Sandbox 35
From Proteopedia
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
<scene name='Sandbox_35/Papain_acid_and_basic_residues/1'>acidic and basic residues</scene> | <scene name='Sandbox_35/Papain_acid_and_basic_residues/1'>acidic and basic residues</scene> | ||
| - | <scene name='Sandbox_35/ | + | <scene name='Sandbox_35/Hydrophobicity_papain/3'>polar and non-polar residue</scene> |
<scene name='Sandbox_35/Papain_polar/1'>polar residues</scene> | <scene name='Sandbox_35/Papain_polar/1'>polar residues</scene> | ||
Revision as of 04:48, 13 November 2011
| Please do NOT make changes to this Sandbox. Sandboxes 30-60 are reserved for use by Biochemistry 410 & 412 at Messiah College taught by Dr. Hannah Tims during Fall 2012 and Spring 2013. |
Contents |
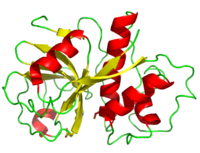
Papain
Introduction
finds its origin from the latex of the papaya fruit and is classified as a sulfhydryl protease.
| |||||||||||
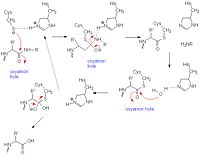
Catalytic Mechanism
References
- ↑ [1]9PAP PDB
- ↑ Wang J, Xiang YF, Lim C. The double catalytic triad, Cys25-His159-Asp158 and Cys25-His159-Asn175, in papain catalysis: role of Asp158 and Asn175. Protein Eng. 1994 Jan;7(1):75-82. PMID:8140097
- ↑ [2] University of Maine
http://www.pdb.org/pdb/explore/explore.do?structureId=2PAD
• Show the secondary structures.
• Compare the distribution of polar residues to that of nonpolar residues.
• Highlight the active site.
• If you can find a PDB file of the enzyme that contains a pseudo-substrate (may be inhibitor), highlight it.
• Show the contacts or attractions that are present between the pseudo-substrate and the protein, and if the enzyme has multiple subunits, show the contacts between the subunits.
• Identify any other ligands that are present in the structure and the types of contacts that are present between them and the protein
http://proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/Sandbox_55#cite_note-18 Table of contents Pictures References (cross links)