Sandbox 45
From Proteopedia
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
== Secondary Structure == | == Secondary Structure == | ||
| - | Bovine Trypsin contains 3? <scene name='Sandbox_45/Bt-helix/1'>alpha helices</scene> of lengths XYandZ. The two <scene name='Sandbox_45/Bt-sheet1/1'>beta sheets</scene>, A and B, are comprised of 7 and 6 strands. Although both appear as such, only B is technically a beta barrel. In the native conformation, these regular secondary structures interact with themselves and one another at a number of locations by numerous forces of attraction. A closer look at helix X,terminal, shows <scene name='Sandbox_45/Helixhold_vanderwaals/1'>van der Waals forces</scene>, <scene name='Sandbox_45/Helixhold_hbond/1'>hydrogen bonding and water bridges</scene> between | + | Bovine Trypsin contains 3? <scene name='Sandbox_45/Bt-helix/1'>alpha helices</scene> of lengths XYandZ. The two <scene name='Sandbox_45/Bt-sheet1/1'>beta sheets</scene>, A and B, are comprised of 7 and 6 strands. Although both appear as such, only B is technically a beta barrel. In the native conformation, these regular secondary structures interact with themselves and one another at a number of locations by numerous forces of attraction. A closer look at helix X,terminal, shows <scene name='Sandbox_45/Helixhold_vanderwaals/1'>van der Waals forces</scene>, <scene name='Sandbox_45/Helixhold_hbond/1'>hydrogen bonding, and water bridges</scene> between the helix and local residues of the remaining peptide. This is significant to its role in the 3D structure of the protein. |
| - | + | <applet load='3LJJ' size='300' frame='true' align='right' caption='Bovine Trypsin' /> | |
| - | + | The <scene name='Sandbox_45/Bt-phillic/3'>distribution</scene> of hydrophilic (green) and hydrophobic (yellow) residues is one of the most important aspects of primary structure. The protein as a whole achieves its native conformation primarily by the hydrophobic collapse of supersecondary structure; hydrophobic side chains are internalized while water molecules interact with the water-soluble side chains pushed to the exterior. The water's (red) <scene name='Sandbox_45/Bt-phillic_waters/2'>interaction</scene> with the surface of the protein shows this, as a <scene name='Sandbox_45/Bt-phillic_waters/3'>transparent</scene> view shows an absence of water within the hydrophobic core. | |
<scene name='Sandbox_45/Disulfide_bonds/1'>Disulfide bonds</scene> also contribute to the stability of the protein. Typically, proteins in an extra-cellular, oxidizing environment contain disulfide bonds that hold the structure together through variable temperature and pH. It follows that trypsin, a digestive protease found in the digestive tract, would require this added stability. | <scene name='Sandbox_45/Disulfide_bonds/1'>Disulfide bonds</scene> also contribute to the stability of the protein. Typically, proteins in an extra-cellular, oxidizing environment contain disulfide bonds that hold the structure together through variable temperature and pH. It follows that trypsin, a digestive protease found in the digestive tract, would require this added stability. | ||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
| - | |||
| - | <applet load='3LJJ' size='300' frame='true' align='right' caption='Bovine Trypsin' /> | ||
| + | == Ligand Binding and Catalysis == | ||
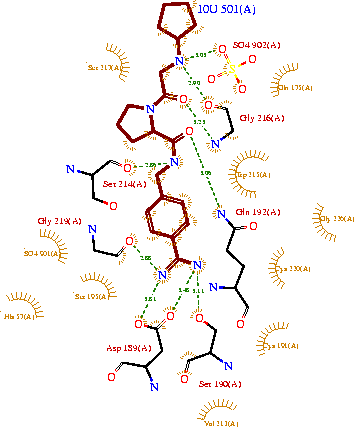
| + | The structure of this particular bovine trypsin was determined in complex with <scene name='Sandbox_45/Btligand/1'>ligand 10U</scene>, formula '''C'''20'''H'''29'''N'''5'''O'''2, along with two <scene name='Sandbox_45/Btsulfates/1'>sulfate ions</scene>(highlighted) and a Calcium ion (green). Four key amino acids interact with Calcium at a <scene name='Sandbox_45/Lig-metal/1'>subsite loop</scene>. The binding of ligand 10U involves <scene name='Sandbox_45/Ligandwaterbridge/1'>water bridges</scene>, direct <scene name='Sandbox_45/Ligandhbond/1'>hydrogen bonding</scene>, and a host of <scene name='Sandbox_45/Ligandhydrophobic/1'>hydrophobic interactions</scene>. | ||
| + | <applet load='3LJJ' size='300' frame='true' align='right' caption='Bovine Trypsin' /> | ||
| - | [[Image:Topographytrypsin.gif|thumb|center|upright=2.0]] | ||
| - | + | <scene name='Sandbox_45/Btsulfates/1'>sulfate ions</scene> | |
| + | key amino acids | ||
| - | <scene name='Sandbox_45/Bt-phillic/1'>hydrophilic residues</scene> | ||
| - | |||
| - | <scene name='Sandbox_45/Bt-phillic/3'>hydrophobic residues</scene> | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | == Ligand Binding and Catalysis == | ||
| - | |||
| - | <applet load='3LJJ' size='300' frame='true' align='right' caption='Bovine Trypsin' /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | <scene name='Sandbox_45/Btligand/1'>ligands</scene> | ||
| - | |||
| - | <scene name='Sandbox_45/Btsulfates/1'>sulfate ions</scene> | ||
| - | |||
| - | key amino acids | ||
| - | <scene name='Sandbox_45/Lig-metal/1'>metal</scene> | ||
[http://http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19388054 calcium in regulation] | [http://http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19388054 calcium in regulation] | ||
Revision as of 04:10, 29 October 2010
Structure of Trypsin
The various interactive tendencies and chemical characteristics of amino acids in this serine protease contribute to the protein's structure and catalytic function. The spacial arrangement of Trypsin's 223 residues in relation to themselves and their aqueous environment is displayed below.
Secondary Structure
Bovine Trypsin contains 3? of lengths XYandZ. The two , A and B, are comprised of 7 and 6 strands. Although both appear as such, only B is technically a beta barrel. In the native conformation, these regular secondary structures interact with themselves and one another at a number of locations by numerous forces of attraction. A closer look at helix X,terminal, shows , between the helix and local residues of the remaining peptide. This is significant to its role in the 3D structure of the protein.
|
The of hydrophilic (green) and hydrophobic (yellow) residues is one of the most important aspects of primary structure. The protein as a whole achieves its native conformation primarily by the hydrophobic collapse of supersecondary structure; hydrophobic side chains are internalized while water molecules interact with the water-soluble side chains pushed to the exterior. The water's (red) with the surface of the protein shows this, as a view shows an absence of water within the hydrophobic core.
also contribute to the stability of the protein. Typically, proteins in an extra-cellular, oxidizing environment contain disulfide bonds that hold the structure together through variable temperature and pH. It follows that trypsin, a digestive protease found in the digestive tract, would require this added stability.
Ligand Binding and Catalysis
The structure of this particular bovine trypsin was determined in complex with , formula C20H29N5O2, along with two (highlighted) and a Calcium ion (green). Four key amino acids interact with Calcium at a . The binding of ligand 10U involves , direct , and a host of .
|
key amino acids