Sandbox Reserved 498
From Proteopedia
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
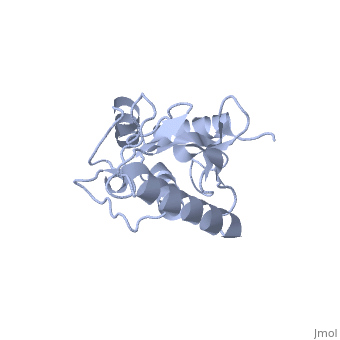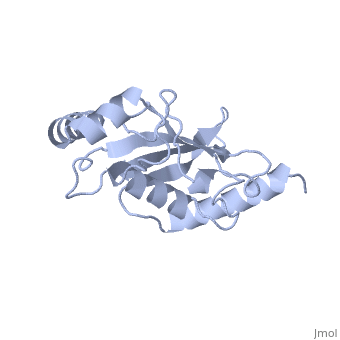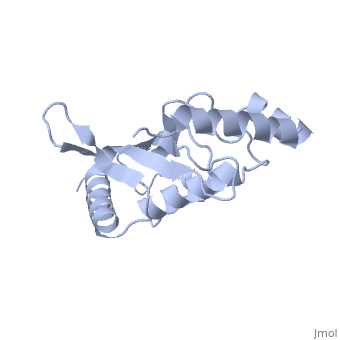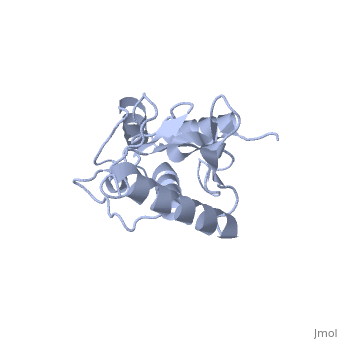
<Structure load='1U9A' size='500' frame='true' align='right' caption='Ubiquitin-conjugating Enzyme, [[Ubc9]]' scene='' /> | <Structure load='1U9A' size='500' frame='true' align='right' caption='Ubiquitin-conjugating Enzyme, [[Ubc9]]' scene='' /> | ||
| - | [[Image:1U9A. | + | [[Image:1U9A.png|250px|left]] |
==Background== | ==Background== | ||
[[Ubc9]], an ubiquitin conjugating enzyme, participates not in the ubiquitinylation pathway but in the sumoylation pathway. This pathway links a SUMO molecule to a targeted protein.(Filip) | [[Ubc9]], an ubiquitin conjugating enzyme, participates not in the ubiquitinylation pathway but in the sumoylation pathway. This pathway links a SUMO molecule to a targeted protein.(Filip) | ||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
Ubc9 is one of the 35 known mammalian ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes. These Ubcs bind to ubiquitin or ubiquitin –like proteins.(Sjored) | Ubc9 is one of the 35 known mammalian ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes. These Ubcs bind to ubiquitin or ubiquitin –like proteins.(Sjored) | ||
| + | ==Structure== | ||
| + | Ubc9 has a conserved structure. It is mostly a rigid conformation. The active site has flexibility and mobility.(Lin) It was crystallized as a monomer.(Tong) | ||
| + | In contrast to other Ubc’s, Ubc9’s surface area that binds SUMO is positively charged whereas the corresponding regions on other Ubc’s is negatively charged or has a neutral potential. SUMO is negatively charged and since ubiquitin is positively charged it cannot bind to Ubc9.(Muller) | ||
| - | + | Ubc9 is considered a Class I of the four different Ubcs classes. A Class I consists mostly of the catalytic core domain that has about 150 residues. It does not have extra C or N terminal extensions as the other classes do.(Tong) | |
| + | |||
| + | The amino acid sequence of Ubc9 is completely identical to the mouse Ubc9 sequence. It has a 56% homology to Saccharomyces cerevisiae and a 66% homology to Schizosaccharomyces pombe. (Tong) | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Location== | ||
| + | The Ubc9 protein is found in various locations within the body in varying amounts. The highest levels were found in the spleen, followed closely by the lung. Moderate levels were found in the kidneys and liver. Low and barely detectable levels were found in the brain, heart, and skeletal muscle.(Filip) | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==SUMO== | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[SUMO]] is a small protein of 101 amino acids. It is only 20% homologous to ubiquitin. (Courey) | ||
| + | Invertebrates have one SUMO gene, while vertebrates have three: SUMO-1, SUMO-2, SUMO-3. (Muller) | ||
| + | SUMO (small ubiquitin like modifier) is also known as UBL1, GMP1, SMTP3, PIC1, and sentrin.(Lin) | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==Pathway== | ||
| + | |||
| + | The sumoylation pathway starts with activation of the SUMO molecule by E1, an ubiquitin-activating enzyme. The ATP dependent activation is by the E1 heterodimer, SAE1/SAE2 (Aos1/Uba2). A thioester bond is formed between the carboxyl terminal of the glycine residue of SUMO and the cysteine residue of SAE2. E1 then transfers SUMO to E2, the ubiquitin conjugating enzyme, Ubc9 (UBE2I). This is a transesterification reaction of the SUMO’s glycine residue to the SH group of the active site of cysteine 93 of Ubc9. The final transfer is SUMO from the SUMO-Ubc9 conjugate to the target protein. SUMO will covalently link via an isopeptide bond to the ε-amino group of the lysine on the target protein. E1 and Ubc9 are recycled for future conjugations. (Filip)(Sjored)(Lin) (Courey) | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Example.jpg]] | ||
Revision as of 10:23, 10 May 2012
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 13/03/2012, through 01/06/2012 for use in the course "Proteins and Molecular Mechanisms" taught by Robert B. Rose at the North Carolina State University, Raleigh, NC USA. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 451 through Sandbox Reserved 500. | |||||||
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing For more help, look at this link: http://www.proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/Help:Getting_Started_in_Proteopedia
BackgroundUbc9, an ubiquitin conjugating enzyme, participates not in the ubiquitinylation pathway but in the sumoylation pathway. This pathway links a SUMO molecule to a targeted protein.(Filip) Ubc9’s conjugation with SUMO and not ubiquitin results in the targeted protein being tagged not for degradation, but to modify the protein for use in regulation, enhancing protein activity, and/or cell cycle functions. (Muller)(Victor) Ubc9 is one of the 35 known mammalian ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes. These Ubcs bind to ubiquitin or ubiquitin –like proteins.(Sjored) StructureUbc9 has a conserved structure. It is mostly a rigid conformation. The active site has flexibility and mobility.(Lin) It was crystallized as a monomer.(Tong) In contrast to other Ubc’s, Ubc9’s surface area that binds SUMO is positively charged whereas the corresponding regions on other Ubc’s is negatively charged or has a neutral potential. SUMO is negatively charged and since ubiquitin is positively charged it cannot bind to Ubc9.(Muller) Ubc9 is considered a Class I of the four different Ubcs classes. A Class I consists mostly of the catalytic core domain that has about 150 residues. It does not have extra C or N terminal extensions as the other classes do.(Tong) The amino acid sequence of Ubc9 is completely identical to the mouse Ubc9 sequence. It has a 56% homology to Saccharomyces cerevisiae and a 66% homology to Schizosaccharomyces pombe. (Tong) LocationThe Ubc9 protein is found in various locations within the body in varying amounts. The highest levels were found in the spleen, followed closely by the lung. Moderate levels were found in the kidneys and liver. Low and barely detectable levels were found in the brain, heart, and skeletal muscle.(Filip) SUMOSUMO is a small protein of 101 amino acids. It is only 20% homologous to ubiquitin. (Courey) Invertebrates have one SUMO gene, while vertebrates have three: SUMO-1, SUMO-2, SUMO-3. (Muller) SUMO (small ubiquitin like modifier) is also known as UBL1, GMP1, SMTP3, PIC1, and sentrin.(Lin)
PathwayThe sumoylation pathway starts with activation of the SUMO molecule by E1, an ubiquitin-activating enzyme. The ATP dependent activation is by the E1 heterodimer, SAE1/SAE2 (Aos1/Uba2). A thioester bond is formed between the carboxyl terminal of the glycine residue of SUMO and the cysteine residue of SAE2. E1 then transfers SUMO to E2, the ubiquitin conjugating enzyme, Ubc9 (UBE2I). This is a transesterification reaction of the SUMO’s glycine residue to the SH group of the active site of cysteine 93 of Ubc9. The final transfer is SUMO from the SUMO-Ubc9 conjugate to the target protein. SUMO will covalently link via an isopeptide bond to the ε-amino group of the lysine on the target protein. E1 and Ubc9 are recycled for future conjugations. (Filip)(Sjored)(Lin) (Courey) |