We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Group:MUZIC:Nebulin
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)

| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
2. To maintain the alignment of adjacent myofibrills (linker of adjacent Z-disks); | 2. To maintain the alignment of adjacent myofibrills (linker of adjacent Z-disks); | ||
3. To regulate muscle contraction (regulator of cross-bridge cycles). | 3. To regulate muscle contraction (regulator of cross-bridge cycles). | ||
| + | |||
| + | Mutations in the Nebulin encoding gene are the most common cause of Nemaline myopathy (NM), a non-dystrophic congenital muscle disorder characterised by muscle weakness. | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
---- | ---- | ||
Revision as of 16:23, 1 July 2011
Contents |
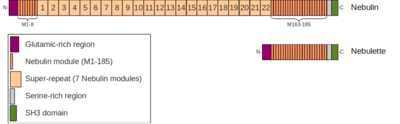
Introduction
| |||||||||||
Domains and interactions
Glutamic rich region
Nebulin modules
Serine rich region
SH3 domain
The Nebulin SH3 domain adopts a ß-Barrel .
References
- ↑ Wang K. Cytoskeletal matrix in striated muscle: the role of titin, nebulin and intermediate filaments. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1984;170:285-305. PMID:6547565
- ↑ Kazmierski ST, Antin PB, Witt CC, Huebner N, McElhinny AS, Labeit S, Gregorio CC. The complete mouse nebulin gene sequence and the identification of cardiac nebulin. J Mol Biol. 2003 May 9;328(4):835-46. PMID:12729758
- ↑ Moncman CL, Wang K. Nebulette: a 107 kD nebulin-like protein in cardiac muscle. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1995;32(3):205-25. PMID:8581976 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/cm.970320305
- ↑ Ottenheijm CA, Granzier H. Lifting the nebula: novel insights into skeletal muscle contractility. Physiology (Bethesda). 2010 Oct;25(5):304-10. PMID:20940435 doi:10.1152/physiol.00016.2010
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Marie-Cecile Pelissier, Michal Harel, Jaime Prilusky, Nikos Pinotsis