We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 714
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
The Human soluble Epoxide hydrolase is a homodimer. Each subunit has <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_714/Catalytic_domains/3'>two catalytic domains</scene>, linked by a proline-rich section. | The Human soluble Epoxide hydrolase is a homodimer. Each subunit has <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_714/Catalytic_domains/3'>two catalytic domains</scene>, linked by a proline-rich section. | ||
| - | The C-terminal domain is called Cytosolic epoxide hydrolase 2: it catalyzes the trans-addition of water to epoxides in order to product glycols. The <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_714/Cter_activesite/3'>active site</scene> is made of five residues. The 3D structure of this active site is maintained by hydrogen bonds, including those created by D496. The two tyrosines (Y383 and Y466) assist the proper positioning of the substrate by polarizing it, thanks to their hydroxyl groups. D335 plays the role of the nucleophilic acid. Finally, H524 plays the role of a base in order to release the final product. | ||
| - | |||
== Mechanism == | == Mechanism == | ||
| + | |||
| + | The C-terminal domain is called Cytosolic epoxide hydrolase 2: it catalyzes the trans-addition of water to epoxides in order to product glycols. The <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_714/Cter_activesite/3'>active site</scene> is made of five residues. The 3D structure of this active site is maintained by hydrogen bonds, including those created by D496. The two tyrosines (Y383 and Y466) assist the proper positioning of the substrate by polarizing it, thanks to their hydroxyl groups. D335 plays the role of the nucleophilic acid. Finally, H524 plays the role of a base in order to release the final product. | ||
Revision as of 19:45, 30 December 2012
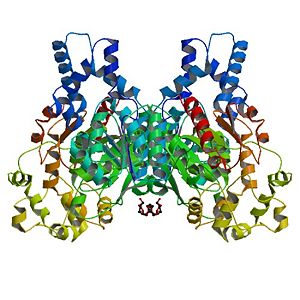
Human Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase: Biological assembly, 1s8o
Contents |
Overview
| |||||||||||
External ressources
References
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors
DUTREUX Fabien, BONHOURE Anna

