speech disorder, much investigation has focused on its evolutionary history in hopes of elucidating the molecular mechanism behind the uniqueness of human speech. Evidence suggests that the protein underwent a recent selective sweep within the same time frame as the rise of language in modern humans, supporting this idea. | |
| + | Chimpanzee, gorilla, and rhesus monkey foxP2 sequences are identical. The human version differs from these primate versions by two amino acid changes: a threonine to asparagine at position 303 and asparagine to serine at position 325. | ||
==DNA Binding== | ==DNA Binding== | ||
| Line 19: | Line 21: | ||
Disease mutations in FOXP2 and related proteins correspond to either the domain-swapping dimer interface or the DNA binding sequence. FOXP2 and FOXP3 are similar enough that the crystal structure of one can be used to explain the effects of mutation on structure in the other. | Disease mutations in FOXP2 and related proteins correspond to either the domain-swapping dimer interface or the DNA binding sequence. FOXP2 and FOXP3 are similar enough that the crystal structure of one can be used to explain the effects of mutation on structure in the other. | ||
| - | === | + | ===Arginine to Histidine at 553=== |
This is the only mutation that has been characterized in the original FOXP2 protein. | This is the only mutation that has been characterized in the original FOXP2 protein. | ||
| - | === | + | ===Isoleucine to Valine at 363=== |
| - | === | + | ===Alanine to Threonine at 385=== |
| - | === | + | ===Arginine to Tryptophan at 397=== |
| - | === | + | ===Phenylalanine to Cystine at 371 and Phenylalanine to Leucine at 371=== |
==References== | ==References== | ||
Revision as of 09:09, 11 March 2010
|
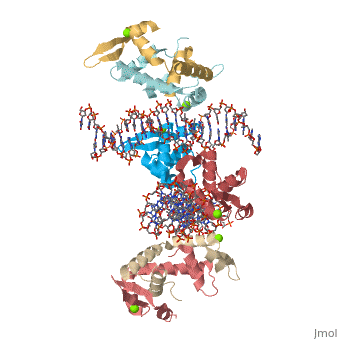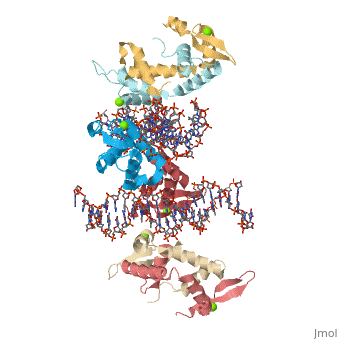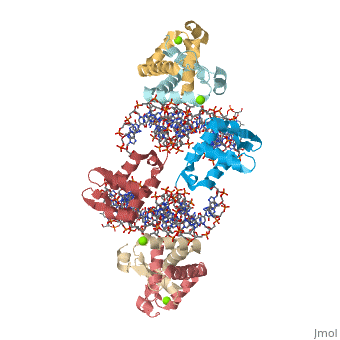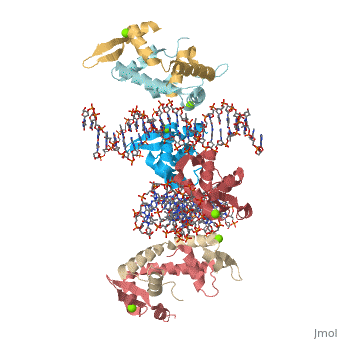
Crystal Structure of Foxp2 bound Specifically to DNA
New Article
|
| |||||||||
| 2a07, resolution 1.90Å () | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligands: | |||||||||
| Gene: | FOXP2, CAGH44, TNRC10 (Homo sapiens) | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Resources: | FirstGlance, OCA, RCSB, PDBsum | ||||||||
| Coordinates: | save as pdb, mmCIF, xml | ||||||||
Contents |
Introduction
FoxP2 is a transcription factor containing a winged-helix DNA binding domain, and is necessary for proper development of the lungs and brain. It is located on human chromosome 7 (7q31), and comprises 715 amino acids in its major splice form. FoxP2 is a member of the FOX (forkhead box) family and foxP subfamily of proteins, all of which contain a 90 amino acid winged-helix DNA binding motif. The foxP subfamily contains motifs like a glutamine-rich region, a leucine zipper, a zinc finger, and a forkhead domain, and is notable for conducting domain swapping.
Evolutionary Conservation
Because foxP2 is the first protein to be solidly linked to a human speech disorder, much investigation has focused on its evolutionary history in hopes of elucidating the molecular mechanism behind the uniqueness of human speech. Evidence suggests that the protein underwent a recent selective sweep within the same time frame as the rise of language in modern humans, supporting this idea. Chimpanzee, gorilla, and rhesus monkey foxP2 sequences are identical. The human version differs from these primate versions by two amino acid changes: a threonine to asparagine at position 303 and asparagine to serine at position 325.
DNA Binding
Domain Swapping
Disease Mutations
Disease mutations in FOXP2 and related proteins correspond to either the domain-swapping dimer interface or the DNA binding sequence. FOXP2 and FOXP3 are similar enough that the crystal structure of one can be used to explain the effects of mutation on structure in the other.
Arginine to Histidine at 553
This is the only mutation that has been characterized in the original FOXP2 protein.
Isoleucine to Valine at 363
Alanine to Threonine at 385
Arginine to Tryptophan at 397
Phenylalanine to Cystine at 371 and Phenylalanine to Leucine at 371
References
- Stroud JC, Wu Y, Bates DL, Han A, Nowick K, Paabo S, Tong H, Chen L. Structure of the forkhead domain of FOXP2 bound to DNA. Structure. 2006 Jan;14(1):159-66. PMID:16407075 doi:10.1016/j.str.2005.10.005
Categories: Homo sapiens | Bates, D L. | Chen, L. | Han, A. | Nowick, K. | Paabo, S. | Stroud, J C. | Tong, H. | Wu, Y. | Double-helix | Forkhead | Homodimer | Magnesium | Monomer | Swapping | Winged-helix