Caspase-3 Regulatory Mechanisms
From Proteopedia
(→Introduction) |
|||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
[[Image:Apop.png | thumb| Caspases in the apoptotic pathway]] | [[Image:Apop.png | thumb| Caspases in the apoptotic pathway]] | ||
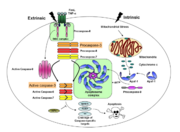
| - | Caspases are '''''c'''''ysteine-'''''asp'''''artic acid prote'''''ases''''' and are key protein facilitators for the faithful execution of apoptosis or programmed cell death. Dysregulation in the apoptotic pathway has been implicated in a variety of diseases such as neurodegeneration, cancer, heart disease and some metabolic disorders. Because of the crucial role of caspases in the the apoptotic pathway, abnormalities in their functions would cause | + | Caspases are '''''c'''''ysteine-'''''asp'''''artic acid prote'''''ases''''' and are key protein facilitators for the faithful execution of apoptosis or programmed cell death. Dysregulation in the apoptotic pathway has been implicated in a variety of diseases such as neurodegeneration, cancer, heart disease and some metabolic disorders. Because of the crucial role of caspases in the the apoptotic pathway, abnormalities in their functions would cause haywire in the apoptotic cascade and can be deleterious to the cell. Caspases are thus being considered as therapeutic targets in apoptosis-related diseases. |
| - | Any apoptotic signal received by the cell causes the activation of initiator caspases (-8 and -9) by associating with other protein platforms to form a functional holoenzyme. These initiator caspases then | + | Any apoptotic signal received by the cell causes the activation of initiator caspases (-8 and -9) by associating with other protein platforms to form a functional holoenzyme. These initiator caspases then cleave the executioner caspases -3, -6, and -7. Caspase-3 specifically functions to cleave downstream apoptotic targets as well as both caspase-6 and -7, which in turn cleave their respective targets to induce cell death. Aside from being able to activate caspase-6 and -7, caspase-3 also regulates caspase-9 activity, operating via a feedback loop. This dual action of caspase-3 confers its distinct regulatory mechanisms, resulting in a wider extent of its effects in the apoptotic cascade. |
---- | ---- | ||
Revision as of 04:04, 13 December 2012
Contents |
Introduction
Caspases are cysteine-aspartic acid proteases and are key protein facilitators for the faithful execution of apoptosis or programmed cell death. Dysregulation in the apoptotic pathway has been implicated in a variety of diseases such as neurodegeneration, cancer, heart disease and some metabolic disorders. Because of the crucial role of caspases in the the apoptotic pathway, abnormalities in their functions would cause haywire in the apoptotic cascade and can be deleterious to the cell. Caspases are thus being considered as therapeutic targets in apoptosis-related diseases.
Any apoptotic signal received by the cell causes the activation of initiator caspases (-8 and -9) by associating with other protein platforms to form a functional holoenzyme. These initiator caspases then cleave the executioner caspases -3, -6, and -7. Caspase-3 specifically functions to cleave downstream apoptotic targets as well as both caspase-6 and -7, which in turn cleave their respective targets to induce cell death. Aside from being able to activate caspase-6 and -7, caspase-3 also regulates caspase-9 activity, operating via a feedback loop. This dual action of caspase-3 confers its distinct regulatory mechanisms, resulting in a wider extent of its effects in the apoptotic cascade.
Overview of Caspase-3 Structure
| |||||||||||
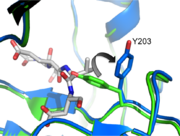
Caspase-3 Loop Bundle and Active Site
| |||||||||||
Caspase-3 Regulation
| |||||||||||
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Scott Eron, Banyuhay P. Serrano, Alexander Berchansky, Yunlong Zhao, Jaime Prilusky, Michal Harel