Immune system
The immune system is the body's way of protecting itself from foreign and potentially harmful microbes such as viruses and bacteria. When an unknown substance enters the body the immune system responds with a cascade of reactions which begin with identification of the microbe and hopefully ends with the neutralization of the pathogen. The identification and recognition of a pathogen however is a tricky process as the immune system must be able to differentiate between its own cells and foreign ones. The inability of the immune system to differentiate between foreign and native cells is potentially dangerous as it could lead to autoimmune diseases which can vary in severity from eczema to lupus. The responsibility of identifying pathogens is put on small glycoproteins called antibodies.
Antibodies
There are 5 main isotypes of antibodies in mammals which allows the immune system to differentiate between the varying types of invasions which in turn ensures that the situation is handled properly and efficiently. The 5 antibody isotypes are IgG, IgM, IgA, IgE, and IgD. IgG is the most common isotype which constitutes about 80% of the total antibodies circulating in the blood. IgM antibodies are found on the surface of B cells, and are usually the first antibodies at the site of an infection. IgA antibodies are found in mucus, tears, sweat, and breast milk where it prevents colonization by pathogens. IgE antibodies are the least abundant isotype however they play an important role in allergic reactions and inflammatory response. IgD antibodies are predominantly found on the surface of B-lymphocytes where they are thought to activate B cells.
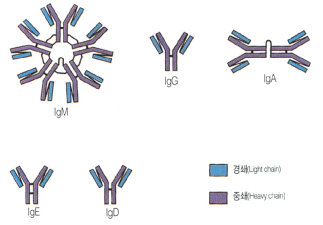
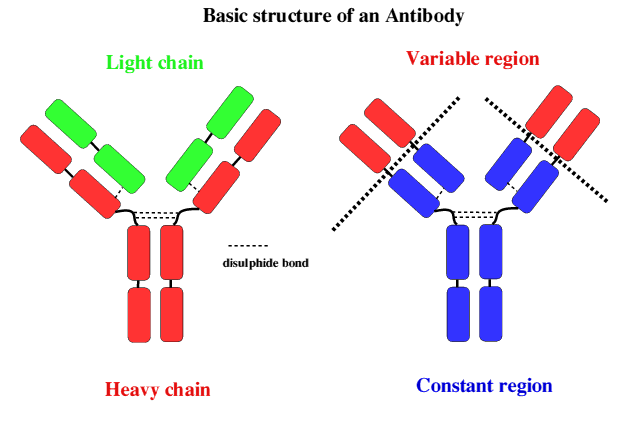
Antibodies are made up of 2 pairs of light and heavy chains. The heavy chains of antibodies are specific to each isotope with: α, δ, ε, γ, and μ corresponding to: IgA, IgD, IgE, IgG, and IgM respectively. The light chain of the antibody is separated into two categories for mammals: lambda (λ) and kappa (κ). Antibodies are further differentiated into two regions: the constant region and the variable region. Like their names suggest, the constant region stays the same for its specific isotope however the variable region changes to accommodate many different antigens. The two ends of the variable region contain sites called Fabs which stands for fragment antigen binding region. This region is the area where the beta sheets of the antibody bind specifically to antigens. The constant region of the antibody is made up of 2 heavy chains specific to each isotope. This region is also called the Fc region or the fragment, crystallizable region. This end of the antibody mediates the next step of immune response for the given isotype which in turn allows for different types of responses.
Type I Hypersensitivity
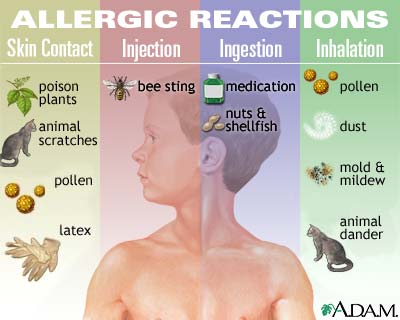
Hypersensitivity diseases, such as food allergy, affect 25% of the world's population. These diseases, which can lead to death, are due to reactions within a person's own immune system. in such cases, specific triggers called antigens, such as proteins in bee venom or grass allergens, bind to IgE antibodies which in turn leads to the degranulation of mast cells. Once mast cells degranulate, an inflammatory response is triggered. Inflammatory responses occur normally within the immune system, however in hypersensitivity diseases, antigens which are typically seen as harmless can lead to massive reactions and can cause anaphylactic shock where the person's blood pressure drops dramatically and their airways swell inhibiting respiration.
Hypersensitivity mechanism
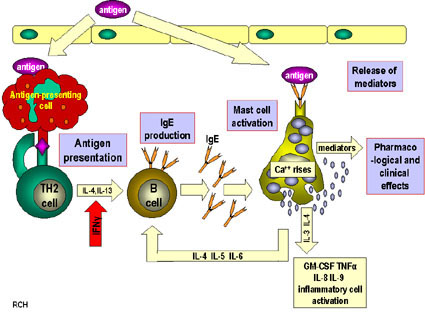
When the immune system is first exposed to an allergen plasma cells differentiate to produce many IgE antibodies specific to the present allergen. These IgE antibodies then bind to Fc epsilon R1 receptors on mast cells with their constant heavy chain region which is also called the Fc region. The binding between mast cells and IgE antibodies is highly favored as the Fc region has an immense affinity for Fc epsilon R1 receptors on the mast cells with a KD of 10^-9M.
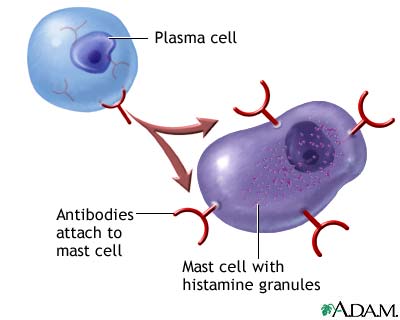
When the immune system is exposed to the allergen a second time, the antigens bind to the IgE antibodies on mast cells which causes them to degranulate. When mast cells degranulate they release histamine, proteoglycans, and serine proteases which make up the inflammatory response. Since mast cells are prepared with so many IgE antibodies, the reaction of the inflammatory response is pretty severe for a normally harmless antigen.
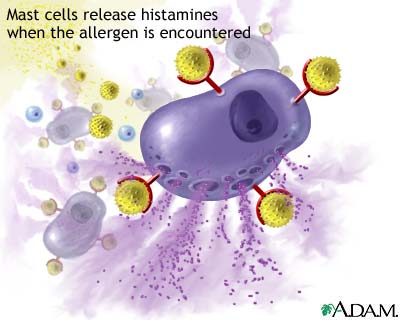
Mechanism of the first and second response to allergen exposure.
Phl p 2 and huMab2
Publication Abstract from PubMed
We report the three-dimensional structure of the complex between the major respiratory grass pollen allergen Phl p 2 and its specific human IgE-derived Fab. The Phl p 2-specific human IgE Fab has been isolated from a combinatorial library constructed from lymphocytes of a pollen allergic patient. When the variable domains of the IgE Fab were grafted onto human IgG1, the resulting Ab (huMab2) inhibited strongly the binding of allergic patients' IgE to Phl p 2 as well as allergen-induced basophil degranulation. Analysis of the binding of the allergen to the Ab by surface plasmon resonance yielded a very low dissociation constant (K(D) = 1.1 x 10(-10) M), which is similar to that between IgE and Fcepsilon;RI. The structure of the Phl p 2/IgE Fab complex was determined by x-ray crystallography to 1.9 A resolution revealing a conformational epitope (876 A(2)) comprised of the planar surface of the four-stranded anti-parallel beta-sheet of Phl p 2. The IgE-defined dominant epitope is discontinuous and formed by 21 residues located mostly within the beta strands. Of the 21 residues, 9 interact directly with 5 of the 6 CDRs (L1, L3, H1, H2, H3) of the IgE Fab predominantly by hydrogen bonding and van der Waals interactions. Our results indicate that IgE Abs recognize conformational epitopes with high affinity and provide a structural basis for the highly efficient effector cell activation by allergen/IgE immune complexes.
High-affinity IgE recognition of a conformational epitope of the major respiratory allergen Phl p 2 as revealed by X-ray crystallography., Padavattan S, Flicker S, Schirmer T, Madritsch C, Randow S, Reese G, Vieths S, Lupinek C, Ebner C, Valenta R, Markovic-Housley Z, J Immunol. 2009 Feb 15;182(4):2141-51. PMID:19201867
From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine.
In this experiment it was determined that IgE antibodies bound to , a grass pollen allergen, in allergic patients rather than IgG antibodies.[1] This was strange because both antibodies are capable of specifically binding Phl p 2 however IgE antibodies are the least abundant in mammalian immune systems whereas IgG antibodies are one of the most abundant. Researchers predicted that the epitope specific heavy chain of the IgE antibody bound to a different epitope on the pollen than did the IgG antibody and that the IgE epitope had a much higher affinity for the antigen than the IgG antibody. To test this hypothesis, researchers took the constant region of an IgG antibody (Fc receptor) and paired it when the variable region of the allergen specific IgE epitope (Fab region). Researchers then termed this new antibody huMab2 which had the IgE Fab region and the IgG Fc region. The huMab2 antibody had a new and a new . It was important for researchers to keep the Fc region of the IgG antibody because the Fc region does not bind mast cells to cause degranulation and allergic reaction when exposed to Phlp2 antigen.
When huMab2 was mixed in solution with mast cell bound IgE antibodies it actually prevented the binding of Phl p 2 with IgE as the IgG like antibody was more abundant and free floating in solution. This was a significant discovery because this research information can be used and applied to further develop the treatment of type I hypersensitivity patients.
The Phl p 2/huMab2-Fab interface:
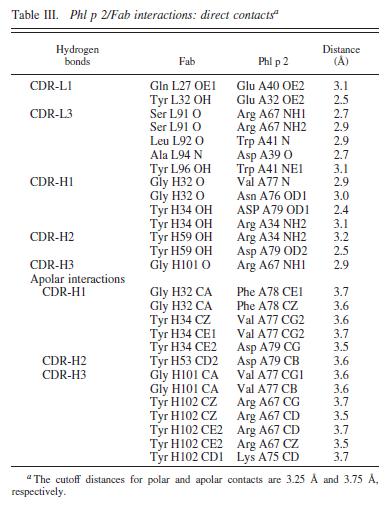
There was a large interface between the antigen and antibody where 21 allergen residues were involved, and 25 Fab residues were involved.
The antibody recognized a four-stranded beta sheet with the residues glu30, glu32, asp34, and his36 on beta 3, ala43 on beta 4, asn65, arg67, phe68, and met74 on beta 6, met74, lys75, asn76, val77, and phe78 on beta 7, and asp39, glu40, trp41, gly73, asp74, asp80, and pro94 in the loops near the c-term on .
3D structures of reverse transcriptase
Reverse transcriptase
Reference
- ↑ Padavattan S, Flicker S, Schirmer T, Madritsch C, Randow S, Reese G, Vieths S, Lupinek C, Ebner C, Valenta R, Markovic-Housley Z. High-affinity IgE recognition of a conformational epitope of the major respiratory allergen Phl p 2 as revealed by X-ray crystallography. J Immunol. 2009 Feb 15;182(4):2141-51. PMID:19201867 doi:182/4/2141







