We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
G09SecL04Tpc2
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | == Outer Surface Protein A (OspA) == | ||
| + | <Structure load='1fj1' size='500' frame='true' align='right' caption='Outer Surface Protein A Fab LA-2 Complex' scene='Insert optional scene name here' /> | ||
| + | |||
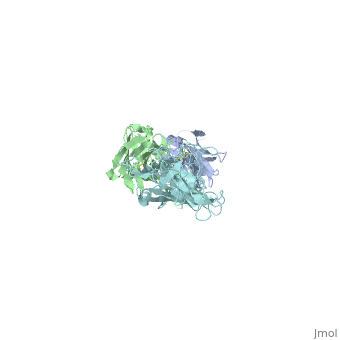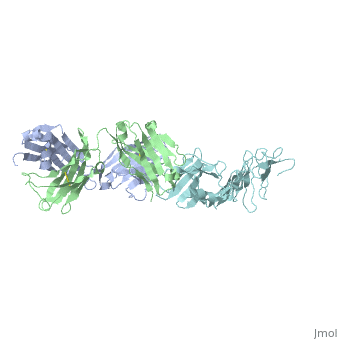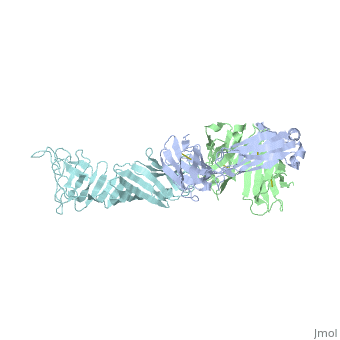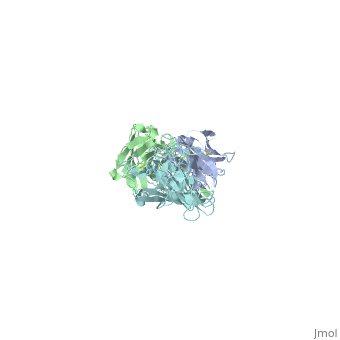
| + | Outer surface protein A (OspA) is a major lipoprotein on the borrelia burgdorferi spirochete which is a causative agent of Lyme Disease. The three loops in the C-terminus define the OspA antigen-antibody complex. The interaction between the loops and the LA-2 (antibody) forms the basis for OspA vaccination. Along with other surface proteins, OspA has many important functions such as late stage neurological disorders that are associated with Lyme Disease. | ||
| + | |||
== Introduction to Lyme Disease == | == Introduction to Lyme Disease == | ||
== Structure == | == Structure == | ||
| - | |||
| - | == Outer Surface Protein A (OspA) == | ||
| - | <Structure load='1fj1' size='500' frame='true' align='right' caption='Outer Surface Protein A Fab LA-2 Complex' scene='Insert optional scene name here' /> | ||
Revision as of 03:30, 16 August 2012
Outer Surface Protein A (OspA)
|
Outer surface protein A (OspA) is a major lipoprotein on the borrelia burgdorferi spirochete which is a causative agent of Lyme Disease. The three loops in the C-terminus define the OspA antigen-antibody complex. The interaction between the loops and the LA-2 (antibody) forms the basis for OspA vaccination. Along with other surface proteins, OspA has many important functions such as late stage neurological disorders that are associated with Lyme Disease.