Sandbox Reserved 497
From Proteopedia
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
<!-- PLEASE ADD YOUR CONTENT BELOW HERE --> | <!-- PLEASE ADD YOUR CONTENT BELOW HERE --> | ||
| - | =Dimethylsulfoniopropionate-Dependent Demethylase(DmdA)= | + | =Dimethylsulfoniopropionate-Dependent Demethylase (DmdA)= |
<Structure load='3TFH' size='500' frame='true' align='right' caption='Dimethylsulfoniopropionate-Dependent Demethylase (DmdA), [[3TFH]]' scene='Insert optional scene name here' /> | <Structure load='3TFH' size='500' frame='true' align='right' caption='Dimethylsulfoniopropionate-Dependent Demethylase (DmdA), [[3TFH]]' scene='Insert optional scene name here' /> | ||
Revision as of 06:26, 2 May 2012
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 13/03/2012, through 01/06/2012 for use in the course "Proteins and Molecular Mechanisms" taught by Robert B. Rose at the North Carolina State University, Raleigh, NC USA. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 451 through Sandbox Reserved 500. | |||||||
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing For more help, look at this link: http://www.proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/Help:Getting_Started_in_Proteopedia
Dimethylsulfoniopropionate-Dependent Demethylase (DmdA)
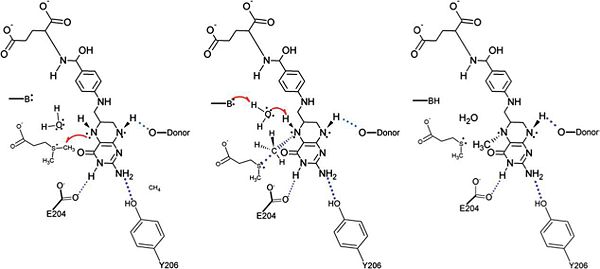
IntroductionDimethylsulfoniproprionate (DMSP) is a common metabolite produced by marine microorganisms and it acts as a significant carbon and sulfur source for marine bacteria. Degradation of DMSP occurs by either the cleavage pathway or the demethylation pathway [1]. The demethylation pathway is characterized by the conversion of DMSP into methylmercaptopropionate (MMPA). Dimethylsulfoniopropionate-Dependendent Demethylase (DmdA) is the first enzyme in the demethylation pathway and facilitates this conversion by acting as a transferase. While the exact mechanism of DmdA is still unknown, a proposed mechanism has recently been published. StructureThe structure of DmdA was recently solved through X-Ray Diffraction [2]. The structure contains 369 amino acids folded into four domains and containing two ligands. Mechanism of ActionThe specific mechanism of DmdA is still being investigated. However, a mechanism was recently proposed [3] Possible ApplicationsReferences
|