Sandbox Reserved 164
From Proteopedia
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
<!-- PLEASE ADD YOUR CONTENT BELOW HERE --> | <!-- PLEASE ADD YOUR CONTENT BELOW HERE --> | ||
<Structure load='3ECU' size='500' frame='true' align='right' caption='Crystal Structure of SOD 1 protein, PDB ID: 3ECU' scene='Insert optional scene name here' /> | <Structure load='3ECU' size='500' frame='true' align='right' caption='Crystal Structure of SOD 1 protein, PDB ID: 3ECU' scene='Insert optional scene name here' /> | ||
| - | |||
== Superoxide Dismutase 1 (SOD 1) == | == Superoxide Dismutase 1 (SOD 1) == | ||
| Line 12: | Line 11: | ||
This protein is coded for by the SOD 1 gene located on chromosome 21 at position 21q22.1 from base pairs 33,031,934 to 33,041,243. <ref name="Sod1">SOD 1. Genetics Home Reference. U.S. National Library of Medicine; 2010</ref> | This protein is coded for by the SOD 1 gene located on chromosome 21 at position 21q22.1 from base pairs 33,031,934 to 33,041,243. <ref name="Sod1">SOD 1. Genetics Home Reference. U.S. National Library of Medicine; 2010</ref> | ||
| - | |||
== Structure == | == Structure == | ||
| Line 19: | Line 17: | ||
== ALS == | == ALS == | ||
| - | Mutations to the SOD 1 protein have been linked to the development of familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. <ref name="Al-Chalabi">Al-Chalabi A, Leigh PN (August 2000). "Recent advances in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis". Curr. Opin. Neurol. 13 (4): 397–405. PMID 10970056.</ref> | + | Mutations to the SOD 1 protein have been linked to the development of familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. <ref name="Al-Chalabi">Al-Chalabi A, Leigh PN (August 2000). "Recent advances in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis". Curr. Opin. Neurol. 13 (4): 397–405. PMID 10970056.</ref> These mutations cause a conformational change that leads to motor neuron death through toxic radical build up, promotion of apoptosis, aggregate formation of misfolded proteins, or over stimulation of the cells.<ref name="Sod1">SOD 1. Genetics Home Reference. U.S. National Library of Medicine; 2010</ref> |
| - | + | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
Revision as of 02:32, 30 March 2011
|
Contents |
Superoxide Dismutase 1 (SOD 1)
SOD1 is one of three oxidoreductase enzymes that is responsible for binding copper and zinc ions to highly reactive oxygen free radicals and transforming them into oxygen and hydrogen peroxide. [1] This occurs in a quick two step mechanism:
M(n+1)+-SOD + O2− → Mn+-SOD + O2
Mn+-SOD + O2− + 2H+ → M(n+1)+-SOD + H2O2[2].
This protein is coded for by the SOD 1 gene located on chromosome 21 at position 21q22.1 from base pairs 33,031,934 to 33,041,243. [3]
Structure
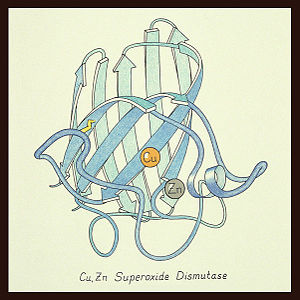
The SOD 1 protein is a homodimer with an amino acid sequence length of 154. SOD 1 has an 8-stranded "Greek key" beta-barrel shape with the active site located between the barrels. The copper and zinc ligands are made up of six histidine side-chains and one aspartate side-chain with the metal ions connected with by a single histidine chain.[2] This first SOD structure was determined by Irwin Fridovich and Joe McCord in 1973 [1][4] with the SOD 1 "Greek key" structure visualized by Dr. Jane Richardson (see below).[2]
ALS
Mutations to the SOD 1 protein have been linked to the development of familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. [5] These mutations cause a conformational change that leads to motor neuron death through toxic radical build up, promotion of apoptosis, aggregate formation of misfolded proteins, or over stimulation of the cells.[3]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 McCord JM, Fridovich I. Superoxide dismutase. An enzymic function for erythrocuprein (hemocuprein). J Biol Chem. 1969 Nov 25;244(22):6049-55. PMID:5389100
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Tainer JA, Getzoff ED, Richardson JS, Richardson DC. Structure and mechanism of copper, zinc superoxide dismutase. Nature. 1983 Nov 17-23;306(5940):284-7. PMID:6316150
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 SOD 1. Genetics Home Reference. U.S. National Library of Medicine; 2010
- ↑ McCord JM, Fridovich I. Superoxide dismutase: the first twenty years (1968-1988). Free Radic Biol Med. 1988;5(5-6):363-9. PMID:2855736
- ↑ Al-Chalabi A, Leigh PN (August 2000). "Recent advances in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis". Curr. Opin. Neurol. 13 (4): 397–405. PMID 10970056.