This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
User:Yadilette Rivera-Colon/Sandbox1
From Proteopedia
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
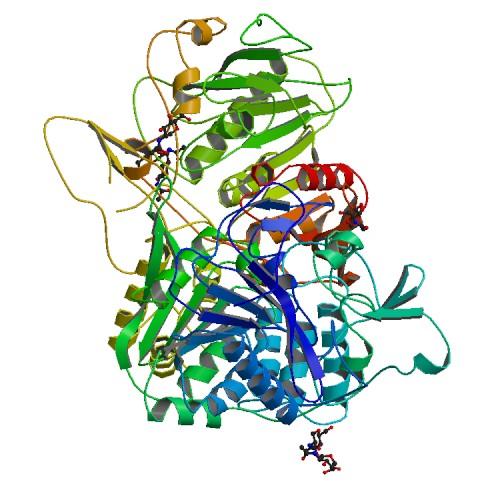
[[Image:PPCA.jpg|frame|Human Lysosomal Protective Protein Cathepsin A]] | [[Image:PPCA.jpg|frame|Human Lysosomal Protective Protein Cathepsin A]] | ||
| - | The human protective protein cathepsin A forms a multi-enzyme complex with beta-galactosidase and neuraminidase in lysosomes. PPCA has so far two functions:a catalytic activity overlapping with that of Cathepsin A and a protective function towards lysosomal beta-galactosidase and neuraminidase. The stability and activity of the latter glycosidases depend on their interaction with PPCA | + | The human protective protein cathepsin A forms a multi-enzyme complex with beta-galactosidase and neuraminidase in lysosomes. PPCA has so far two functions:a catalytic activity overlapping with that of Cathepsin A and a protective function towards lysosomal beta-galactosidase and neuraminidase. The stability and activity of the latter glycosidases depend on their interaction with PPCA [1]. |
{{Clear}} | {{Clear}} | ||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
PPCA, is synthesized as a 542 amino acid precursor with a molecular weight of 54kDa. and it dimerizes soon after synthesis. The sequence contains two glycosylation sites, Asn 117 and Asn 305. It also contains nine cysteines. The spinning protein (<scene name='User:Yadilette_Rivera-Colon/Sandbox1/Glycosylation_sites_ppca/1'>PPCA Glycosylation sites</scene> ) is human protective protein with the glycosylation sites represented in stick model colored by atom. | PPCA, is synthesized as a 542 amino acid precursor with a molecular weight of 54kDa. and it dimerizes soon after synthesis. The sequence contains two glycosylation sites, Asn 117 and Asn 305. It also contains nine cysteines. The spinning protein (<scene name='User:Yadilette_Rivera-Colon/Sandbox1/Glycosylation_sites_ppca/1'>PPCA Glycosylation sites</scene> ) is human protective protein with the glycosylation sites represented in stick model colored by atom. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===References: === | ||
| + | [1] Jackman, H. L., Morris, P. W., Deddish, P. A., Skidgel, R. A. and Erdos, E. G. (1992) J. Biol. Chem. 267, 2872-2875 | ||
Revision as of 23:19, 28 April 2010
Human Lysosomal Protective Protein Cathepsin A (PPCA)
The human protective protein cathepsin A forms a multi-enzyme complex with beta-galactosidase and neuraminidase in lysosomes. PPCA has so far two functions:a catalytic activity overlapping with that of Cathepsin A and a protective function towards lysosomal beta-galactosidase and neuraminidase. The stability and activity of the latter glycosidases depend on their interaction with PPCA [1].
|
PPCA Glycosylation sites
PPCA, is synthesized as a 542 amino acid precursor with a molecular weight of 54kDa. and it dimerizes soon after synthesis. The sequence contains two glycosylation sites, Asn 117 and Asn 305. It also contains nine cysteines. The spinning protein ( ) is human protective protein with the glycosylation sites represented in stick model colored by atom.
References:
[1] Jackman, H. L., Morris, P. W., Deddish, P. A., Skidgel, R. A. and Erdos, E. G. (1992) J. Biol. Chem. 267, 2872-2875