We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 390
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
===Mutation of Glycine at position 465=== | ===Mutation of Glycine at position 465=== | ||
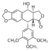
According to earlier experiments, the glycine at position 465 in this structure is proposed to lie very close to the cleavage site and it’s is therefore expected to be involved in ATP hydrolysis. So the change of residue 465 from <scene name="Glycine.pngj">glycine</scene> to a more negatively charged <scene name="Aspatic.pngj">(aspartic acid)</scene> is determined to create some localized hydrogen bonding at the backbone that can potentially alter the conformation of the enzyme (this change is determined to alter the charge interactions involved in binding site). | According to earlier experiments, the glycine at position 465 in this structure is proposed to lie very close to the cleavage site and it’s is therefore expected to be involved in ATP hydrolysis. So the change of residue 465 from <scene name="Glycine.pngj">glycine</scene> to a more negatively charged <scene name="Aspatic.pngj">(aspartic acid)</scene> is determined to create some localized hydrogen bonding at the backbone that can potentially alter the conformation of the enzyme (this change is determined to alter the charge interactions involved in binding site). | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | <scene name="Glycine.pngj">glycine</scene> at | ||
| - | |||
| - | <scene name="Glycine.pngj">glycine</scene> at position 465 | ||
| - | |||
| - | <scene name="Aspatic.pngj">text to be added</scene> | ||
| - | <scene name="Aspatic.pngj">Aspactic acid</scene> at position 465 | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
Revision as of 02:42, 21 November 2012
Human topoisomerase IIbeta in complex with DNA and etoposide
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Wu CC, Li TK, Farh L, Lin LY, Lin TS, Yu YJ, Yen TJ, Chiang CW, Chan NL. Structural basis of type II topoisomerase inhibition by the anticancer drug etoposide. Science. 2011 Jul 22;333(6041):459-62. PMID:21778401 doi:10.1126/science.1204117
- ↑ Kathryn L. Gilroy, Chrysoula Leontiou, Kay Padget, Jeremy H. Lakey and Caroline A. Austin* "mAMSA resistant human topoisomerase IIβ mutation G465D has reduced ATP hydrolysis activity” Oxford JournalsLife Sciences Nucleic Acids Research Volume 34, Issue 5Pp. 1597-1607. DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkl057
- ↑ Wu CC, Li TK, Farh L, Lin LY, Lin TS, Yu YJ, Yen TJ, Chiang CW, Chan NL. Structural basis of type II topoisomerase inhibition by the anticancer drug etoposide. Science. 2011 Jul 22;333(6041):459-62. PMID:21778401 doi:10.1126/science.1204117