This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Nuclear receptor
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
(New page: == Nuclear Receptor == === Structure === ==== DBD (DNA Binding Domain) ==== ==== LBD (Ligand Binding Domain) ==== <StructureSection load='1ie8' size='350' side='right' caption='Structure ...) |
m |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
==== DBD (DNA Binding Domain) ==== | ==== DBD (DNA Binding Domain) ==== | ||
==== LBD (Ligand Binding Domain) ==== | ==== LBD (Ligand Binding Domain) ==== | ||
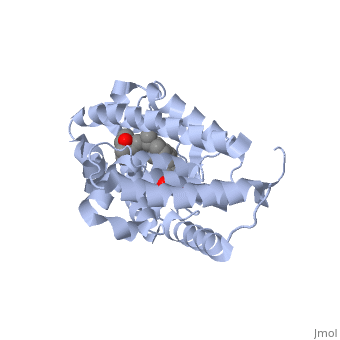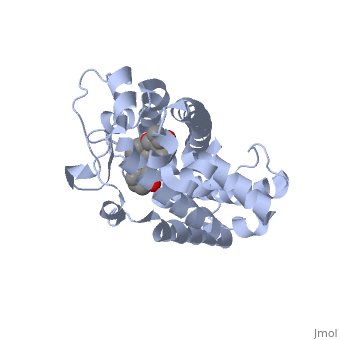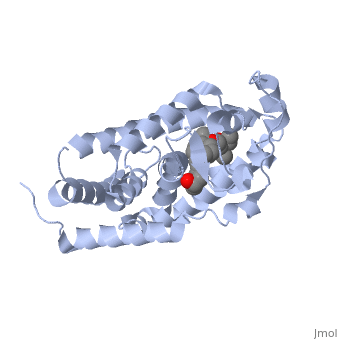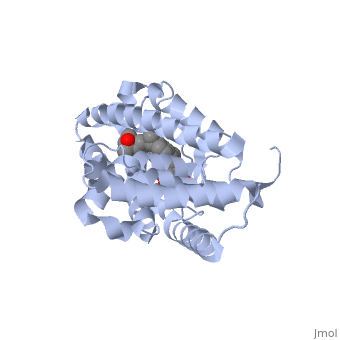
| - | <StructureSection load='1ie8' size='350' side='right' caption='Structure of | + | <StructureSection load='1ie8' size='350' side='right' caption='Structure of the LBD of a VDR (vitamin D receptor) complexed to 1alpha,25(OH)(2)D(3) and the 20-epi analogs(PDB entry [[1ie8]])' scene=''> |
| - | The LBD of | + | The structure of the LBD is strongly conserved throughout the familly of nuclear receptors. |
| + | It is completely folded and composed of a beta-sheet, and 12 alpha-helices arranged in a three layered sandwich. | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
Revision as of 08:14, 6 September 2012
Contents |
Nuclear Receptor
Structure
DBD (DNA Binding Domain)
LBD (Ligand Binding Domain)
| |||||||||||