This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Pertussis Toxin-ATP Complex
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
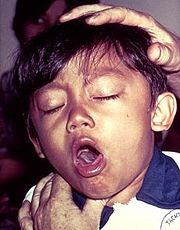
<StructureSection load=1bcp size='500' side='right' caption='Pertussis Toxin-ATP complex ([[1bcp]])' scene=''>[[Image:230px-Pertussis.jpg|left|thumb|A young boy coughing due to pertussis.]] | <StructureSection load=1bcp size='500' side='right' caption='Pertussis Toxin-ATP complex ([[1bcp]])' scene=''>[[Image:230px-Pertussis.jpg|left|thumb|A young boy coughing due to pertussis.]] | ||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
| - | '''Pertussis Toxins''' (PT) is a protein-based exotoxin and major virulence factor produced by the bacterium [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bordetella_pertussis ''Bordetella pertussis''].<ref name=Hazes>PMID: 8637000</ref> PT causes [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Whooping_cough pertussis], which is also known at whooping cough and is highly contagious bacterial disease. The disease is caused by the bacterium colonizing the respiratory tract where it then establishes an infection.<ref name=Carbonetti>PMID: 14573656</ref> This disease had been characterized by severe coughing that can last up to six weeks and in some countries lasting nearly 100 days.<ref name=Carbonetti>PMID: 17418639</ref>It has been documented in some cases that PT can cause [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Subconjunctival_hemorrhage subconjunctival hemorrhages], [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rib_fracture rib fractures], [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hernias hernias], fainting and [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vertebral_artery_dissection vertebral artery dissection].<ref name=cornia>PMID: 20736473</ref> | + | '''Pertussis Toxins''' (PT) is a protein-based exotoxin and major virulence factor produced by the bacterium [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bordetella_pertussis ''Bordetella pertussis''].<ref name=Hazes>PMID: 8637000</ref> PT causes [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Whooping_cough pertussis], which is also known at [http://proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php?title=Pertussis_Toxin-ATP_Complex&act whooping cough] and is highly contagious bacterial disease. The disease is caused by the bacterium colonizing the respiratory tract where it then establishes an infection.<ref name=Carbonetti>PMID: 14573656</ref> This disease had been characterized by severe coughing that can last up to six weeks and in some countries lasting nearly 100 days.<ref name=Carbonetti>PMID: 17418639</ref>It has been documented in some cases that PT can cause [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Subconjunctival_hemorrhage subconjunctival hemorrhages], [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rib_fracture rib fractures], [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hernias hernias], fainting and [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vertebral_artery_dissection vertebral artery dissection].<ref name=cornia>PMID: 20736473</ref> |
As of 2010, the worldwide incidence of whooping cough has been estimated to 48.5 million cases and nearly 295,000 deaths per year.<ref name=Bettiol>PMID: 20091541</ref> With that in mind, whooping cough can affect people of any age; however, before vaccines were available the disease was most common in infants and young children but now children are immunized and the high percentage of cases are seen among adolescents. | As of 2010, the worldwide incidence of whooping cough has been estimated to 48.5 million cases and nearly 295,000 deaths per year.<ref name=Bettiol>PMID: 20091541</ref> With that in mind, whooping cough can affect people of any age; however, before vaccines were available the disease was most common in infants and young children but now children are immunized and the high percentage of cases are seen among adolescents. | ||
Revision as of 22:05, 15 November 2011
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 1.11 1.12 Hazes B, Boodhoo A, Cockle SA, Read RJ. Crystal structure of the pertussis toxin-ATP complex: a molecular sensor. J Mol Biol. 1996 May 17;258(4):661-71. PMID:8637000 doi:10.1006/jmbi.1996.0277
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Carbonetti NH, Artamonova GV, Mays RM, Worthington ZE. Pertussis toxin plays an early role in respiratory tract colonization by Bordetella pertussis. Infect Immun. 2003 Nov;71(11):6358-66. PMID:14573656
- ↑ Cornia PB, Hersh AL, Lipsky BA, Newman TB, Gonzales R. Does this coughing adolescent or adult patient have pertussis? JAMA. 2010 Aug 25;304(8):890-6. PMID:20736473 doi:10.1001/jama.2010.1181
- ↑ Bettiol S, Thompson MJ, Roberts NW, Perera R, Heneghan CJ, Harnden A. Symptomatic treatment of the cough in whooping cough. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010 Jan 20;(1):CD003257. PMID:20091541 doi:10.1002/14651858.CD003257.pub3
- ↑ Weiss AA, Johnson FD, Burns DL. Molecular characterization of an operon required for pertussis toxin secretion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 1;90(7):2970-4. PMID:8464913
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Kaslow HR, Burns DL. Pertussis toxin and target eukaryotic cells: binding, entry, and activation. FASEB J. 1992 Jun;6(9):2684-90. PMID:1612292
- ↑ Kenneth Todar, PhD. (2008). http://www.textbookofbacteriology.net/pertussis.html
- ↑ Plaut RD, Carbonetti NH. Retrograde transport of pertussis toxin in the mammalian cell. Cell Microbiol. 2008 May;10(5):1130-9. Epub 2007 Dec 31. PMID:18201245 doi:10.1111/j.1462-5822.2007.01115.x
- ↑ Kenneth Todar, PhD. (2008). http://www.textbookofbacteriology.net/pertussis.html
- ↑ Kenneth Todar, PhD. (2008). http://www.textbookofbacteriology.net/pertussis.html
- ↑ Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. http://www.cdc.gov/pertussis/clinical/treatment.html
- ↑ Altunaiji S, Kukuruzovic R, Curtis N, Massie J. Antibiotics for whooping cough (pertussis). Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007 Jul 18;(3):CD004404. PMID:17636756 doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004404.pub3
- ↑ Kenneth Todar, PhD. (2008). http://www.textbookofbacteriology.net/pertussis.html