This is a joint project of students at La Cañada High School, La Cañada Flintridge, California USA, and students at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, California USA, mentored by Professor Remo Rohs.
A Base Pairing Variant Enhances p53 Binding to a Consensus Site
Introduction and Biological Role of the Tumor Suppressor p53
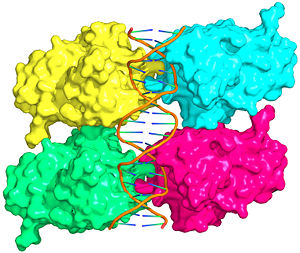
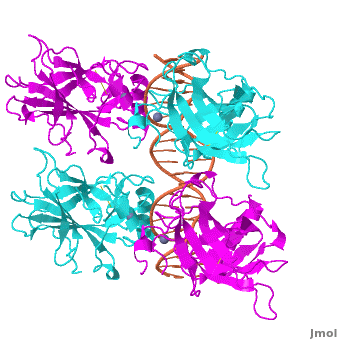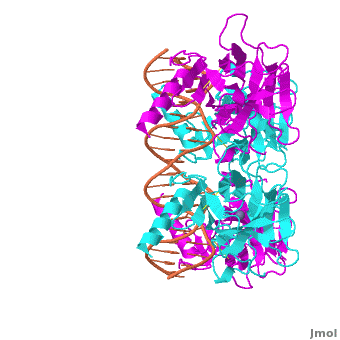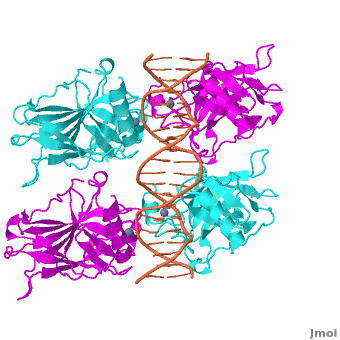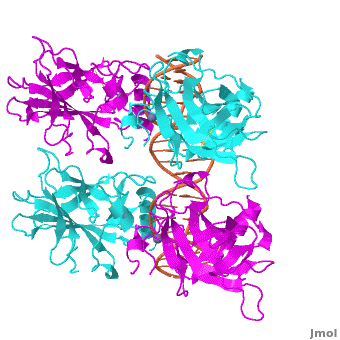
Figure 1: Crystal structure of a p53 DBD tetramer-DNA complex;
PDB ID# 3KZ8[1].
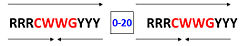
Figure 2: p53 consensus site; R= A or G, Y= C or T, and W=A or T.
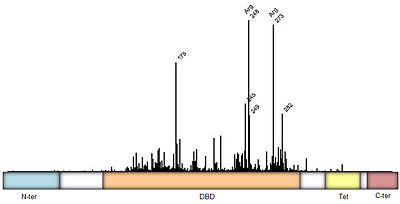
Figure 3: Frequency of p53 mutants associated with cancer derived from
IARC TP53 database. Domain architecture; N-ter=N-terminal, DBD=DNA binding domain
[1], Tet=Tetramerization
[2], and C-ter=C-terminal domain. Intermediate regions are fairly disordered.
Also known as the Guardian of the Genome, the tumor suppressor p53 is crucial in the natural defense against human cancer. The protein is activated by stress factors that can compromise the genomic integrity of the cell. This activation unleashes the function of p53 as a transcription factor. It binds as a tetramer (Figure 1) to a large range of DNA response elements. The p53 consensus site (Figure 2) is formed by two decameric half-sites, each containing a core element (red), that are separated by a variable number of base pairs (blue).
Binding of p53 to different response elements leads to distinct biological responses, such as cell-cycle arrest, senescence, or apoptosis. These different pathways correspond, at least in part, to differences in p53-DNA binding affinity and stability, which are determined by specific protein-DNA interactions.
Mutations of p53 residues are associated with 50% of human cancers. Such mutations are predominantly located in the p53-DNA binding domain (DBD),based on an analysis of human tumors (Figure 3). Particularly, arginine residues in the p53-DNA interface were found in tumors with high frequencies.
Structural Description of p53-DNA Complex
Domain Architecture and Tetramerization
The p53 protein consists of the N-terminal transactivation domain, the DNA binding domain (DBD) or core, the tetramerization domain (see its structure below), and the C-terminal regulatory domain (Figure 3). This Proteopedia page discusses protein-DNA recognition by p53, thus focusing on the DBD of p53 (, PDB ID 3KZ8).
The DBD in tetrameric form binds to a DNA response element (), which consists of two DNA half sites. These decameric half sites can be separated by a DNA spacer of flexible length but in this case, the spacer is of length zero base pairs. The with each magenta-cyan dimer binding to one half site of the response element[3].
The p53 DBD assumes the conformation of an , which binds the response element in the major groove. A functionally important and, thus, stabilizes the fold of the DBD.
Protein-Protein Interactions
The human p53 tetramer forms a relatively small and, in comparison, a large . The actual molecular interactions and strength in binding can vary as functions of the sequence and spacer length of the response element.
Major Groove Base Readout
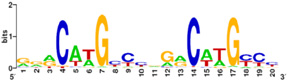
Figure 5: p53 binding site motif with G/C base pairs most conserved. PLoS has provided permission for usage of this figure
[4].
Protein side chains and base pairs form direct contacts in the major groove. Among which, the contributes most to binding specificity. This highly specific readout is due to the . As a result of this base readout the G/C base pairs in the CWWG core elements are the most conserved positions in p53 response elements (Figure 5).
Another important contact is formed with the . Lys120 is very important biologically because acetylation of this residue is known to trigger the apoptotic response of p53.
DNA Backbone Contact
Another arginine residue, forming a salt bridge, and seems to be important for human p53-DNA binding. Moreover, Arg273 is the second most common missense mutation in human cancer (Figure 3).
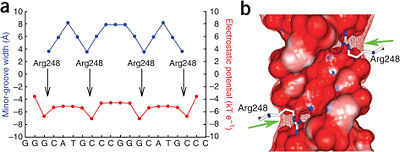
Figure 6: DNA shape readout of narrow minor groove regions with enhanced electrostatic potential by Arg248. Nature Publishing Group has provided permission for usage of this figure
[1].
Minor Groove Shape Readout
Most commonly, however, the residue Arg248 is found mutated in human tumors. although it does not usually form hydrogen bonds with the bases. Arg248 was shown to recognize regions of narrow minor groove associated with enhanced negative electrostatic potential (Figure 6)[1]. This observation provides a novel molecular explanation of the importance of Arg248 for p53-DNA binding and its role in cancer. The described mechanism known as shape readout was found to be broadly employed by arginine residues[5].
Hoogsteen vs. Watson-Crick Base Pair in p53 Binding Sites
The distinct is due to a transition of the four A/T base pairs of the CATG core elements to a Hoogsteen base pairing geometry. Regions with Hoogsteen base pairs compared to regions with Watson-Crick base pairs.
The reason for this deformation of the double helix is the with the approximately 180 degree rotation of adenine around the glycosidic bond and formation of hydrogen bonds with thymine at a different edge of the adenine base compared to , depicted here for the identical base pair in a p53 response element with different sequence from PDB ID# 3KMD.
Tetramerization Domain
Aside from the DBD, the only other domain for which structural information is available is the tetramerization domain [Figure 7, ], which forms as a dimer of dimers with one alpha helix and one beta strand contributed by each p53 monomer. The tetramerization domain is not present in the crystal structure of the DBD (Figure 4).
Further Reading
Within Proteopedia:
Hoogsteen base pairs have previously been found in protein-DNA complexes but usually associated with drastic deformations of the DNA. Only in one case of a homeodomain protein, a Hoogsteen base pair was identified in undistorted B-DNA[6].
As for p53-DNA recognition, Hoogsteen base pairs are not present in the complex with a different DNA sequence [7] but the DNA undergoes a different deformation not observed in the complex with Hoogsteen base pairing. Since transient Hoogsteen base pairs have been detected in naked DNA with preferences for CA and TA dincucleotides[8], the observation of the base pairing variant in p53-DNA complexes indicates a sequence-speific feature of the response element either recognized or stabilized by p53.
A more general discussion of structural origins of binding specificity in protein-DNA recognition has been published along with a suggestion for a new classification of protein-DNA readout modes that goes beyond the historical description of direct and indirect readout[9].
Acknowledgements
This Proteopedia page originates from the partnership of the Rohs Laboratory at the University of Southern California with La Cañada High School. This partnership was initiated by Remo Rohs and Patty Compeau in September 2011 as Bioinformatics Institute, which is part of the Institutes of the 21st Century. Advice and technical help by Proteopedia editors Eran Hodis, Eric Martz, Jaime Prilusky, and Joel Sussman is acknowledged.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Kitayner M, Rozenberg H, Rohs R, Suad O, Rabinovich D, Honig B, Shakked Z. Diversity in DNA recognition by p53 revealed by crystal structures with Hoogsteen base pairs. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2010;17(4):423-9. PMID:20364130.
- ↑ Jeffrey PD, Gorina S, Pavletich NP. Crystal structure of the p53 tetramerization domain. Science 1995;267:1498-502. PMID:7878469.
- ↑ Kitayner M, Rozenberg H, Kessler N, Rabinovich D, Shaulov L, Haran TE, Shakked Z. Structural basis of DNA recognition by p53 tetramers. Mol Cell. 2006 Jun 23;22(6):741-53. PMID:16793544.
- ↑ Horvath MM, Wang X, Resnick MA, Bell DA. Divergent evolution of human p53 binding sites: cell cycle versus apoptosis. PLoS Genet. 2007 Jul;3(7):e127. PMID:17677004.
- ↑ Rohs R, West SM, Sosinsky A, Liu P, Mann RS, Honig B. The role of DNA shape in protein-DNA recognition. Nature. 2009;461(7268):1248-53. PMID:19865164.
- ↑ Aishima J, Gitti RK, Noah JE, Gan HH, Schlick T, Wolberger C. A Hoogsteen base pair embedded in undistorted B-DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002;30(23):5244-52. PMID:12466549.
- ↑ Chen Y, Dey R, Chen L. Crystal structure of the p53 core domain bound to a full consensus site as a self-assembled tetramer. Structure. 2010;18(2):246-56. PMID:20159469.
- ↑ Nikolova EN, Kim E, Wise AA, O'Brien PJ, Andricioaei I, Al-Hashimi HM. Transient Hoogsteen base pairs in canonical duplex DNA. Nature. 2011;470(7335):498-502. PMID:21270796.
- ↑ Rohs R, Jin X, West SM, Joshi R, Honig B, Mann RS. Origins of specificity in protein-DNA recognition. Annu Rev Biochem. 2010;79:233-69. PMID:20334529.