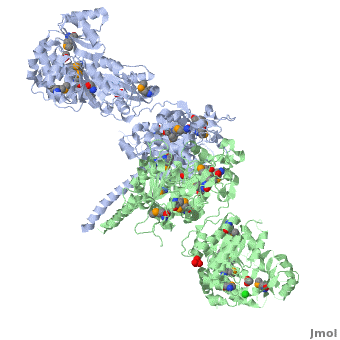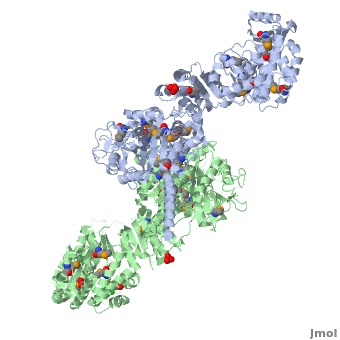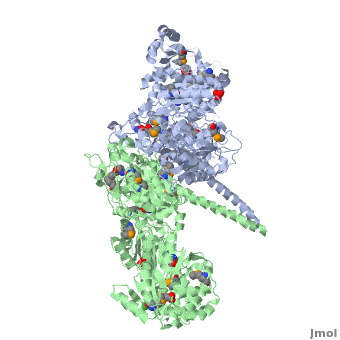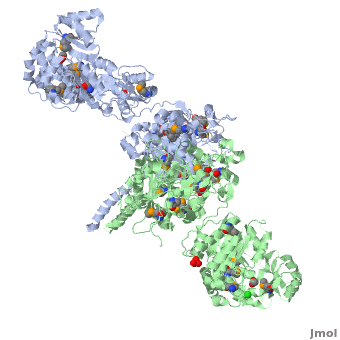
6-deoxyerythronolide B synthase (DEBS)
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<StructureSection load='' size='450' side='right' scene='User:Tsung-Yi_Lin/6-deoxyerythronolide_B_synthase/Ks-at_dimer/2' caption=''> | <StructureSection load='' size='450' side='right' scene='User:Tsung-Yi_Lin/6-deoxyerythronolide_B_synthase/Ks-at_dimer/2' caption=''> | ||
One of the '''[[CBI Molecules]]''' being studied in the [http://www.umass.edu/cbi/ University of Massachusetts Amherst Chemistry-Biology Interface Program] at UMass Amherst and on display at the [http://www.molecularplayground.org/ Molecular Playground]. | One of the '''[[CBI Molecules]]''' being studied in the [http://www.umass.edu/cbi/ University of Massachusetts Amherst Chemistry-Biology Interface Program] at UMass Amherst and on display at the [http://www.molecularplayground.org/ Molecular Playground]. | ||
| - | |||
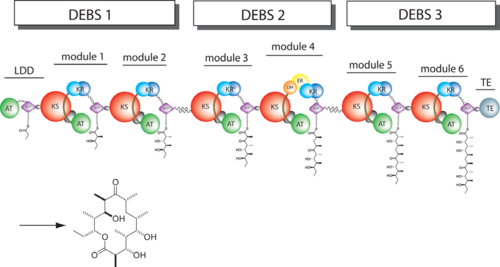
Polyketides are a large and structurally diverse class of natural products produced by bacteria, fungi, and plants. They exhibit a wide variety of biological activities including antibiotic, antitumor, anticancer, among others. | Polyketides are a large and structurally diverse class of natural products produced by bacteria, fungi, and plants. They exhibit a wide variety of biological activities including antibiotic, antitumor, anticancer, among others. | ||
| Line 23: | Line 22: | ||
===Acyl Carrier Protein (ACP)=== | ===Acyl Carrier Protein (ACP)=== | ||
| - | |||
Molecular Playground banner: "the communicator". | Molecular Playground banner: "the communicator". | ||
| - | < | + | <scene name='6-deoxyerythronolide_B_synthase_(DEBS)/Cv/1'>Solution structure of acyl carrier protein domain from module 2 of 6-deoxyerythronolide B synthase (DEBS)</scene> ([[2ju1]]). |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
The ACP has no known catalytic activity. However it is central to the polyketide synthesis process by acting as a workbench upon which a round of chain extension is performed, interacting with every domain present within its module, as well as the downstream module. It accepts building blocks from AT, and then the growing chain from KS. Furthermore, it presents the extended chain to any ketoreductase (KR), dehydratase (DH), and enoyl reductase (ER) domains present, and finally passes the chain to the downstream KS or thioesterase (TE). | The ACP has no known catalytic activity. However it is central to the polyketide synthesis process by acting as a workbench upon which a round of chain extension is performed, interacting with every domain present within its module, as well as the downstream module. It accepts building blocks from AT, and then the growing chain from KS. Furthermore, it presents the extended chain to any ketoreductase (KR), dehydratase (DH), and enoyl reductase (ER) domains present, and finally passes the chain to the downstream KS or thioesterase (TE). | ||
Revision as of 12:14, 1 May 2013
| |||||||||||
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Tsung-Yi Lin, Alexander Berchansky, Lawrence Sheringham Borketey, Joel L. Sussman, Jon Amoroso, David Canner, Jaime Prilusky