Journal:JBSD:30
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)

| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
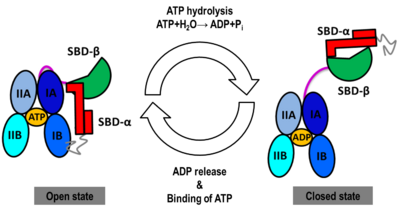
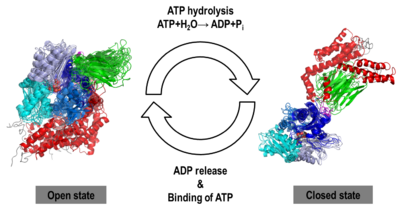
The Hsp70s assists in the folding of other proteins through cycles of binding and release of unfolded polypeptide chains in the SBD (Figure 1). The cycle is governed by the nucleotide-binding status of the NBD: in the ATP-bound Hsp70, the SBD is opened with fast binding and release of the protein substrate and the SBD and the NBD are docked, whereas in the ADP-bound and nucleotide-free states (APO), the SBD is assumed to be closed with low binding and release rate of the protein substrate, with the SBD and the NBD undocked. The transition between the ATP (open conformation) and the ADP states of Hsp70 (closed conformation) is triggered by the ATP binding to the NBD, which induces a conformational change of the interdomain linker, and the opening of the SBD through an allosteric mechanism which is not fully elucidated (see static image below). The ATP hydrolysis restores the closed conformation of the SBD. Rebinding of ATP to the nucleotide-free Hsp70 restarts the cycle of the chaperone. In vivo, the ATP hydrolysis and nucleotide exchange rates are increased by co-chaperones. Because of their critical roles in many cellular processes and based on evidence that their mechanisms involve cycles of conformational changes, there has been a strong interest in elucidating the structures of human Hsp70 in its two main conformations, i.e. ATP and ADP-bound. Structures of human Hsp70 are of first interest for the design of drugs in new cancer therapies. However, only the structure of the NBD of hHsp70 was solved by X-ray. Truncated structures comprising both the NBD and the SBD were solved for the bacterial E. coli Hsp70 homolog in the closed state (PDB ID: [[2kho]]) and for the yeast ''S. cerevisiae'' Hsp110 homolog in the open state (PDB ID: [[3c7n]]). | The Hsp70s assists in the folding of other proteins through cycles of binding and release of unfolded polypeptide chains in the SBD (Figure 1). The cycle is governed by the nucleotide-binding status of the NBD: in the ATP-bound Hsp70, the SBD is opened with fast binding and release of the protein substrate and the SBD and the NBD are docked, whereas in the ADP-bound and nucleotide-free states (APO), the SBD is assumed to be closed with low binding and release rate of the protein substrate, with the SBD and the NBD undocked. The transition between the ATP (open conformation) and the ADP states of Hsp70 (closed conformation) is triggered by the ATP binding to the NBD, which induces a conformational change of the interdomain linker, and the opening of the SBD through an allosteric mechanism which is not fully elucidated (see static image below). The ATP hydrolysis restores the closed conformation of the SBD. Rebinding of ATP to the nucleotide-free Hsp70 restarts the cycle of the chaperone. In vivo, the ATP hydrolysis and nucleotide exchange rates are increased by co-chaperones. Because of their critical roles in many cellular processes and based on evidence that their mechanisms involve cycles of conformational changes, there has been a strong interest in elucidating the structures of human Hsp70 in its two main conformations, i.e. ATP and ADP-bound. Structures of human Hsp70 are of first interest for the design of drugs in new cancer therapies. However, only the structure of the NBD of hHsp70 was solved by X-ray. Truncated structures comprising both the NBD and the SBD were solved for the bacterial E. coli Hsp70 homolog in the closed state (PDB ID: [[2kho]]) and for the yeast ''S. cerevisiae'' Hsp110 homolog in the open state (PDB ID: [[3c7n]]). | ||
[[Image:JBSD30.png|left|400px|thumb|<font color='blue'><b>NBD-IA is in blue</b></font>, <span style="color:deepskyblue;background-color:black;font-weight:bold;">NBD-IB is in deepskyblue</span>, <span style="color:lightsteelblue;background-color:black;font-weight:bold;">NBD-IIA is in lightsteelblue</span>, <span style="color:cyan;background-color:black;font-weight:bold;">NBD-IIB is in cyan</span>, <font color='magenta'><b>Linker is in magenta</b></font>, <span style="color:lime;background-color:black;font-weight:bold;">SBD-β is in green</span>, <font color='red'><b>SBD-α is in red</b></font>, <span style="color:darkgray;background-color:black;font-weight:bold;">C-terminal is in gray</span>]] | [[Image:JBSD30.png|left|400px|thumb|<font color='blue'><b>NBD-IA is in blue</b></font>, <span style="color:deepskyblue;background-color:black;font-weight:bold;">NBD-IB is in deepskyblue</span>, <span style="color:lightsteelblue;background-color:black;font-weight:bold;">NBD-IIA is in lightsteelblue</span>, <span style="color:cyan;background-color:black;font-weight:bold;">NBD-IIB is in cyan</span>, <font color='magenta'><b>Linker is in magenta</b></font>, <span style="color:lime;background-color:black;font-weight:bold;">SBD-β is in green</span>, <font color='red'><b>SBD-α is in red</b></font>, <span style="color:darkgray;background-color:black;font-weight:bold;">C-terminal is in gray</span>]] | ||
| + | {{Clear}} | ||
'''4. Conformational heterogeneity observed in MD simulations''' | '''4. Conformational heterogeneity observed in MD simulations''' | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
- ↑ Nicolai A, Delarue P, Senet P. Conformational dynamics of full-length inducible human Hsp70 derived from microsecond molecular dynamics simulations in explicit solvent. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2012 Oct 17. PMID:23075261 doi:10.1080/07391102.2012.726190
This page complements a publication in scientific journals and is one of the Proteopedia's Interactive 3D Complement pages. For aditional details please see I3DC.