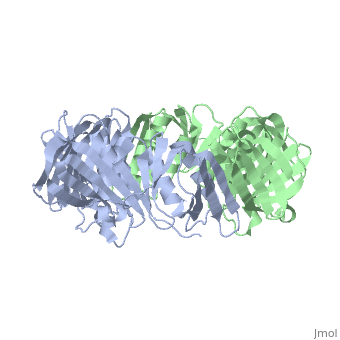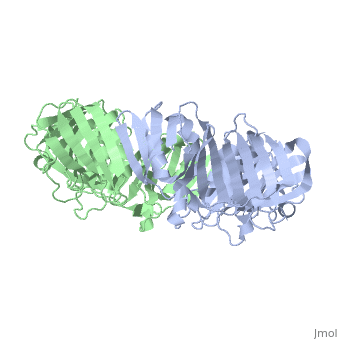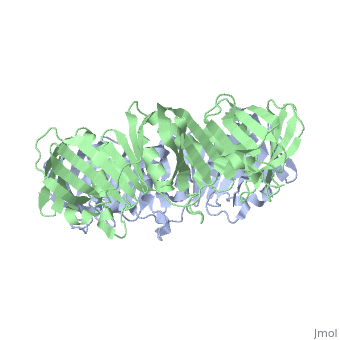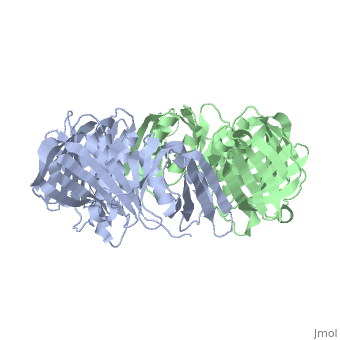
Polymerase III homoenzyme beta subunit
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | + | ||
[[Image:2pol.png|left|200px]] | [[Image:2pol.png|left|200px]] | ||
Revision as of 09:45, 8 November 2012
Introduction
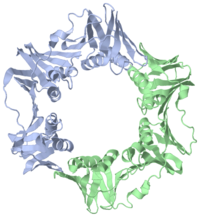
The of the Polymerase III holoenzyme is one of ten subunits in the Pol III multisubunit complex, which catalyzes the synthesis of both the leading and lagging strands of DNA in E. Coli. While the core Pol III enzyme (consisting of the alpha, sigma and theta subunits) dissociates from the DNA after replicating approximately 12 residues, the holoenzyme complex has a processivity of more than 5,000 residues. The increase in replication processing is due to the beta subunit.
| |||||||||||
See Also
Reference
- Kong XP, Onrust R, O'Donnell M, Kuriyan J. Three-dimensional structure of the beta subunit of E. coli DNA polymerase III holoenzyme: a sliding DNA clamp. Cell. 1992 May 1;69(3):425-37. PMID:1349852
- Indiani C, O'Donnell M. The replication clamp-loading machine at work in the three domains of life. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Oct;7(10):751-61. Epub 2006 Sep 6. PMID:16955075 doi:10.1038/nrm2022