User:Wayne Decatur/Sandbox Glutamate receptor
From Proteopedia
m |
m (→Domains) |
||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
*The 'top' layer is composed of the | *The 'top' layer is composed of the | ||
*<scene name='User:Wayne_Decatur/Sandbox_Glutamate_receptor/Lbd_domain/4'>The ligand-binding domain (LBD)</scene> participates directly in agonist/competitive antagonist binding, affects activation gating, and is the portion that forms the 'middle' layer. | *<scene name='User:Wayne_Decatur/Sandbox_Glutamate_receptor/Lbd_domain/4'>The ligand-binding domain (LBD)</scene> participates directly in agonist/competitive antagonist binding, affects activation gating, and is the portion that forms the 'middle' layer. | ||
| - | ::<scene name='User:Wayne_Decatur/Sandbox_Glutamate_receptor/Lbd_zk1/2'>The competitive antagonist ZK200775 | + | ::<scene name='User:Wayne_Decatur/Sandbox_Glutamate_receptor/Lbd_zk1/2'>The competitive antagonist ZK200775 is bound to the LBD</scene> in the structure. |
::<scene name='User:Wayne_Decatur/Sandbox_Glutamate_receptor/Zk1_zoom/1'>ZK200775, a phosphonate quinoxalinedione AMPA antagonist</scene><ref>PMID: 9724812</ref>, was studied as a treatment for stroke because it had demonstrated neuroprotective efficacy in experimental models of stroke and tolerability in healthy volunteers; however, in a multicenter, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled phase II trial, it was found to have significant sedative effects in patients with acute stroke which precludes its further development as a neuroprotective agent<ref>PMID: 16131799</ref>. | ::<scene name='User:Wayne_Decatur/Sandbox_Glutamate_receptor/Zk1_zoom/1'>ZK200775, a phosphonate quinoxalinedione AMPA antagonist</scene><ref>PMID: 9724812</ref>, was studied as a treatment for stroke because it had demonstrated neuroprotective efficacy in experimental models of stroke and tolerability in healthy volunteers; however, in a multicenter, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled phase II trial, it was found to have significant sedative effects in patients with acute stroke which precludes its further development as a neuroprotective agent<ref>PMID: 16131799</ref>. | ||
*<scene name='User:Wayne_Decatur/Sandbox_Glutamate_receptor/Tmd_domain/2'>The transmembrane domain (TMD)</scene> is the portion that forms the membrane-spanning on the 'bottom' of the solved structure. | *<scene name='User:Wayne_Decatur/Sandbox_Glutamate_receptor/Tmd_domain/2'>The transmembrane domain (TMD)</scene> is the portion that forms the membrane-spanning on the 'bottom' of the solved structure. | ||
Revision as of 03:16, 5 July 2010
Contents |
Background
The glutamate receptor is the ion channel that keeps neurons in touch. Citations [1][2] .
About the Structure of the Glutamate Receptor
| |||||||
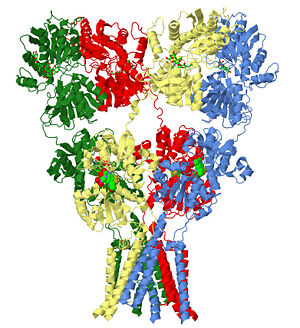
| glutamate receptor (3kg2), resolution 3.6Å () | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resources: | FirstGlance, OCA, PDBsum, RCSB | ||||||
| Coordinates: | save as pdb, mmCIF, xml | ||||||
The homomeric rat GluA2 receptor that are arranged to form a 'Y'-shape with the [3].
Domains
The subunits themselves are modular [4]and in the major domains are found in layers in the tetrameric structure. .
- The 'top' layer is composed of the
- participates directly in agonist/competitive antagonist binding, affects activation gating, and is the portion that forms the 'middle' layer.
- in the structure.
- [5], was studied as a treatment for stroke because it had demonstrated neuroprotective efficacy in experimental models of stroke and tolerability in healthy volunteers; however, in a multicenter, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled phase II trial, it was found to have significant sedative effects in patients with acute stroke which precludes its further development as a neuroprotective agent[6].
- is the portion that forms the membrane-spanning on the 'bottom' of the solved structure.
- To help give a better idea of how the glutamate receptor is oriented on the cell surface in the membrane lipid bilayer, as calculated by the Orientations of Proteins in Membranes database (University of Michigan, USA) is shown with the red patch of spheres indicating the boundary of the hydrophobic core closet to the outside of the cell and the dark blue patch of spheres indicating the boundary closest to the inside of the cell.

- The carboxy-terminal domain that plays a role in both receptor localization and regulation is not seen in the structure but would be below the transmembrane domain as it is cytoplasmic.
Transmembrane domain architecture
I NEED TO LABEL THE SEGMENTS BY COLOR- SHOULD I LIST THEM TOO? PROBABLY!!
Segments shown
To better show the contributions of each of the membrane segments to the interactions, . [Note: this scene generates a substantial surface which may take about a minute to calculate. Be patient.]
PDB Entry
3kg2 is a 4 chains structure of sequences from Rattus norvegicus. Full crystallographic information is available from OCA. Although it is billed as the first structure of a full-length glutamate receptor, the carboxy-terminal domain is not present in the structure.
Reference for the structure
- Sobolevsky AI, Rosconi MP, Gouaux E. X-ray structure, symmetry and mechanism of an AMPA-subtype glutamate receptor. Nature. 2009 Dec 10;462(7274):745-56. Epub . PMID:19946266 doi:10.1038/nature08624
Related Structures
- 3kgc GluA2 ligand-binding core complex bound with glutamate
- 2a5t GluN1-GluN2A ligand-binding domain heterodimer
- 2a5s GluN2A ligand-binding domain bound with glutamate
See Also
References
- ↑ Sobolevsky AI, Rosconi MP, Gouaux E. X-ray structure, symmetry and mechanism of an AMPA-subtype glutamate receptor. Nature. 2009 Dec 10;462(7274):745-56. Epub . PMID:19946266 doi:10.1038/nature08624
- ↑ Wollmuth LP, Traynelis SF. Neuroscience: Excitatory view of a receptor. Nature. 2009 Dec 10;462(7274):729-31. PMID:20010675 doi:10.1038/462729a
- ↑ Sobolevsky AI, Rosconi MP, Gouaux E. X-ray structure, symmetry and mechanism of an AMPA-subtype glutamate receptor. Nature. 2009 Dec 10;462(7274):745-56. Epub . PMID:19946266 doi:10.1038/nature08624
- ↑ Wo ZG, Oswald RE. Unraveling the modular design of glutamate-gated ion channels. Trends Neurosci. 1995 Apr;18(4):161-8. PMID:7539962
- ↑ Turski L, Huth A, Sheardown M, McDonald F, Neuhaus R, Schneider HH, Dirnagl U, Wiegand F, Jacobsen P, Ottow E. ZK200775: a phosphonate quinoxalinedione AMPA antagonist for neuroprotection in stroke and trauma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998 Sep 1;95(18):10960-5. PMID:9724812
- ↑ Walters MR, Kaste M, Lees KR, Diener HC, Hommel M, De Keyser J, Steiner H, Versavel M. The AMPA antagonist ZK 200775 in patients with acute ischaemic stroke: a double-blind, multicentre, placebo-controlled safety and tolerability study. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2005;20(5):304-9. Epub 2005 Aug 30. PMID:16131799 doi:10.1159/000087929
Page started with original page seeded by OCA on Wed Dec 16 11:24:54 2009 for 3kg2.