Calcium-free Calmodulin
From Proteopedia
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
Calmodulin is a molecule that has been studied extensively in its functions within the cell, and has an important role in relaying Ca2+ signals within the cytosol. <ref name="1CRT">Hoeflich, K.P., & Ikura, M.. Calmodulin in action: diversity in target recognition and activation mechanisms, Cell. 2002 108:739-742</ref> It does this by binding to Ca2+, undergoing a conformational change, and may interact with various proteins within the cell.<ref name="1CRT"/><ref name="4CRT">PMID: 7552748</ref><ref name="3CRT">PMID: 3145979</ref> Once bound to a target protein, it undergoes a further conformational change and may activate certain systems. For example, there is a Ca2+ pump in the plasma membrane pump that is activated by the binding of Ca2+-bound calmodulin, and then uses ATP to drive the Ca2+ out of the cell. <ref name="6CRT">PMID: 12838335</ref> | Calmodulin is a molecule that has been studied extensively in its functions within the cell, and has an important role in relaying Ca2+ signals within the cytosol. <ref name="1CRT">Hoeflich, K.P., & Ikura, M.. Calmodulin in action: diversity in target recognition and activation mechanisms, Cell. 2002 108:739-742</ref> It does this by binding to Ca2+, undergoing a conformational change, and may interact with various proteins within the cell.<ref name="1CRT"/><ref name="4CRT">PMID: 7552748</ref><ref name="3CRT">PMID: 3145979</ref> Once bound to a target protein, it undergoes a further conformational change and may activate certain systems. For example, there is a Ca2+ pump in the plasma membrane pump that is activated by the binding of Ca2+-bound calmodulin, and then uses ATP to drive the Ca2+ out of the cell. <ref name="6CRT">PMID: 12838335</ref> | ||
| - | + | =='''Calcium-bound Calmodulin'''== | |
[[Image:3cln.png|left|200px]] | [[Image:3cln.png|left|200px]] | ||
| - | The structure of calcium-bound calmodulin had previously been discovered using x-ray crystallography <ref name="3CRT"/> | + | The structure of calcium-bound calmodulin had previously been discovered using x-ray crystallography. <ref name="3CRT"/> It was then theorized that knowledge of the structure of calcium-free calmodulin would give greater insight into the function of the protein. Attempts were made to crystallize the calcium-free (or apo) form, but to no avail, thus it was decided that the only way to get a good idea of the structure would be to use several NMR experiments. <ref name="4CRT"/> |
| - | ==='''Calcium-bound Calmodulin'''=== | ||
| - | [[Image:calmodulin.png|left|200px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | =='''Calcium-free Calmodulin'''== | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:calmodulin.png|right|200px]] | ||
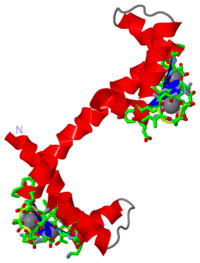
| + | The structure of calcium-free calmodulin was discovered by doing several different NMR experiments that included ROE, reverse labelling of Phe residues, and 3-bond J-couplings. <ref name="4CRT"/> It was theorized that by comparing the results of the NMR experiments for the apo calmodulin with the calcium-bound calmodulin, information could be gleaned as to the structural changes that occur when calcium is bound. It was discovered that the series of residues | ||
| Line 30: | Line 37: | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
| - | <ref group="xtra">PMID:3145979</ref><references group="xtra"/> | ||
| - | <ref group="xtra">PMID:7552748</ref><references group="xtra"/> | ||
Revision as of 06:29, 1 April 2010
Please do NOT make changes to this Sandbox until after April 23, 2010. Sandboxes 151-200 are reserved until then for use by the Chemistry 307 class at UNBC taught by Prof. [[User:Andrea Gorrell|Andrea Chris Truscott
Calcium-free Calmodulin
General InformationCalmodulin is a molecule that has been studied extensively in its functions within the cell, and has an important role in relaying Ca2+ signals within the cytosol. [1] It does this by binding to Ca2+, undergoing a conformational change, and may interact with various proteins within the cell.[1][2][3] Once bound to a target protein, it undergoes a further conformational change and may activate certain systems. For example, there is a Ca2+ pump in the plasma membrane pump that is activated by the binding of Ca2+-bound calmodulin, and then uses ATP to drive the Ca2+ out of the cell. [4] Calcium-bound CalmodulinThe structure of calcium-bound calmodulin had previously been discovered using x-ray crystallography. [3] It was then theorized that knowledge of the structure of calcium-free calmodulin would give greater insight into the function of the protein. Attempts were made to crystallize the calcium-free (or apo) form, but to no avail, thus it was decided that the only way to get a good idea of the structure would be to use several NMR experiments. [2]
Calcium-free CalmodulinThe structure of calcium-free calmodulin was discovered by doing several different NMR experiments that included ROE, reverse labelling of Phe residues, and 3-bond J-couplings. [2] It was theorized that by comparing the results of the NMR experiments for the apo calmodulin with the calcium-bound calmodulin, information could be gleaned as to the structural changes that occur when calcium is bound. It was discovered that the series of residues
References
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Christopher Truscott, David Canner, Alexander Berchansky, Michal Harel, Andrea Gorrell