Introduction
Rhodopsin
Rhodopsin, a homodimeric protein, is a highly characterized G protein-coupled receptor found in membranous disks of the outer segments of rod and cone cells, though rhodopsin is more concentrated in rod cells which are sensitive to light but cannot discriminate colors. Rhodopsin is part of the superfamily of G protein-coupled receptors that mediate responses to visual, olfactory, hormonal, and neurotransmitter signals among others[1]. Rhodopsin is involved in visual signal transduction and the visual system in classic G protein-coupled receptor mechanisms[2].
G Protein-Coupled Receptors
Rhodopsin is a member of the superfamily of G protein-coupled receptors that incorporate the activation of G proteins in their modulation of signaling and intracellular actions. Rhodopsin shares similar membrane topology with the members of the superfamily (Family A of the G protein-coupled receptors) which include the seven transmembrane helices, an extracellular N terminus and cytoplasmic C terminus[3]. The seven-helical pattern is found from archaebacteria (specifically studied is bacteriorhodopsin) to humans, both which share the same retinylidene chromophore as well [2]. As the crystal structure for any G protein-coupled receptor with the seven transmembrane domain has only been solved for rhodopsin, rhodopsin may act as a reference for the structure and function relationship for other G protein-coupled receptors[3]. Like most G protein-coupled receptors, the activated rhodopsin catalyzes uptake of GTP by the heterotrimeric G protein, in this case transducin, which interacts with the cytoplasmic loops of the receptor[4]. However, the covalent binding nature of rhodopsin to its retinal ligand is unlike most G protein-coupled receptors. As well, another difference of rhodopsin from the members of this superfamily relates to light as the inducer for activation[3].
Structure
Rhodopsin Architecture
Rhodopsin consists of seven mostly α-helical transmembrane domains (H1-H7) linked sequentially by extracellular and cytoplasmic loops (E1-E3 and C1-C3 respectively), with the extracellular amino-terminal tail and the cytoplasmic carboxyl-terminal tail[2]. Four of the helices are tilted and three of the helices are approximately perpendicular to the membrane plane[5]. There is notable interaction between the four extracellular domains, but only a few associations are observed with the cytoplasmic domains[6]. Helix 7 is close to being elongated around the Lysine 296 retinal attachment site, and also contains the residues Proline 291 and Proline 303, with Proline 303 being part of a conserved motif[6]. Near the retinal region, there is a within the Extracellular Helix 2 that runs almost parallel to the chromophore held in place and is stabilized by the essential conserved
. This loop also potentially contacts the chromophore through Glutamine 181 and Tyrosine 191[2].
are observed to be located in the extracellular domains of rhodopsin; specifically, the water molecules around the second extracellular loop between Helix 4 and 5 solvate the loop when the loop interacts with the retinal chromophore and possibly contribute to its flexibility should rearrangement occur[7].
There is the presence of a cationic amphipathic Helix 8, known as the fourth cytoplasmic loop, that spans from and is formed from the C-terminal tail anchoring to the membrane by
, which are . This helix runs approximately parallel to the cytoplasmic surface and is involved in Gtγ binding[6], as well as the modulation of rhodopsin-transducin interactions and rhodopsin-phospholipid interactions[2].
A metal zinc ion bridge chelated by histidine side-chains and connected to the cytoplasmic ends of Helix 3 and 6 is observed to prevent receptor activation. This perhaps indicates that separation of these cytoplasmic ends would contribute to rhodopsin activation[4].
The structure of rhodopsin may provide stability to the important Schiff base linkage with the retinal by affecting its hydrolysis, limiting its interactions with solvent, and inhibiting its release when hydrolyzed, thus encouraging rebinding of the Schiff base linkage[8].
Retinal Chromophore of Rhodopsin
Rhodopsin consists of an opsin apoprotein and a in its active site. Rhodopsin is bound covalently to the 11-cis retinal, the chromophore or "ligand," (shown in yellow) and this retinal is found in deeply in the core of the helices, in a hydrophobic site, parallel to the lipid bilayer[9]. Comparatively, it is situated more towards the extracellular planes of the membrane bilayer [2]. The retinal is attached in the active site of rhodopsin through a protonated Schiff base (an N-substituted imine) bond to the ε-amino group of Lysine 296 residue (shown in green) on the C-terminal Helix 7, with this linkage creating a positive charge on the chromophore [5]. The protonated Schiff base of rhodopsin is stabilized through residue electrostatic interaction with the counterion, holding the inactive rhodopsin in its state[3].
As this ligand is bound in the 12-s-trans conformation, there arises the non-bonding interactions between the C-13 methyl group and C-10 hydrogen that contribute to non-planarity. This leads to the ability of the chromophore polyene tail to undergo fast photoisomerization around the C-11=C-12 double bond during light-induced activation[10]. Also, it is found that the C-11=C-12 double bond is pre-twisted in the ground state of rhodopsin, which is partly attributed to the C20 methyl group attached to C13 through interaction with Tryptophan 265. This pre-twist may give insight on the features of isomerization about this bond upon light activation[7].
Somewhat enclosing this chromophore is a retinal binding pocket partially formed by the N-terminal domain overlaying the extracellular turns including the second extracellular loop, which folds into the molecular center[11].
Function
Visual Signal Transduction
Photoisomerization of 11-cis Retinal
The 11-cis retinal (retinylidene) Schiff base functions as an inverse agonist and is prominently involved in the activation of rhodopsin. The primary step in rhodopsin photoactivation occurs in the photoisomerization of rhodopsin, as light energy absorbed from a photon is converted into chemical energy. As a photon is absorbed by the retina, the 11-cis retinylidene ligand is switched into an all-trans retinal configuration[10]. In this extremely efficient <200 fs process, the protein-binding pocket, initially fitted to accommodate the 11-cis conformation of the chromophore, is preserved, which restrains the relaxation of the chromophore. The strained relaxation of conformational energy changes the protein state into the active form[10].
Adjustment and Thermal Relaxation of the Protein
Upon activation, movement and slight adjustment of helices are observed, with the inner faces of Helix 2, 3, 6 and 7 becoming more exposed[4]. As Helices 3 and 6 move outward, the binding site for transducin is more accessible as there is opening between cytoplasmic loops[9].
Following activation, a slower thermal relaxation process occurs. This involves conformational changes in the retinal and opsin to result in fully active Metarhodopsin II[11].
Formation of the Metarhodopsin II State
Rhodopsin forms to Metarhodopsin II, the intermediate signaling state where interaction occurs with the G protein. This millisecond process is accompanied by movement in the helices, uptake of protons in the cytoplasm, and the breakage of the salt bridge between Glutamine 113 and the protonated Schiff base. The Schiff base deprotonates and the proton is transferred to the Glutamine 113 counterion, destabilizing the ground state [6]. As well, this Metarhodopsin II formation may be dependent on the protonation too of the conserved , thus destabilizing the constraint on Arginine 135[6].
There is positive enthalpy associated with the formation of Metarhodopsin II. This formation of the active state, also linked with the increase in entropy, is suggested to release the constraints in the helices and expose the cytoplasmic binding sites[6]. An important part of this process includes the 9-methyl group of retinal, which is suggested to provide a scaffold for proton transfers essential for the formation of the active state[6].
Signaling Cascade and Polarization of the Cell Membrane
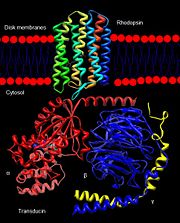
Rhodopsin interaction with transducin.
The excited rhodopsin interacts with a large number of transducin molecules, found in the cytoplasmic face of the disk membrane. Transducin is a member of the heterotrimeric GTP-binding proteins family, and it binds to GDP in the dark. This interaction generates a signaling cascade where transducin molecules are activated through the trigger of GDP-GTP nucleotide exchange in the α subunit[11]. Each activated transducin dissociates into Tα-GTP and Tβγ subunits, and Tα-GTP activates cGMP-specific phosphodiesterase by binding and removing its inhibitory subunit[12].
The cGMP phosphodiesterase is an integral protein of the retina with its active site on the cytoplasmic side of the disk. Its inhibitory subunit tightly binds to it in the dark and suppresses its activity. The now activated phosphodiesterase degrades many molecules of cGMP, efficiently decreasing the concentration of cGMP[12]. This results in the closing of the cGMP-gated cation channels in the plasma membrane of the outer segment. The cell hyperpolarizes due to the decrease in the influx of sodium and calcium ions, which results in the decrease of the release of glutamate into the synaptic cleft. This electric signal of this hyperpolarization is sent to the brain through ranks of interconnecting neurons and then through the optic nerve[11].
Visual Signal Termination
Recovery of the Pre-stimulus State
In the event of a decrease in light intensity, GTP is hydrolyzed and the α-subunit of transducin reassociates with the βγ subunits, releasing the inhibitory subunit of phosphodiesterase. This subunit reassociates with phosphodiesterase and inhibits its activity[12].
The concentration of cGMP is returned to the “dark” state by the conversion of GTP to cGMP by guanylyl cyclase, activated through the efflux of calcium ions through the sodium/calcium ion exchanger. The reduction in the concentration of calcium ions also inhibits phosphodiesterase activity. Both actions reopen the cation channels and restore the system to pre-stimulus state[12].
Phosphorylation and Deactivation of Rhodopsin
Rhodopsin kinase phosphorylates rhodopsin and arrestin binds to the phosphorylated domain of rhodopsin, preventing further signal transduction from Metarhodopsin II of activated rhodopsin and transducin[8]. It phosphorylates both Metarhodopsin II and cone opsins. The majority of the phosphorylation sites are in the cytoplasmic C-terminal region of rhodopsin with seven hydroxy-amino acids. The most favoured amino acids are [13], and these residues form an arrangement in rhodopsin that do not appear to be exposed to the solvent. Interactions with the C-terminal tail and a portion of the Cytoplasmic loop 3 appear to be broken for the phosphorylation of the hydroxyl groups[6]. For the next cycle of activation of rhodopsin, rhodopsin has to be dephosphorylated, and have the all-trans retinal replaced with the 11-cis retinal[9].
Altogether, the different states of rhodopsin which include the short-lived, photo-rhodopsin, batho-rhodopsin, and lumi-rhodopsin, and longer-lived meta-rhodopsins give information about the structural status of the molecule during activation[6].
Opsin
Topology Overview
The overall dimeric structure of opsin is similar to rhodopsin, with seven transmembrane helices linked by three extracellular loops and three cytoplasmic loops and a cytoplasmic Helix 8. The small differences between the topology of the two proteins include a short helical turn in the cytoplasmic loop 1 in opsin, 1.5-2.5 helical turns longer in Helix 5 for opsin in comparison to rhodopsin, and a large outward tilt of Helix 6 of opsin[14]. Also, in contrast to rhodopsin, opsin has two openings of the retinal-binding pocket; one of the openings is between Helix 1 and Helix 7, and the other opening is between the extracellular ends of Helix 5 and 6. This opening is formed by the residues [14]. The two openings suggest different sites of retinal entrance and exit in retinal channeling[14].
Activity
The ability of opsin to activate transducin is modulated by both 11-cis retinal and the all-trans retinal; the 11-cis retinal reduces its activity while the all-trans retinal enhances it through non-covalent interactions [15]. This may give insight on the ability of all-trans retinal, in combination with opsin, to alter the photoreceptor sensitivities[15].
Colour Vision
Opsins are also photoreceptor proteins and are concentrated in cone cells, cells that are less sensitive to light but can discriminate colours. Opsins are slightly different light receptors than rhodopsin in that they can detect light from different spectrums and distinguish between their wavelengths. The ability to differentiate between colours is related to the three types of cone cells, each using one of the three related opsin photoreceptors[12].
† PDB structure used in this section: 3cap

