This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
DOPA decarboxylase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | == | + | ==Your Heading Here (maybe something like 'Structure')==<StructureSection load='1dq8' size='500' side='right' caption='Pig DOPA decarboxylase complex with inhibitor carbidopa, vitamin B6 phosphate and sulfate, [[1js3]] ' scene=''> |
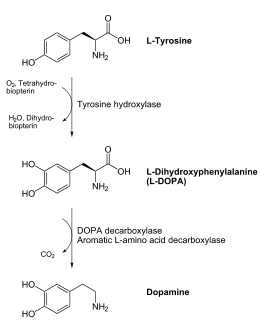
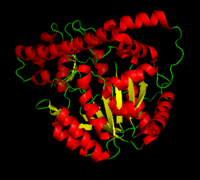
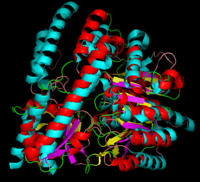
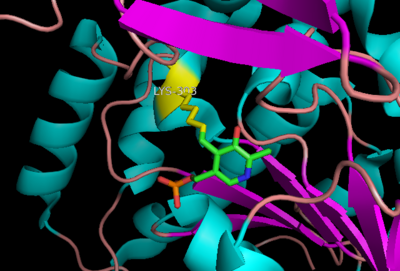
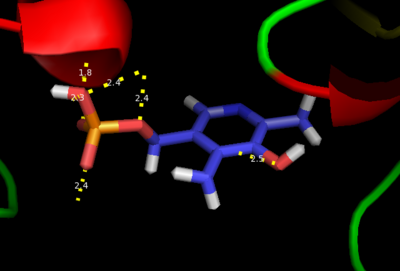
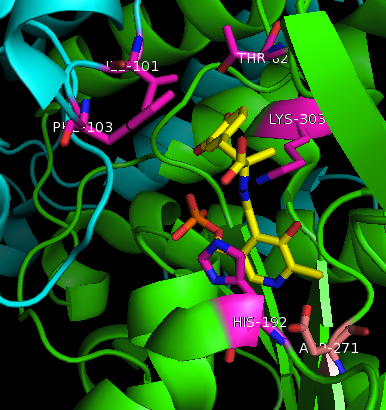
| - | + | '''DOPA decarboxylase''' (DDC, aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase, tryptophan decarboxylase, 5-hydroxytryptophan decarboxylase, AAAD) is an approximately 104 kDa protein that belongs to the '''aspartate aminotransferase family''' (fold type 1) of '''[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pyridoxal_phosphate ''PLP'']-dependent''' (vitamin B6-dependent) enzymes. The catalytically active form of the enzyme exists as a homodimer, typical of this class of enzymes.<ref name="schneider">PMID:10673430 </ref> The homodimeric form of the enzyme purified from [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sus_scrofa ''sus scrofa''] is shown in complex with the inhibitor '''[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Carbidopa ''carbidopa'']''' to the right. [[image:dopa.png|thumb|left|500px|'''dopamine synthesis''']] | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | ''' | + | |
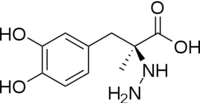
DOPA decarboxylase is responsible for the synthesis of '''[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dopamine ''dopamine'']''' and [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Serotoninn ''serotonin''] from '''[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/L-dopa ''L-DOPA'']''' and [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/L-5-Hydroxytryptophan ''L-5-hydroxytryptophan''], respectively. Due to its role in dopamine biosynthesis, DOPA decarboxylase has been implicated in '''[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Parkinson%27s_disease ''Parkinson's disease'']''', a disease thought to be the result of the degeneration of dopamine-producing cells in the brain. In fact, decarboxylation of L-DOPA by DOPA decarboxylase is the controlling step for the formation of dopamine in patients with Parkinson's <ref name="hadjiiconstantinou">PMID:1904055 </ref> Currently, treatment for the disease is aimed at DOPA decarboxylase inhibition. Since dopamine cannot cross the blood-brain barrier, it cannot be used to directly treat Parkinson's disease. Thus, exogenously administered L-DOPA is the primary treatment for patients suffering from this neurodegenerative disease. Unfortunately, DOPA decarboxylase rapidly converts L-DOPA to dopamine in the blood stream, with only a small percentage reaching the brain. By inhibiting the enzyme, greater amounts of exogenously administered L-DOPA can reach the brain, where it can then be converted to dopamine. <ref name="burkhard">PMID:11685243 </ref> | DOPA decarboxylase is responsible for the synthesis of '''[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dopamine ''dopamine'']''' and [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Serotoninn ''serotonin''] from '''[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/L-dopa ''L-DOPA'']''' and [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/L-5-Hydroxytryptophan ''L-5-hydroxytryptophan''], respectively. Due to its role in dopamine biosynthesis, DOPA decarboxylase has been implicated in '''[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Parkinson%27s_disease ''Parkinson's disease'']''', a disease thought to be the result of the degeneration of dopamine-producing cells in the brain. In fact, decarboxylation of L-DOPA by DOPA decarboxylase is the controlling step for the formation of dopamine in patients with Parkinson's <ref name="hadjiiconstantinou">PMID:1904055 </ref> Currently, treatment for the disease is aimed at DOPA decarboxylase inhibition. Since dopamine cannot cross the blood-brain barrier, it cannot be used to directly treat Parkinson's disease. Thus, exogenously administered L-DOPA is the primary treatment for patients suffering from this neurodegenerative disease. Unfortunately, DOPA decarboxylase rapidly converts L-DOPA to dopamine in the blood stream, with only a small percentage reaching the brain. By inhibiting the enzyme, greater amounts of exogenously administered L-DOPA can reach the brain, where it can then be converted to dopamine. <ref name="burkhard">PMID:11685243 </ref> | ||
| Line 77: | Line 73: | ||
#'''Architecture''': up-down bundle | #'''Architecture''': up-down bundle | ||
#'''Topology''': dopa decarboxylase | #'''Topology''': dopa decarboxylase | ||
| + | |||
| + | </StructureSection> | ||
==3D structures of DOPA decarboxylase== | ==3D structures of DOPA decarboxylase== | ||
Revision as of 01:29, 20 January 2012
==Your Heading Here (maybe something like 'Structure')==
| |||||||||||
3D structures of DOPA decarboxylase
Update November 2011
3k40 – DDC – Drosophila melanogaster
1js3 – pDDC + inhibitor – pig
1js6 - pDDC
3rbf, 3rbl – hDDC – human
3rch – hDDC + vitamin B6 phosphate + pyridoxal phosphate
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Schneider G, Kack H, Lindqvist Y. The manifold of vitamin B6 dependent enzymes. Structure. 2000 Jan 15;8(1):R1-6. PMID:10673430
- ↑ Miles EW. The tryptophan synthase alpha 2 beta 2 complex. Cleavage of a flexible loop in the alpha subunit alters allosteric properties. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 15;266(17):10715-8. PMID:1904055
- ↑ Burkhard P, Dominici P, Borri-Voltattorni C, Jansonius JN, Malashkevich VN. Structural insight into Parkinson's disease treatment from drug-inhibited DOPA decarboxylase. Nat Struct Biol. 2001 Nov;8(11):963-7. PMID:11685243 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nsb1101-963
- ↑ Percudani R, Peracchi A. A genomic overview of pyridoxal-phosphate-dependent enzymes. EMBO Rep. 2003 Sep;4(9):850-4. PMID:12949584 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/sj.embor.embor914
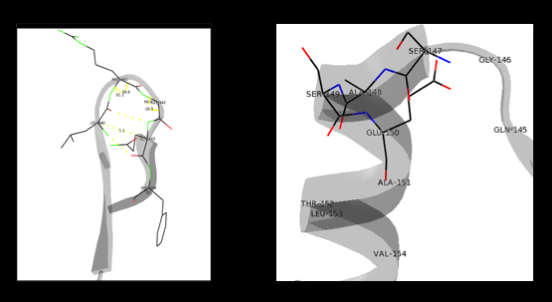
- ↑ Aurora R, Rose GD. Helix capping. Protein Sci. 1998 Jan;7(1):21-38. PMID:9514257 doi:10.1002/pro.5560070103
- ↑ Jansonius JN. Structure, evolution and action of vitamin B6-dependent enzymes. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 1998 Dec;8(6):759-69. PMID:9914259
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Ishii S, Mizuguchi H, Nishino J, Hayashi H, Kagamiyama H. Functionally important residues of aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase probed by sequence alignment and site-directed mutagenesis. J Biochem. 1996 Aug;120(2):369-76. PMID:8889823
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Brittany Todd, David Canner, Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, Brian Hernandez