Sandbox Reserved 459
From Proteopedia
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
#1. '''''Blood serum amylase'''''- Blood serum amylase may be measured for purposes of medical diagnosis. A normal concentration is in the range 21-101 U/L. A higher than normal concentration may reflect one of several medical conditions, including acute inflammation of the pancreas. When the pancreas is diseased or inflamed, amylase is released into the blood. Blood serum amylase can also aid in diagnosing a perforated peptic ulcer, torsion of an ovarian cyst, strangulation ileus, macroamylasemia and mumps. Amylase may be measured in other body fluids, including urine and peritoneal fluid. | #1. '''''Blood serum amylase'''''- Blood serum amylase may be measured for purposes of medical diagnosis. A normal concentration is in the range 21-101 U/L. A higher than normal concentration may reflect one of several medical conditions, including acute inflammation of the pancreas. When the pancreas is diseased or inflamed, amylase is released into the blood. Blood serum amylase can also aid in diagnosing a perforated peptic ulcer, torsion of an ovarian cyst, strangulation ileus, macroamylasemia and mumps. Amylase may be measured in other body fluids, including urine and peritoneal fluid. | ||
| - | #2. '''''Amylase deficiency'''''- | + | #2. '''''Amylase deficiency'''''- One of the leading cause for amylase deficiency is a high carbohydrate diet. High volume of complex carbohydrate in the diet results in increased demand for amylase to convert them into simple sugars. After prolonged period of time, the levels of amylase fall below normal which result in amylase deficiency. Amylase is involved in anti-inflammatory reactions such as those caused by the release of histamine and similar substances. The inflammatory response usually occurs in organs which are in contact with the outside world such as the lungs and skin. |
| + | Therefore, an amylase deficiency can include skin problems such as psoriasis, eczema, hives, insect bites, allergic bee and bug stings. atopic dermatitis, and all types of herpes. Lung problems, including asthma and emphysema, require amylase plus other enzyme formulas depending on the particular condition. | ||
Revision as of 17:11, 4 May 2012
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 13/03/2012, through 01/06/2012 for use in the course "Proteins and Molecular Mechanisms" taught by Robert B. Rose at the North Carolina State University, Raleigh, NC USA. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 451 through Sandbox Reserved 500. | |||||||
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing For more help, look at this link: http://www.proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/Help:Getting_Started_in_Proteopedia
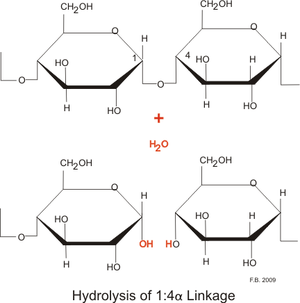
AmylaseIntroductionAmylase is categorized in a class of enzymes known as hydrolases. Hydrolases are enzymes which use water to cleave chemical bonds, usually dividing a large molecule into two smaller molecules. Examples of common hydrolases include esterases, proteases, glycosidases, nucleosidases, and lipases. Hydrolases carry out important degradative reactions in the body. During digestion, lipases hydrolyze lipids and proteases convert protein to amino acids. Hydrolases cleave large molecules into fragments used for synthesis , the excretion of waste materials, or as sources of carbon for the production of energy. Amylase is an enzyme that catalyses the breakdown of starch into sugars. Amylase is present in human saliva, where it begins the chemical process of digestion. Food that contains much starch but little sugar, such as rice and potato, taste slightly sweet as they are chewed because amylase turns some of their starch into sugar in the mouth. The pancreas also makes amylase (alpha amylase) to hydrolyse dietary starch into disaccharides and trisaccharides which are converted by other enzymes to glucose to supply the body with energy. Plants and some bacteria also produce amylase. As diastase, amylase was the first enzyme to be discovered and isolated. Amylase in all organisms has the function of breaking down complex carbohydrates.
StructureTo examine the crystal structure of human salivary amylase, X-ray crystallography was used with a resolution of 1.60 Å. The active site of alpha-amylase contains a trio of acidic groups that do most of the work. Ca2+ is a common for alpha amylase.The Ca2+ ion is bound to Asnl00, Arg158, Asp167, His201 and three water molecules. The Cl- ion is bound to Arg195, Asn298 and Arg337 and one water molecule. The highly mobile glycine-rich loop 304-310 may act as a gateway for substrate binding and be involved in a `trap-release' mechanism in the hydrolysis of substrates. Strategic placement of calcium and chloride ions, as well as histidine and tryptophan residues may play a role in differentiating between the glycone and aglycone ends of the polysaccharide substrates. Salivary amylase also possesses a suitable site for binding to enamel surfaces and provides potential sites for the binding of bacterial adhesins. . Salivary amylase folds into a multidomain structure consisting of three domains, A, B and C. Domain A has a (a/b)8- barrel structure, domain B has no definite topology and domain C has a Greek-key barrel structure. Circular dichroism spectroscopic data revealed the native alpha-amylase to contain 25% , 21% , and 54% random coils. It is generally assumed that in proteins hydrophobic residues are not favorable at solvent-exposed sites, and that amino acid substitutions on the surface have little effect on protein thermostability. Contrary to these assumptions, hyperthermostable variants of alpha amylase have been identified that result from the incorporation of at the surface.
Mechanism of Action
Medical Implications or Possible Applications
Therefore, an amylase deficiency can include skin problems such as psoriasis, eczema, hives, insect bites, allergic bee and bug stings. atopic dermatitis, and all types of herpes. Lung problems, including asthma and emphysema, require amylase plus other enzyme formulas depending on the particular condition. |