Clegg TBP sandbox
From Proteopedia
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
==General Structure of TBP== | ==General Structure of TBP== | ||
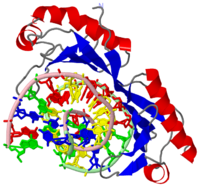
| - | The TBP has two imperfect direct repeats that form a <scene name='Clegg_TBP_sandbox/Saddle/1'>saddle</scene> shaped structure with <scene name='Clegg_TBP_sandbox/Stirrup/2'>stirrups</scene>forming a concave like DNA binding surface | + | The TBP has two imperfect direct repeats that form a <scene name='Clegg_TBP_sandbox/Saddle/1'>saddle</scene> shaped structure with <scene name='Clegg_TBP_sandbox/Stirrup/2'>stirrups</scene> forming a concave like DNA binding surface. This allows for an induced-fit mechanism. The imperfect direct repeats differ by two residues. The first is a deletion of a residue at the end of helix H2. The second is the addition of a proline in helix H2' that enables a <scene name='Clegg_TBP_sandbox/Proline/1'>bend</scene> that does not occur on H2.‘<ref>Crystal structure of a human TATA box-binding protein/TATA element complex., Nikolov DB, Chen H, Halay ED, Hoffman A, Roeder RG, Burley SK, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 May 14;93(10):4862-7. PMID:8643494</ref>’ When the TBP binds to the TATA box a conformation change takes place and the DNA strand is <scene name='Clegg_TBP_sandbox/Bend/1'>bent</scene> 80 degrees. This conformational change promotes the recruitment of other general transcription factors. A total of seven <scene name='Clegg_TBP_sandbox/Lysines/1'>lysine</scene> residues interact with DNA backbone. Four of these residues Lys-204, Lys-214, Lys-295, and Lys 305 allow for the partial charge neutralization within the TATA box. Serveral arginines also interact with the DNA strand these residues include: <scene name='Clegg_TBP_sandbox/Lysines/3'>Arg-192</scene>, Arg-199, Arg-290. The TBP is crucual protien that recognizes the promoter region of DNA and allows for other general transcription factors to bind and form a complex which can eventually lead to transcripton. |
Revision as of 06:13, 26 November 2012
| |||||||||
| 1cdw, resolution 1.90Å () | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Resources: | FirstGlance, OCA, RCSB, PDBsum | ||||||||
| Coordinates: | save as pdb, mmCIF, xml | ||||||||
TATA Binding Protein Overview
In order to initiate transcription in eukaryotes, protein factors, known as general transcription factors (GTF), and RNA polymerase must bind to promoter regions of DNA. When all the GTFs are bound into one complex it is known as the preinitiation complex (PIC). The assembly of the PIC stats with the TBP binding to the promoter, followed by TFIIA and TFIIB, next TFIIF binds RNA Polymerase II and transports it to the complex, and finally TFIIE and TFIIH are recruited to complete the complex.‘[1]’ This mechanism/assembly enables the start of transcription.
General Structure of TBP
The TBP has two imperfect direct repeats that form a shaped structure with forming a concave like DNA binding surface. This allows for an induced-fit mechanism. The imperfect direct repeats differ by two residues. The first is a deletion of a residue at the end of helix H2. The second is the addition of a proline in helix H2' that enables a that does not occur on H2.‘[2]’ When the TBP binds to the TATA box a conformation change takes place and the DNA strand is 80 degrees. This conformational change promotes the recruitment of other general transcription factors. A total of seven residues interact with DNA backbone. Four of these residues Lys-204, Lys-214, Lys-295, and Lys 305 allow for the partial charge neutralization within the TATA box. Serveral arginines also interact with the DNA strand these residues include: , Arg-199, Arg-290. The TBP is crucual protien that recognizes the promoter region of DNA and allows for other general transcription factors to bind and form a complex which can eventually lead to transcripton.