We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
User:Brian Hernandez/DOPA Decarboxylase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
---- | ---- | ||
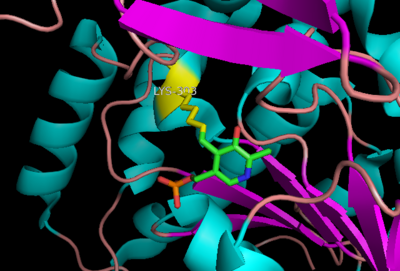
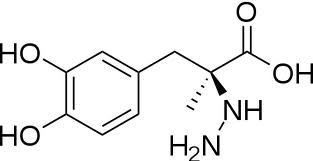
| - | DOPA decarboxylase (Aromatic L-Amino Acid Decarboxylase, tryptophan decarboxylase, 5-hydroxytryptophan decarboxylase, AAAD, or [[DDC]]) is an essential [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lyase lyase] enzyme responsible for the conversion (via decarboxylation) of L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine (L-DOPA) and L-5-hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP) to dopamine and serotonin. This 104 kDa protein is a tightly associated α<sub>2</sub>-dimer that belongs to the '''aspartate aminotransferase family''' (fold type 1) of PLP-dependent (vitamin B6-dependent) enzymes, and can be found in abundance in the nervous system, as well as the kidney. Because of its role in the biosynthesis of dopamine, DDC has been utilized in the treatment of [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Parkinson's_disease Parksinon's disease]- a chronic, progressively neurological disorder, thought to be the result of degeneration of dopamine-producing cells in the '''substantia nigra pars compacta''' (brain structure in the mesencephalon that plays an important role in reward, addiction, and movement) of the brain. | + | DOPA decarboxylase (Aromatic L-Amino Acid Decarboxylase, tryptophan decarboxylase, 5-hydroxytryptophan decarboxylase, AAAD, or [[DDC]]) is an essential [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lyase lyase] enzyme responsible for the conversion (via decarboxylation) of L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine (L-DOPA) and L-5-hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP) to dopamine and serotonin<ref name=Christenson>PMID: PMC426454 </ref>. This 104 kDa protein is a tightly associated α<sub>2</sub>-dimer that belongs to the '''aspartate aminotransferase family''' (fold type 1) of PLP-dependent (vitamin B6-dependent) enzymes, and can be found in abundance in the nervous system, as well as the kidney. Because of its role in the biosynthesis of dopamine, DDC has been utilized in the treatment of [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Parkinson's_disease Parksinon's disease]- a chronic, progressively neurological disorder, thought to be the result of degeneration of dopamine-producing cells in the '''substantia nigra pars compacta''' (brain structure in the mesencephalon that plays an important role in reward, addiction, and movement) of the brain. |
==Structure== | ==Structure== | ||
Revision as of 06:29, 29 November 2011
| |||||||||||
3D structures of DOPA decarboxylase
3k40 – DDC – Drosophila melanogaster
1js3 – pDDC + inhibitor – pig
1js6 - pDDC
3rbf, 3rbl – hDDC – human
3rch – hDDC + vitamin B6 phosphate + pyridoxal phosphate