Introduction
Caspases in the apoptotic pathway
Caspases are cysteine-aspartic acid proteases and are key protein facilitators for the faithful execution of apoptosis or programmed cell death. Dysregulation in the apoptotic pathway has been implicated in a variety of diseases such as neurodegeneration, cancer, heart disease and some metabolic disorders. Because of the crucial role of caspases in the the apoptotic pathway, abnormalities in their functions would cause haywire in the apoptotic cascade and can be deleterious to the cell. Caspases are thus being considered as therapeutic targets in apoptosis-related diseases.
Any apoptotic signal received by the cell causes the activation of initiator caspases (-8 and -9) by associating with other protein platforms to form a functional holoenzyme. These initiator caspases then cleave the executioner caspases -3, -6, and -7. Caspase-3 specifically functions to cleave downstream apoptotic targets as well as both caspase-6 and -7, which in turn cleave their respective targets to induce cell death. Aside from being able to activate caspase-6 and -7, caspase-3 also regulates caspase-9 activity, operating via a feedback loop. This dual action of caspase-3 confers its distinct regulatory mechanisms, resulting in a wider extent of its effects in the apoptotic cascade.
Overview of Caspase-3 Structure
Dimer Formation
Caspase-3 shares many structural characteristics with other caspases. It is synthesized in the cell in its zymogen form, consisting of an N-terminal prodomain followed by a large and small subunit linked to each other by an intersubunit linker. Like other executioner caspases, caspase-3 has a short N-terminal prodomain the function of which remains unknown. Maturation of the enzyme involves at least two cleavage events- one to remove the N-terminal prodomain and the other to cleave the intersubunit linker. These two cleavage events have been shown to occur in a sequential fashion, with the cleavage between the small (p12) and large (p17) subunits preceding the pro domain removal. The high specificity of caspases directs the cleavage of the intersubunit linker at specific aspartate residues and generates the mature form of the enzyme. Caspase-3 in its functional form is a ; each heterodimer is formed and stabilized by hydrophobic interactions between the large and small subunit. ß-sheets from each heterodimer then interact resulting in a 12-stranded , around which α-helices are positioned.
The active pocket of caspase-3 is defined by . Binding of a , such as DEVD-CHO to the active site of the enzyme induces a conformational change that allows the L2 and L2' loops to interlock and stabilize the active site . Like caspase-7, caspase-3 recognizes a Asp-X-X-Asp sequence as a cleavage site in its protein substrates.
Caspase-3 Loop Bundle and Active Site
Importance of Loop Orientation
Caspases are extremely dependent on the orientation and geometry of their active site loops. If the loops are not ordered properly the enzyme fails to function. Caspase-3 has four active site loops on each half of the dimer constituting the active site bundle. Proteolytic activity is dependent on cleavage of an intersubunit linker, which releases loop 2 (L2) and L2’. . This allows L2 to make critical contacts with L3 and L4, allowing them to organize the active site, bind substrate, and orient the nucleophilic cysteine 163 (bright green) so that it can cleave after aspartate residues.
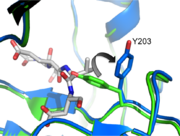
Taking a closer look at L2 and L2’ we can see a critical interaction involving on L2. This residue makes two hydrogen bonds with backbone amides of V189’ and E190’ on L2', stabilizing L2 in the proper position. This reinforcement allows L2 to contact L3 so as to twist the active site cysteine into the proper orientation to attack the substrate. It also causes a conformational change at Tyrosine 203 (Tyrosine 203 Flip). Initially, the hydroxyl group on the tyrosine occupies the P1 position in the active site, blocking substrate binding (green, pdb 1QX3). However, when L2 contacts L2' and finds the proper orientation, Y203 rotates 90 degrees (blue, pdb 2H5I) and leaves a hole for P1 of the substrate (substrate shown in gray). In addition, L2 can now contact L4 at K260. This secures L4 and allows it to make contacts in the P4 position, which greatly influence substrate specificity.
Caspase-3 Active Site
The active site of caspase-3 utilizes a cysteine-histidine dyad, which has an exquisite specificity for cleaving after aspartate residues. Therefore, caspase-3, by definition, will have an aspartate in the pocket. Uncleavable peptide substrates are often used in crystallography to bind to the active site. This will orient the delicate but deadly active site loops in order to facilitate the visualization of the chemistry of cleavage. The nucleophilic Cysteine 163 will work in concert with the second active site residue, Histidine 121, to attack the substrate. This reaction will ultimately cleave the peptide bond following the aspartate.
In order to be active and cleave specific apoptotic targets, Caspase-3 must be able to first bind substrate. There are several essential interactions responsible for securing the substrate before cleavage. The binding pocket at is a hydrophobic patch made up of Y204, W206, and F250 (dark blue residues). This creates a hydrophobic pocket for the P2 residue (in this case, valine), helping it stick to the protein. At there are contacts that contribute to the specificity of caspase-3. Asparagine 208 hydrogen bonds with an aspartate at P4 along with the backbone nitrogen of F250, creating a preference for a carboxylic acid at the P4 site.
Caspase-3 Regulation
Exosite and Allosteric Site
Since all caspases have very similar active site chemistry, other regions in the protein that can confer either activation or inhibition to the enzyme needs to be explored. For example, exosites in caspase-7 have been identified and were observed to improve activity (Boucher, Blais et al. 2012). Caspase-7 also has an inhibitory allosteric site that could bind with the small molecule FICA, resulting in a zymogen-like conformation (Hardy, Lam et al. 2004) and abolishing activity.
Although there are still no evident exosites found in caspase-3, some allosteric sites, most of which are located on the dimer interface, have been interrogated by mutagenesis and have been shown to modulate the activity of caspase-3 or even procaspase-3. Although only procaspase-3 was detected with little activity because the orientation of ILA (prematured L2 loop) and ILB loop cannot form an active site pocket, it is sill quite interesting to discover how these mutations are able to rescue activity of the zymogen form (Bose, Pop et al. 2003).
One interesting mutation, V266E, improves caspase-3 activity dramatically. Even in the uncleavable procaspase-3 (D5A, D26A, D175A), V266E mutant zymogen is still pseudo-activated, showing a 60-fold increase in activity. Intriguingly, V266E does not undergo many conformational changes around the active site in its cleaved form. Based on the crystal structure of this mutant, the L2’ loop is partially disordered at 185’-180’. Moreover, this active procaspase-3 variant cannot be inhibited by endogenous XIAP like normal cleaved caspase-3. So it provides an option for apoptosis stimuli with intrinsic efficiency.
It was found recently that changing other critical residues (V266H, Y197C, E124A) on the dimer interface might play an important role on inhibition of caspase-3 by altering hydrogen bond patterns or through a relay of subtle conformational changes that spreads across the whole dimer.
Post translational Modification
Caspase-3 has been reported to be phosphorylated at Ser-150 by p38-MAPK and directly inhibits its activity. Conversely, phosphorylation of caspase-3 by protein kinase C zeta (PKC-ζ) was shown to promote autocleavage and activation.
Aside from phosphorylation, caspase-3 is also known to be ubiquitinylated and nitrosylated, however the underlying mechanismsand effect of these modifications are still unclear.
Natural Inhibitors
X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis proteins (XIAP) contains the second baculovirus IAP repeat domain (BIR2) targeting caspase-3 and caspase-7. The domain sits directly in the active site of caspase-3 and completely inhibits the protein. The region binding the active site runs in the opposite direction of normal caspase-3 substrates, thus occupying P1 through P4 but avoiding cleavage by the protease. This unique method of inhibition is a critical regulatory mechanism used in cells to control apoptotic caspase activity.