User:Gourinchas Geoffrey/Sandbox 205
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
| + | <StructureSection load='1buy' size='500' side='right' caption='Structure Erythropoietin (PDB entry [[1buy]])' scene='User:Gourinchas_Geoffrey/Sandbox_205/Photo_of_the_structure/1'></scene>'> | ||
== Structure == | == Structure == | ||
| - | + | ||
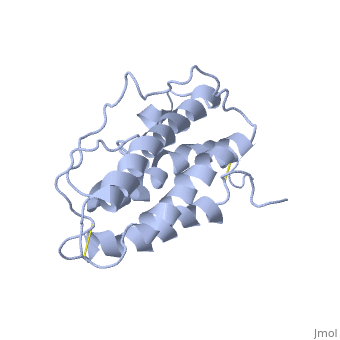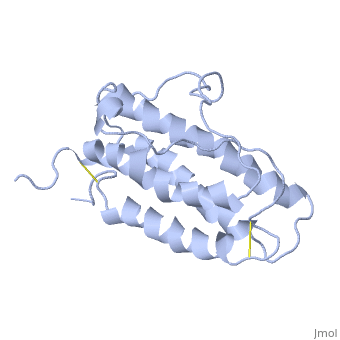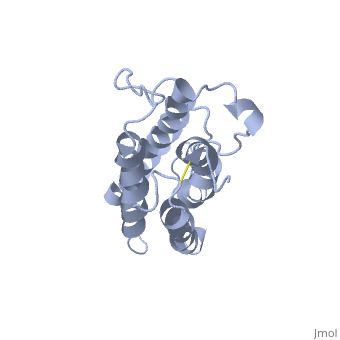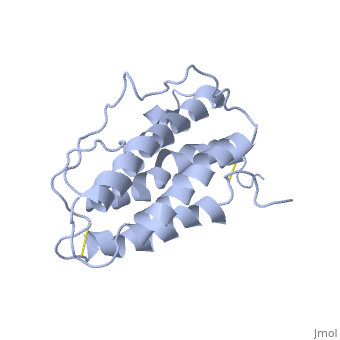
| + | This hormone weight 30.4kD and is constituted to 166 amino acids. | ||
It is composed to 4 alpha-helix: αA, αB, αC and αD which are associated the some in front of the others. | It is composed to 4 alpha-helix: αA, αB, αC and αD which are associated the some in front of the others. | ||
| Line 34: | Line 36: | ||
| - | == | + | |
| + | == Optimal angle for Erythropoietin binding to his receptor. == | ||
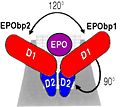
| + | [[Image:orientation.jpg|120px|left|thumb|Erythropoeitin with his receptor]] | ||
Syed and al. in 1998 have showed that Erythropoietin optimal binds at his receptor if only there is an angle of 120° between the two sites of the receptor. | Syed and al. in 1998 have showed that Erythropoietin optimal binds at his receptor if only there is an angle of 120° between the two sites of the receptor. | ||
The intracellular surface create by ths angle of 120° allows the optimal induction of Erythropoietin by the intracellulaire way of Kinase. </StructureSection> | The intracellular surface create by ths angle of 120° allows the optimal induction of Erythropoietin by the intracellulaire way of Kinase. </StructureSection> | ||
Revision as of 12:43, 28 November 2011
HUMAN ERYTHROPOIETIN
|
Erythropoietin is a glycoprotein hormone which is involved in Erythropoiesis, which is the red blood cells production. It allows the differenciation of the erythrocyte precursors in the bone marrow.
| |||||||||||