This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Group:MUZIC:Myozenin
From Proteopedia

(→Introduction) |
(→Introduction) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Introduction== | == Introduction== | ||
| - | The '''f'''ilamin-C α-'''a'''ctinin '''t'''elethonin '''Z'''-disc binding protein ('''FATZ''') is a protein family of three isoforms: FATZ-1, FATZ-2, FATZ-3, which are expressed in muscle cells.<ref> PMID: 10984498</ref> This protein family, that is also known as '''Myozenin''' or '''Calsarcin''', is mainly localized in the Z-disc, although recently it has been described that FATZ-2 appears in cardiac nuclei. <ref>PMID: 20170660</ref> The expression of the three isoforms has been shown to be fibre type specific. For instance, FATZ-1 and FATZ-3 are exclusively expressed in skeletal muscle fast-twitch fibres while FATZ-2 is expressed in cardiac and slow-twitch fibres <ref>PMID: 11114196</ref><ref>PMID: 11842093</ref>. FATZ proteins have multiple binding partners in the Z-disc, which involve them in different functions like the Z-disc formation and maintenance | + | The '''f'''ilamin-C α-'''a'''ctinin '''t'''elethonin '''Z'''-disc binding protein ('''FATZ''') is a protein family of three isoforms: FATZ-1, FATZ-2, FATZ-3, which are expressed in muscle cells.<ref> PMID: 10984498</ref> This protein family, that is also known as '''Myozenin''' or '''Calsarcin''', is mainly localized in the Z-disc, although recently it has been described that FATZ-2 appears in cardiac nuclei. <ref>PMID: 20170660</ref> The expression of the three isoforms has been shown to be fibre type specific. For instance, FATZ-1 and FATZ-3 are exclusively expressed in skeletal muscle fast-twitch fibres while FATZ-2 is expressed in cardiac and slow-twitch fibres <ref>PMID: 11114196</ref><ref>PMID: 11842093</ref>. FATZ proteins have multiple binding partners in the Z-disc, which involve them in different functions like the Z-disc formation and maintenance or in signaling pathways like the calcineurin/NFAT <ref>PMID: 15543153</ref>. Therefore, the FATZ protein family could be seen as one example of Z-disc proteins where signalling and structural support converge. |
==Sequence Annotation== | ==Sequence Annotation== | ||
Revision as of 13:25, 7 December 2012
Contents |
Introduction
The filamin-C α-actinin telethonin Z-disc binding protein (FATZ) is a protein family of three isoforms: FATZ-1, FATZ-2, FATZ-3, which are expressed in muscle cells.[1] This protein family, that is also known as Myozenin or Calsarcin, is mainly localized in the Z-disc, although recently it has been described that FATZ-2 appears in cardiac nuclei. [2] The expression of the three isoforms has been shown to be fibre type specific. For instance, FATZ-1 and FATZ-3 are exclusively expressed in skeletal muscle fast-twitch fibres while FATZ-2 is expressed in cardiac and slow-twitch fibres [3][4]. FATZ proteins have multiple binding partners in the Z-disc, which involve them in different functions like the Z-disc formation and maintenance or in signaling pathways like the calcineurin/NFAT [5]. Therefore, the FATZ protein family could be seen as one example of Z-disc proteins where signalling and structural support converge.
Sequence Annotation
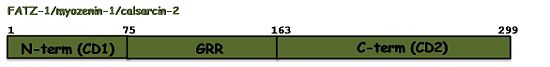
The sequence annotation of FATZ-1 is related to the sequence conservation profile among the three isoforms, which share well conserved N-terminal and C-terminal regions. Therefore, the N-terminal of FATZ-1 was named conserved domain 1 (CD1, 1-75aa) and its C-terminal conserved domain 2 (CD2, 172-299aa). Both regions are connected by a stretch of amino acids with a 39.5% of glycine; consequently, this region was named the glycine rich region (GRR, 75-171aa)[6] Q9NP98. Although the N-terminal and C-terminal regions of the other two isoforms could be also named CD1 and CD2; no such sequence annotations exist in their UniProtKB entries Q9NPC6Q8TDC0.Function and Interactions
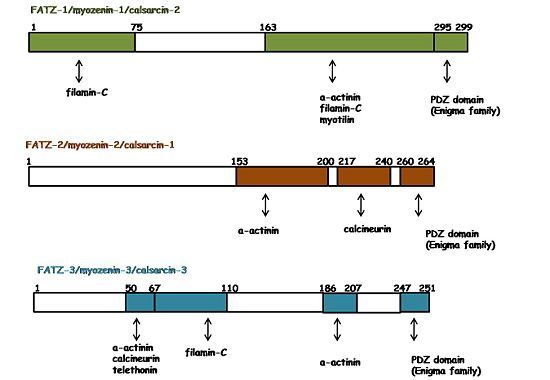
The three isoforms of FATZ have a plethora of interacting partners which are additionally shared by all of them. As shown by the figure on the right, they interact with several Z-disc proteins. For instance: α-actinin-2, filamin-C, myotilin, telethonin, calcineurin and ZASP/Cypher (in general the Enigma protein family) [7][8][9][10][11][12]. In general, those interactions and their binding regions were found by yeast two-hybrid assays, co-immunoprecipitation, and pull down assays.The interaction of FATZ-1 with α-actinin-2 was reported simultaneously by three different groups [13][14][15]. It was documented with the three isoforms of FATZ, which showed their binding regions within the CD2. Furthermore, the data suggested a binding interface on α-actinin-2 starting in the middle of the SR2, followed by the SR3 and the SR4. The studies of Stout and co-workers suggested that the complex formation between FATZ-1 and α-actinin-2 is one of the most important steps in the early stages of myofibril formation, when the Z-disc is called Z-body and is just beginning its assembling process. The FATZ-1::α-actinin-2 complex and also myotilin, which also interacts with both proteins, were one of the earliest seen in Z-bodies. In addition, their results showed that the interaction between FATZ-1 and α-actinin-2 was a required step to incorporate telethonin in the Z-disc, which would be mediated by a conformational change in FATZ-1 [16].
FATZ-1 has been suggested to perform other functions, like bridging filamin-C and α-actinin-2. However, it was reported in a competitive binding assay that α-actinin-2 displaces filamin-C form FATZ-1. Therefore, it is still an open question whether a ternary complex could exist and what its physiological role would be [17].
It was shown that FATZ-2, expressed exclusively in cardiomyocites, is a negative modulator of the phosphatase activity of calcineurin. Calcineurin is an important protein of the signaling pathway controlling the cell response to pressure overload and its phosphatase activity on members of the nuclear factor of activated T-cell (NFAT) family activates the translocation of the last ones from the cytoplasm to the nucleus. Once NFATs reach their target genes in the nucleus, their expression is regulated and the cell proliferation program is activated [18].
Pathology
In experimental models, it has been shown that the absence of FATZ-2 led to up-regulation of calcineurin phosphatase activity and cellular proliferation; in consequence, inducing hypertrophic cardiomyopathy(HCM). [19] The study of families with this disease has suggested that mutations S48P and I246M in FATZ-2 where associated with familial HCM. [20]Nevertheless, another study has also shown that mutations in FATZ-2 are rare causes of familial HCM. [21]. Given that, whether FATZ-2 is a marker of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy or not is still under debate and more studies shall be done to clearly define its role in this disease.
References
- ↑ Faulkner G, Pallavicini A, Comelli A, Salamon M, Bortoletto G, Ievolella C, Trevisan S, Kojic' S, Dalla Vecchia F, Laveder P, Valle G, Lanfranchi G. FATZ, a filamin-, actinin-, and telethonin-binding protein of the Z-disc of skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 2000 Dec 29;275(52):41234-42. PMID:10984498 doi:10.1074/jbc.M007493200
- ↑ Paulsson AK, Franklin S, Mitchell-Jordan SA, Ren S, Wang Y, Vondriska TM. Post-translational regulation of calsarcin-1 during pressure overload-induced cardiac hypertrophy. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2010 Jun;48(6):1206-14. Epub 2010 Feb 17. PMID:20170660 doi:10.1016/j.yjmcc.2010.02.009
- ↑ Frey N, Richardson JA, Olson EN. Calsarcins, a novel family of sarcomeric calcineurin-binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Dec 19;97(26):14632-7. PMID:11114196 doi:10.1073/pnas.260501097
- ↑ Frey N, Olson EN. Calsarcin-3, a novel skeletal muscle-specific member of the calsarcin family, interacts with multiple Z-disc proteins. J Biol Chem. 2002 Apr 19;277(16):13998-4004. Epub 2002 Feb 12. PMID:11842093 doi:10.1074/jbc.M200712200
- ↑ Frey N, Barrientos T, Shelton JM, Frank D, Rutten H, Gehring D, Kuhn C, Lutz M, Rothermel B, Bassel-Duby R, Richardson JA, Katus HA, Hill JA, Olson EN. Mice lacking calsarcin-1 are sensitized to calcineurin signaling and show accelerated cardiomyopathy in response to pathological biomechanical stress. Nat Med. 2004 Dec;10(12):1336-43. Epub 2004 Nov 14. PMID:15543153 doi:nm1132
- ↑ Takada F, Vander Woude DL, Tong HQ, Thompson TG, Watkins SC, Kunkel LM, Beggs AH. Myozenin: an alpha-actinin- and gamma-filamin-binding protein of skeletal muscle Z lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Feb 13;98(4):1595-600. Epub 2001 Feb 6. PMID:11171996 doi:10.1073/pnas.041609698
- ↑ Takada F, Vander Woude DL, Tong HQ, Thompson TG, Watkins SC, Kunkel LM, Beggs AH. Myozenin: an alpha-actinin- and gamma-filamin-binding protein of skeletal muscle Z lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Feb 13;98(4):1595-600. Epub 2001 Feb 6. PMID:11171996 doi:10.1073/pnas.041609698
- ↑ Frey N, Olson EN. Calsarcin-3, a novel skeletal muscle-specific member of the calsarcin family, interacts with multiple Z-disc proteins. J Biol Chem. 2002 Apr 19;277(16):13998-4004. Epub 2002 Feb 12. PMID:11842093 doi:10.1074/jbc.M200712200
- ↑ von Nandelstadh P, Ismail M, Gardin C, Suila H, Zara I, Belgrano A, Valle G, Carpen O, Faulkner G. A class III PDZ binding motif in the myotilin and FATZ families binds enigma family proteins: a common link for Z-disc myopathies. Mol Cell Biol. 2009 Feb;29(3):822-34. Epub 2008 Dec 1. PMID:19047374 doi:10.1128/MCB.01454-08
- ↑ Gontier Y, Taivainen A, Fontao L, Sonnenberg A, van der Flier A, Carpen O, Faulkner G, Borradori L. The Z-disc proteins myotilin and FATZ-1 interact with each other and are connected to the sarcolemma via muscle-specific filamins. J Cell Sci. 2005 Aug 15;118(Pt 16):3739-49. Epub 2005 Aug 2. PMID:16076904 doi:10.1242/jcs.02484
- ↑ Frey N, Richardson JA, Olson EN. Calsarcins, a novel family of sarcomeric calcineurin-binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Dec 19;97(26):14632-7. PMID:11114196 doi:10.1073/pnas.260501097
- ↑ Faulkner G, Pallavicini A, Comelli A, Salamon M, Bortoletto G, Ievolella C, Trevisan S, Kojic' S, Dalla Vecchia F, Laveder P, Valle G, Lanfranchi G. FATZ, a filamin-, actinin-, and telethonin-binding protein of the Z-disc of skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 2000 Dec 29;275(52):41234-42. PMID:10984498 doi:10.1074/jbc.M007493200
- ↑ Faulkner G, Pallavicini A, Comelli A, Salamon M, Bortoletto G, Ievolella C, Trevisan S, Kojic' S, Dalla Vecchia F, Laveder P, Valle G, Lanfranchi G. FATZ, a filamin-, actinin-, and telethonin-binding protein of the Z-disc of skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 2000 Dec 29;275(52):41234-42. PMID:10984498 doi:10.1074/jbc.M007493200
- ↑ Takada F, Vander Woude DL, Tong HQ, Thompson TG, Watkins SC, Kunkel LM, Beggs AH. Myozenin: an alpha-actinin- and gamma-filamin-binding protein of skeletal muscle Z lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Feb 13;98(4):1595-600. Epub 2001 Feb 6. PMID:11171996 doi:10.1073/pnas.041609698
- ↑ Frey N, Olson EN. Calsarcin-3, a novel skeletal muscle-specific member of the calsarcin family, interacts with multiple Z-disc proteins. J Biol Chem. 2002 Apr 19;277(16):13998-4004. Epub 2002 Feb 12. PMID:11842093 doi:10.1074/jbc.M200712200
- ↑ Wang J, Shaner N, Mittal B, Zhou Q, Chen J, Sanger JM, Sanger JW. Dynamics of Z-band based proteins in developing skeletal muscle cells. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 2005 May;61(1):34-48. PMID:15810059 doi:10.1002/cm.20063
- ↑ Takada F, Vander Woude DL, Tong HQ, Thompson TG, Watkins SC, Kunkel LM, Beggs AH. Myozenin: an alpha-actinin- and gamma-filamin-binding protein of skeletal muscle Z lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Feb 13;98(4):1595-600. Epub 2001 Feb 6. PMID:11171996 doi:10.1073/pnas.041609698
- ↑ Frey N, Barrientos T, Shelton JM, Frank D, Rutten H, Gehring D, Kuhn C, Lutz M, Rothermel B, Bassel-Duby R, Richardson JA, Katus HA, Hill JA, Olson EN. Mice lacking calsarcin-1 are sensitized to calcineurin signaling and show accelerated cardiomyopathy in response to pathological biomechanical stress. Nat Med. 2004 Dec;10(12):1336-43. Epub 2004 Nov 14. PMID:15543153 doi:nm1132
- ↑ Frey N, Barrientos T, Shelton JM, Frank D, Rutten H, Gehring D, Kuhn C, Lutz M, Rothermel B, Bassel-Duby R, Richardson JA, Katus HA, Hill JA, Olson EN. Mice lacking calsarcin-1 are sensitized to calcineurin signaling and show accelerated cardiomyopathy in response to pathological biomechanical stress. Nat Med. 2004 Dec;10(12):1336-43. Epub 2004 Nov 14. PMID:15543153 doi:nm1132
- ↑ Osio A, Tan L, Chen SN, Lombardi R, Nagueh SF, Shete S, Roberts R, Willerson JT, Marian AJ. Myozenin 2 is a novel gene for human hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Circ Res. 2007 Mar 30;100(6):766-8. Epub 2007 Mar 8. PMID:17347475 doi:10.1161/01.RES.0000263008.66799.aa
- ↑ Posch MG, Thiemann L, Tomasov P, Veselka J, Cardim N, Garcia-Castro M, Coto E, Perrot A, Geier C, Dietz R, Haverkamp W, Ozcelik C. Sequence analysis of myozenin 2 in 438 European patients with familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Med Sci Monit. 2008 Jul;14(7):CR372-4. PMID:18591919