Matrix metalloproteinase
From Proteopedia
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
==MT1-MMP-TIMP-1 complex== | ==MT1-MMP-TIMP-1 complex== | ||
| - | <StructureSection load='M1.pdb' size='500' side='right' scene='MT1-MMP-TIMP-1_complex/Cv2/8' caption=''> | ||
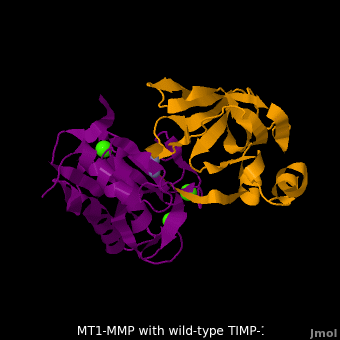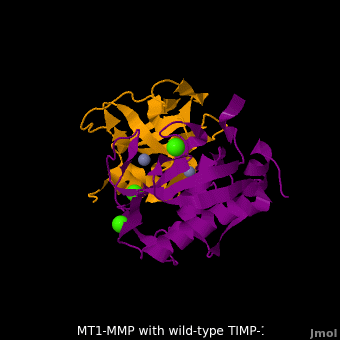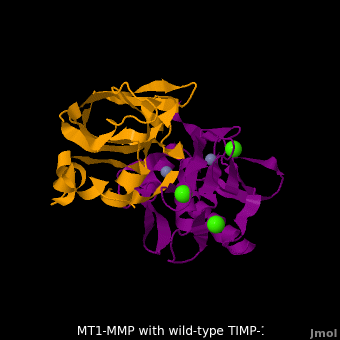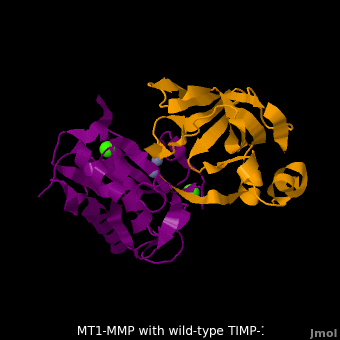
The human matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) family comprises a large group of structurally homologous zinc-dependent endopeptidases (''e.g.'' <scene name='MT1-MMP-TIMP-1_complex/Cv2/9'>membrane type-1 matrix metalloproteinase (MT1-MMP)</scene> <font color='darkmagenta'><b>(darkmagenta)</b></font> and <scene name='MT1-MMP-TIMP-1_complex/Cv/14'>membrane type-3 matrix metalloproteinase (MT3-MMP)</scene> <font color='magenta'><b>(magenta)</b></font>, <scene name='MT1-MMP-TIMP-1_complex/Cv2/10'>click to see structural comparison</scene>) that perform a wide variety of biological roles. In general, the MMPs are inhibited unselectively by all four known tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases (TIMPs 1-4) which have 40-50% sequence identity. For example, <scene name='MT1-MMP-TIMP-1_complex/Cv/14'>membrane type-3 matrix metalloproteinase (MT3-MMP)</scene> can form complex with <scene name='MT1-MMP-TIMP-1_complex/Cv/12'>wild-type TIMP-1</scene> ([[1uea]], <font color='orange'><b>colored orange</b></font>). <scene name='MT1-MMP-TIMP-1_complex/Cv/13'>The WT-TIMP-1 binding interface</scene> <font color='cyan'><b>(cyan)</b></font> is mainly composed of the N-terminal segment that approaches the active site, the AB loop (Thr33-Tyr35), the CD loop (Ala65-Cys70), and the EF loop (Thr97-Ser100). The pivotal residue, threonine 98 (Thr98), is shown as <font color='red'><b>red sticks</b></font>. In general, <scene name='MT1-MMP-TIMP-1_complex/Cv1/2'>five main chain hydrogen bonds</scene> (Cys1-Ser68, Val69-Met66, Gly71-Met66, Cys70-Glu67, and Cys70-Thr98) are intimately involved in the conformational stability of TIMP binding interface when bound to MMP. | The human matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) family comprises a large group of structurally homologous zinc-dependent endopeptidases (''e.g.'' <scene name='MT1-MMP-TIMP-1_complex/Cv2/9'>membrane type-1 matrix metalloproteinase (MT1-MMP)</scene> <font color='darkmagenta'><b>(darkmagenta)</b></font> and <scene name='MT1-MMP-TIMP-1_complex/Cv/14'>membrane type-3 matrix metalloproteinase (MT3-MMP)</scene> <font color='magenta'><b>(magenta)</b></font>, <scene name='MT1-MMP-TIMP-1_complex/Cv2/10'>click to see structural comparison</scene>) that perform a wide variety of biological roles. In general, the MMPs are inhibited unselectively by all four known tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases (TIMPs 1-4) which have 40-50% sequence identity. For example, <scene name='MT1-MMP-TIMP-1_complex/Cv/14'>membrane type-3 matrix metalloproteinase (MT3-MMP)</scene> can form complex with <scene name='MT1-MMP-TIMP-1_complex/Cv/12'>wild-type TIMP-1</scene> ([[1uea]], <font color='orange'><b>colored orange</b></font>). <scene name='MT1-MMP-TIMP-1_complex/Cv/13'>The WT-TIMP-1 binding interface</scene> <font color='cyan'><b>(cyan)</b></font> is mainly composed of the N-terminal segment that approaches the active site, the AB loop (Thr33-Tyr35), the CD loop (Ala65-Cys70), and the EF loop (Thr97-Ser100). The pivotal residue, threonine 98 (Thr98), is shown as <font color='red'><b>red sticks</b></font>. In general, <scene name='MT1-MMP-TIMP-1_complex/Cv1/2'>five main chain hydrogen bonds</scene> (Cys1-Ser68, Val69-Met66, Gly71-Met66, Cys70-Glu67, and Cys70-Thr98) are intimately involved in the conformational stability of TIMP binding interface when bound to MMP. | ||
Revision as of 13:29, 14 August 2013
| |||||||||||
3D structures of matrix metalloproteinase
Updated June 2012
MMP1 interstitial or fibroblast collagenase
1su3 – pro-hMMP – human
2clt – hMMP (mutant)
3shi, 1hfc - hMMP catalytic domain
2tcl, 966c - hMMP catalytic domain + inhibitor
2ayk, 3ayk, 4ayk - hMMP catalytic domain - NMR
1fbl – MMP - pig
MMP2 gelatinase-A
1qib, 1ck7 - hMMP catalytic domain (mutant)
1rtg - hMMP hemopexin-like domain
1ks0 – hMMP first fibronectin type II domain – NMR
1cxw - hMMP second fibronectin type II domain – NMR
1j7m - hMMP third fibronectin type II domain (mutant) – NMR
1gen – hMMP C terminal
1eak – pro-hMMP catalytic domain (mutant) + peptide inhibitor
3ayu - hMMP catalytic domain (mutant) + peptide inhibitor
1hov, 1eub - hMMP catalytic domain + inhibitor– NMR
1gxd – pro-hMMP (mutant) + TIMP-2
MMP3 stromelysin 1
1qia, 1qic, 1cqr, 1slm - hMMP catalytic domain
3ohl, 3oho, 1g49, 1ciz, 1b8y, 1caq, 1usn, 2usn, 1ums, 1umt, 2d1n, 2d1o, 2ow9, 1bqo, 1g4k, 1b3d, 1biw, 1c3i, 1d5j, 1d7x, 1d8f, 1d8m, 1g05, 1hfs, 1hy7, 2srt- hMMP catalytic domain + inhibitor
1c8t - hMMP catalytic domain (mutant) + inhibitor
1uea - hMMP catalytic domain + TIMP-1
1oo9 - hMMP catalytic domain + TIMP-1 N terminal
2jt5, 2jt6, 2jnp, 3usn, 1sln, 1bm6 - hMMP catalytic domain + inhibitor – NMR
MMP7 matrilysin
2y6c, 2y6d, 2ddy, 1mmp, 1mmq, 1mmr – hMMP catalytic domain + inhibitor
MMP8 neutrophil collagenase
2oy4, 1mnc - hMMP catalytic domain
3dng, 3dpe, 3dpf, 1zp5, 1jh1, 1jj9, 1i76, 1a85, 1mmb, 1zs0, 1zvx, 1lbc – hMMP catalytic domain + inhibitor
1i73, 2oy2, 1jan, 1jao, 1jap, 1jaq - hMMP catalytic domain + peptide inhibitor
1a86 - hMMP catalytic domain + aspartate-based inhibitor
MMP9 gelatinase-B
1l6j - pro-hMMP
1itv – hMMP haemopexin-like domain
1gkc - hMMP catalytic domain + inhibitor
2ovx, 2ovz, 2ow0, 2ow1, 2ow2, 1gkd - hMMP catalytic domain (mutant) + inhibitor
MMP10 stromelysin 2
1q3a - hMMP catalytic domain (mutant)
3v96 - hMMP catalytic domain + metalloproteinase inhibitor
MMP11 stromelysin 3
1hv5 - hMMP catalytic domain + inhibitor
MMP12 macrophage
3ba0, 2oxu - hMMP
2krj, 2k9c - hMMP catalytic domain – NMR
1jk3, 1jiz, 2oxu - hMMP catalytic domain
2poj - hMMP catalytic domain (mutant) - NMR
2jxy - hMMP hemopexin-like domain - NMR
3n2u, 3n2v, 2wo8, 2wo9, 2woa, 1utt, 1utz, 1ros – hMMP catalytic domain + inhibitor
3lk8, 3lik, 3lil, 3lir, 3ljg, 3nx7, 3lka, 3ehx, 3ehy, 3f15, 3f16, 3f17, 3f18, 3f19, 3f1a, 1y93, 1rmz, 1os2, 1os9, 2hu6 - hMMP catalytic domain (mutant) + inhibitor
2oxn, 2oxz, 2oxw - hMMP catalytic domain (mutant) + peptide
2k2g, 2z2d - hMMP catalytic domain + inhibitor - NMR
2w0d, 1ycm, 1z3j - hMMP catalytic domain (mutant) + inhibitor - NMR
MMP13 collagenase 3
1cxv - MMP catalytic domain - mouse
1pex – hMMP hemopexin-like domain
2yig, 3ljz, 3kec, 3kej, 3kek, 3kry, 3i7g, 3i7i, 3elm, 2pjt, 2ozr, 1xuc, 1xud, 1xur, 1you, 1ztq, 3o2x, 3zxh, 4a7b, 1fls, 1fm1, 456c, 830c – hMMP catalytic domain + inhibitor
2e2d - hMMP catalytic domain + TIMP-2
MMP14 Membrane T1
3ma2 – hMMP residues 112-292 + TIMP-1 (mutant)
1buv, 1bqq - hMMP + TIMP-2
3c7x – hMMP hemopexin-like domain
MMP16 Membrane T3
1rm8 - hMMP catalytic domain + inhibitor
MMP20 enamelysin
2jsd - hMMP catalytic domain + inhibitor - NMR
MMP23 CA-MMP
2k72 – hMMP residues 254-290 - NMR
MMP adamalysin
1iag – MMP – diamondback rattlesnake
References
- ↑ Grossman M, Tworowski D, Dym O, Lee MH, Levy Y, Murphy G, Sagi I. Intrinsic protein flexibility of endogenous protease inhibitor TIMP-1 controls its binding interface and effects its function. Biochemistry. 2010 Jun 14. PMID:20545310 doi:10.1021/bi902141x