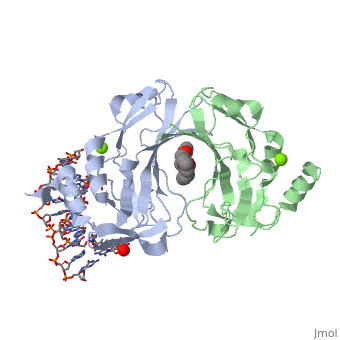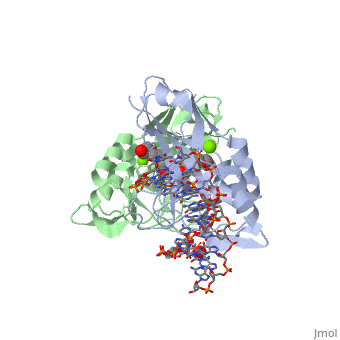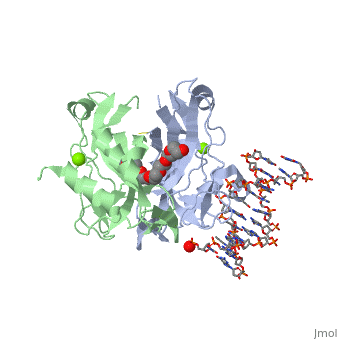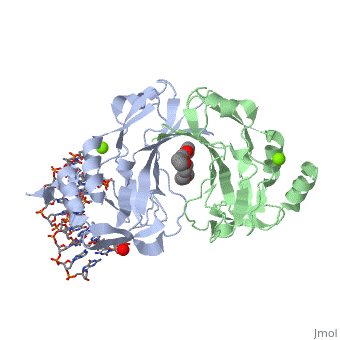
2x6v
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | + | ==CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF HUMAN TBX5 IN THE DNA-BOUND AND DNA-FREE FORM== | |
| - | + | <StructureSection load='2x6v' size='340' side='right' caption='[[2x6v]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 2.20Å' scene=''> | |
| - | {{ | + | == Structural highlights == |
| + | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[2x6v]] is a 4 chain structure with sequence from [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Homo_sapiens Homo sapiens]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=2X6V OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=2X6V FirstGlance]. <br> | ||
| + | </td></tr><tr id='ligand'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Ligand|Ligands:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><scene name='pdbligand=MG:MAGNESIUM+ION'>MG</scene>, <scene name='pdbligand=PE4:2-{2-[2-(2-{2-[2-(2-ETHOXY-ETHOXY)-ETHOXY]-ETHOXY}-ETHOXY)-ETHOXY]-ETHOXY}-ETHANOL'>PE4</scene></td></tr> | ||
| + | <tr id='related'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Related_structure|Related:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat">[[2x6u|2x6u]]</td></tr> | ||
| + | <tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=2x6v FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=2x6v OCA], [http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=2x6v RCSB], [http://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/2x6v PDBsum]</span></td></tr> | ||
| + | </table> | ||
| + | == Evolutionary Conservation == | ||
| + | [[Image:Consurf_key_small.gif|200px|right]] | ||
| + | Check<jmol> | ||
| + | <jmolCheckbox> | ||
| + | <scriptWhenChecked>select protein; define ~consurf_to_do selected; consurf_initial_scene = true; script "/wiki/ConSurf/x6/2x6v_consurf.spt"</scriptWhenChecked> | ||
| + | <scriptWhenUnchecked>script /wiki/extensions/Proteopedia/spt/initialview01.spt</scriptWhenUnchecked> | ||
| + | <text>to colour the structure by Evolutionary Conservation</text> | ||
| + | </jmolCheckbox> | ||
| + | </jmol>, as determined by [http://consurfdb.tau.ac.il/ ConSurfDB]. You may read the [[Conservation%2C_Evolutionary|explanation]] of the method and the full data available from [http://bental.tau.ac.il/new_ConSurfDB/chain_selection.php?pdb_ID=2ata ConSurf]. | ||
| + | <div style="clear:both"></div> | ||
| + | <div style="background-color:#fffaf0;"> | ||
| + | == Publication Abstract from PubMed == | ||
| + | TBX5, a member of the T-box transcription factor family, plays an important role in heart and limb development. More than 60 single point or deletion mutations of human TBX5 are associated with Holt-Oram syndrome that manifests itself as heart and limb malformations in 1 out of 100,000 live births. The majority of these mutations are located in the TBX5 T-box domain. We solved the crystal structures of the human TBX5 T-box domain in its DNA-unbound form and in complex with a natural DNA target site allowing for the first time the comparison between unbound and DNA-bound forms. Our analysis identifies a 3(10)-helix at the C-terminus of the T-box domain as an inducible recognition element, critically required for the interaction with DNA, as it only forms upon DNA binding and is unstructured in the DNA-unbound form. Using circular dichroism, we characterized the thermal stability of six TBX5 mutants containing single point mutations in the T-box domain (M74V, G80R, W121G, G169R, T223M, and R237W) and compared them with wild-type protein. Mutants G80R and W121G show drastically reduced thermal stability, while the other mutants only show a marginal stability decrease. For all TBX5 mutants, binding affinities to specific and nonspecific DNA sequences were determined using isothermal titration calorimetry. All TBX5 mutants show reduced binding affinities to a specific DNA target site, although to various degrees. Interestingly, all tested TBX5 mutants differ in their ability to bind unspecific DNA, indicating that both sequence-specific and unspecific binding might contribute to the misregulation of target gene expression. | ||
| - | + | Structural basis of TBX5-DNA recognition: the T-box domain in its DNA-bound and -unbound form.,Stirnimann CU, Ptchelkine D, Grimm C, Muller CW J Mol Biol. 2010 Jul 2;400(1):71-81. Epub 2010 May 5. PMID:20450920<ref>PMID:20450920</ref> | |
| - | + | ||
| + | From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine.<br> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
*[[T-box proteins|T-box proteins]] | *[[T-box proteins|T-box proteins]] | ||
*[[TBX5|TBX5]] | *[[TBX5|TBX5]] | ||
| - | + | == References == | |
| - | == | + | <references/> |
| - | < | + | __TOC__ |
| + | </StructureSection> | ||
[[Category: Homo sapiens]] | [[Category: Homo sapiens]] | ||
| - | [[Category: Grimm, C | + | [[Category: Grimm, C]] |
| - | [[Category: Mueller, C W | + | [[Category: Mueller, C W]] |
| - | [[Category: Ptchelkine, D | + | [[Category: Ptchelkine, D]] |
| - | [[Category: Stirnimann, C U | + | [[Category: Stirnimann, C U]] |
[[Category: Developmental protein]] | [[Category: Developmental protein]] | ||
[[Category: Dna-binding]] | [[Category: Dna-binding]] | ||
Revision as of 14:13, 17 December 2014
CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF HUMAN TBX5 IN THE DNA-BOUND AND DNA-FREE FORM
| |||||||||||