This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Sandbox UC 10
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
<StructureSection load='1dq8' size='500' side='right' caption='N-TERMINAL ACTIN-BINDING DOMAIN OF HUMAN DYSTROPHIN (PDB entry [[1dxx]])' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='1dq8' size='500' side='right' caption='N-TERMINAL ACTIN-BINDING DOMAIN OF HUMAN DYSTROPHIN (PDB entry [[1dxx]])' scene=''> | ||
| - | |||
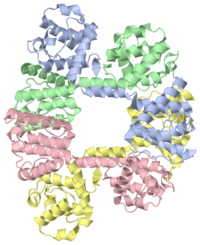
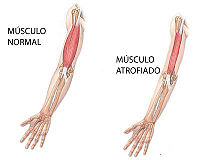
Dystrophin is an essential component of skeletal muscle cells. Its N-terminal domain binds to F-actin and its C terminus binds to the dystrophin-associated glycoprotein (DAG) complex in the membrane. | Dystrophin is an essential component of skeletal muscle cells. Its N-terminal domain binds to F-actin and its C terminus binds to the dystrophin-associated glycoprotein (DAG) complex in the membrane. | ||
| Line 28: | Line 27: | ||
| - | == QUIZ !! == | + | == QUIZ TIME !! == |
<quiz display=simple> | <quiz display=simple> | ||
Revision as of 20:14, 19 December 2012
N-TERMINAL ACTIN-BINDING DOMAIN OF HUMAN DYSTROPHIN
| |||||||||||
QUIZ TIME !!
Referencias
- ↑ Nadeau D, Marchand C. Change in the kinetics of sulphacetamide tissue distribution in Walker tumor-bearing rats. Drug Metab Dispos. 1975 Nov-Dec;3(6):565-76. PMID:1234
- ↑ Rubinstein MH. A new granulation method for compressed tablets [proceedings]. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1976 Dec;28 Suppl:67P. PMID:12345