Sandbox Reserved 469
From Proteopedia
(→Function) |
(→References) |
||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
Dissociation of TBP from DNA is an extremely long period of time when compared to other proteins with dissociation half times in vitro have been measured from 15 minutes to 1 hour and more. There are 2 regulator proteins that have been found to have global effect of TBP, and these are Mot1 and NC24. Mot1 is an ATPase which uses an ATP hydrolysis to displace TBP from DNA. NC2 functions as a heterodimer of TBP that prevents the formation of the preintiation complex by blocking TBP from binding DNA<ref>Auble DT. The dynamic personality of TATA-binding protein.</ref>. | Dissociation of TBP from DNA is an extremely long period of time when compared to other proteins with dissociation half times in vitro have been measured from 15 minutes to 1 hour and more. There are 2 regulator proteins that have been found to have global effect of TBP, and these are Mot1 and NC24. Mot1 is an ATPase which uses an ATP hydrolysis to displace TBP from DNA. NC2 functions as a heterodimer of TBP that prevents the formation of the preintiation complex by blocking TBP from binding DNA<ref>Auble DT. The dynamic personality of TATA-binding protein.</ref>. | ||
| - | == References == | ||
References: {{reflist}} | References: {{reflist}} | ||
Revision as of 18:12, 1 May 2012
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 13/03/2012, through 01/06/2012 for use in the course "Proteins and Molecular Mechanisms" taught by Robert B. Rose at the North Carolina State University, Raleigh, NC USA. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 451 through Sandbox Reserved 500. | ||||||
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing For more help, look at this link: http://www.proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/Help:Getting_Started_in_Proteopedia
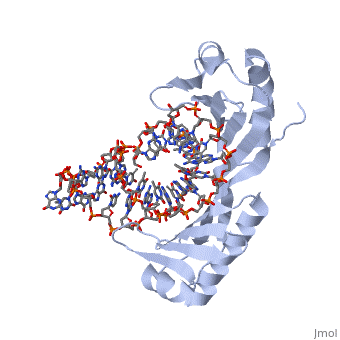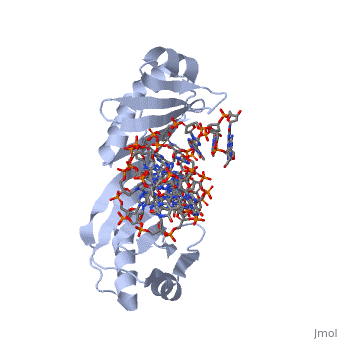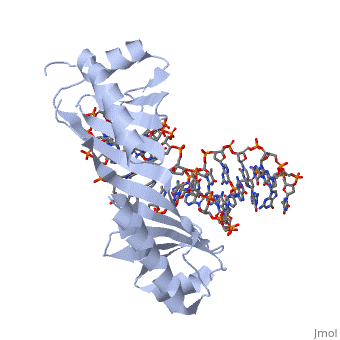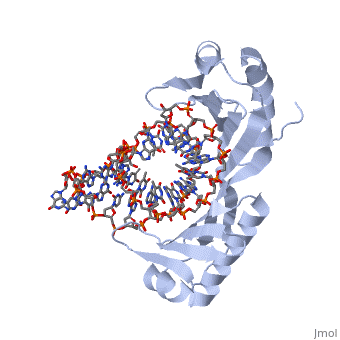
TATA Binding Protein (TBP)TBP (TATA Binding Protein) is a general transcription factor. Along with several other transcription factors TBP serves as a guide for the docking of RNA Polymerase II. TBP binds DNA at around 25-30 base pairs from the transcriptional start site in genes with promoters that contain a TATA box[1]. TBP is a component of the TF II B complex which along with several other general transcription factors makes up the preinitiation complex for RNA Polymerase II[2]. StructureTBP is a quite small single chain protein which has a saddle shape. Although the 3D picture shows 2 molecules the TBP is a single unit protein that does not have an oligomeric structure. The concave portions of the protein which bind to DNA are highly conserved. By contrast, the upper portion of the “saddle” is much more variable from species to species. This is due to the fact that the upper part of TBP is not in contact with DNA, nor is it directly involved with the binding of DNA. Unlike most proteins TBP binds DNA through the minor groove instead of the major groove. FunctionTBP plays a key role for the initiation of transcription in eukaryotic organisms. The function is not only to help target the sequence of DNA that is to be used for transcription as stated above, but TBP also functions to help initiate the transcription bubble. This is accomplished by bending the DNA to approximately an 80o angle which locally unwinds the DNA and is widely thought to be the method by which transcription is initiated. When the DNA is locally unwound, RNA polymerases and other proteins are recruited to help stabilize the DNA. This protein recruitment also initiates the beginning phases of transcription. Bending of The DNA has been determined to be a two step process. Step 1 is intercalation of DNA by a phenylalanine residue of the TBP. Intercalation occurs between the first and second base pairs at the 5’ end of the TATA box. This creates the first intermediate of DNA bent at a 45o angle This TBP DNA complex is given added stability from the binding of TF II B. Step number 2 is another phenylalanine residue intercalating the DNA between the last two base pairs at the 3’ end of the TATA box. Again the intercalation bends the DNA another 45o and is then stabilized by TF II B[3]. Dissociation of TBP from DNA is an extremely long period of time when compared to other proteins with dissociation half times in vitro have been measured from 15 minutes to 1 hour and more. There are 2 regulator proteins that have been found to have global effect of TBP, and these are Mot1 and NC24. Mot1 is an ATPase which uses an ATP hydrolysis to displace TBP from DNA. NC2 functions as a heterodimer of TBP that prevents the formation of the preintiation complex by blocking TBP from binding DNA[4].
|