Molecular Playground/Human Galactosamine-6-sulfatase
From Proteopedia
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
One of the [[CBI Molecules]] being studied in the [http://www.umass.edu/cbi/ University of Massachusetts Amherst Chemistry-Biology Interface Program] at UMass Amherst and on display at the [http://www.molecularplayground.org/ Molecular Playground]. | One of the [[CBI Molecules]] being studied in the [http://www.umass.edu/cbi/ University of Massachusetts Amherst Chemistry-Biology Interface Program] at UMass Amherst and on display at the [http://www.molecularplayground.org/ Molecular Playground]. | ||
| - | ===Human | + | ===Human galactosamine-6-sulfatase (GALNS)=== |
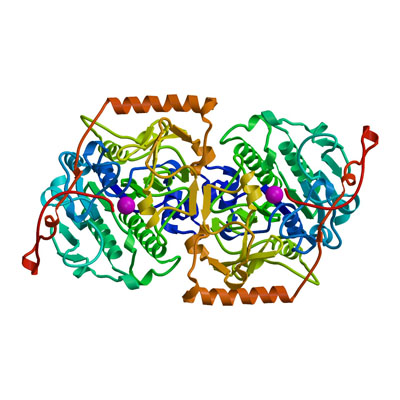
| - | [[Image: | + | [[Image:GALNS.jpg|frame|Human N-acetyl-galactosamine-6-sulfatase]] |
| - | The human | + | The human lysosomal galactosamine-6-sulfatase (E.C. 3.1.6.4), also known as N-acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfatase, removes sulfate groups from a terminal N-acetyl-galactose-6-sulfate (or galactose-6-sulfate) in mucopolysaccharides such as keratan sulfate and chondroitin-6-sulfate Defects in GALNS lead to accumulation of mucopolysaccharides, resulting in the development of the lysosomal storage disease mucopolysaccharidosis 4A (also known as Morquio A disease[1]. |
{{Clear}} | {{Clear}} | ||
| - | <applet load=' | + | <applet load='4FDJ' size='[450,338]' frame='true' align='right' |
| - | caption=' | + | caption='human lysosomal galactosamine-6-sulfatase (4FDI)' scene=''User:Yadilette_Rivera-Colon/Sandbox1/Loadedfrompdb/4'/> |
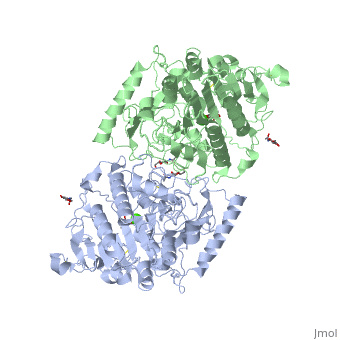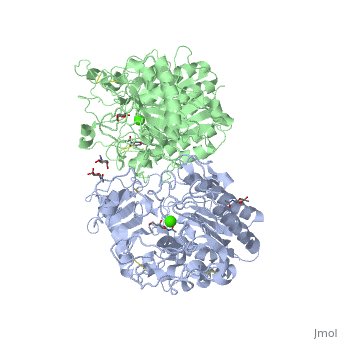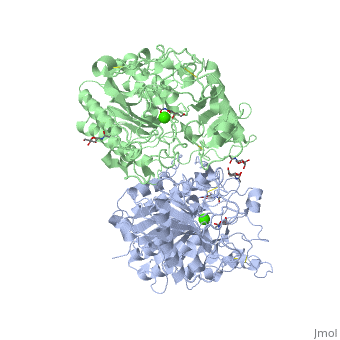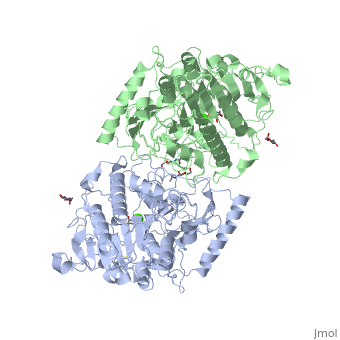
| - | === | + | === GALNS active site === |
| - | + | Sulfatases require maturation of a side chain residue into a catalytic nucleophile. In GALNS, the polypeptide chain encodes a cysteine at residue 79 at the start of the motif CXPXRXXL. The formylglycine generating enzyme recognizes this motif and converts Cys79 into a formylglycine aldehyde. Hydration of the aldehyde by a water molecule generates the gem diol nucleophile dihydroxyalanine, which ligates Ca2+ in the active site. The spinning protein (<scene name='User:Yadilette_Rivera-Colon/Sandbox1/GALNS_active_site/1'>GALNS active site</scene> ) is human human lysosomal galactosamine-6-sulfatase with GalNac in the active site represented by stick. | |
==Additional Resources== | ==Additional Resources== | ||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
===References: === | ===References: === | ||
| - | [1] | + | [1]Muenzer, J. Neufeld, E.F. The Mucopolysaccharidoses: In The Metabolic Basis of Inherited Disease, 8th ed. McGraw-Hill: Medical Publishing Division, 2001; Vol. 3 p 3431-3452. |
| - | Molecular Playground banner: | + | Molecular Playground banner: Human lysosomal galactosamine-6-sulfatase |
Revision as of 17:51, 18 September 2012
One of the CBI Molecules being studied in the University of Massachusetts Amherst Chemistry-Biology Interface Program at UMass Amherst and on display at the Molecular Playground.
Contents |
Human galactosamine-6-sulfatase (GALNS)
The human lysosomal galactosamine-6-sulfatase (E.C. 3.1.6.4), also known as N-acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfatase, removes sulfate groups from a terminal N-acetyl-galactose-6-sulfate (or galactose-6-sulfate) in mucopolysaccharides such as keratan sulfate and chondroitin-6-sulfate Defects in GALNS lead to accumulation of mucopolysaccharides, resulting in the development of the lysosomal storage disease mucopolysaccharidosis 4A (also known as Morquio A disease[1].
|
GALNS active site
Sulfatases require maturation of a side chain residue into a catalytic nucleophile. In GALNS, the polypeptide chain encodes a cysteine at residue 79 at the start of the motif CXPXRXXL. The formylglycine generating enzyme recognizes this motif and converts Cys79 into a formylglycine aldehyde. Hydration of the aldehyde by a water molecule generates the gem diol nucleophile dihydroxyalanine, which ligates Ca2+ in the active site. The spinning protein ( ) is human human lysosomal galactosamine-6-sulfatase with GalNac in the active site represented by stick.
Additional Resources
For additional information, see: Metabolic Disorders
References:
[1]Muenzer, J. Neufeld, E.F. The Mucopolysaccharidoses: In The Metabolic Basis of Inherited Disease, 8th ed. McGraw-Hill: Medical Publishing Division, 2001; Vol. 3 p 3431-3452.
Molecular Playground banner: Human lysosomal galactosamine-6-sulfatase
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Yadilette Rivera-Colon, Ralph A. Francescone III, David Canner, Lynmarie K Thompson