Reverse transcriptase
From Proteopedia
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
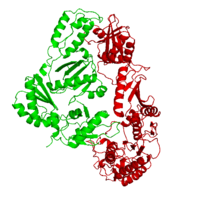
[[Image:1hmv1.png|left|200px|thumb|Crystal Structure of unliganded HIV-1 Reverse transcriptase, [[1hmv]]]] | [[Image:1hmv1.png|left|200px|thumb|Crystal Structure of unliganded HIV-1 Reverse transcriptase, [[1hmv]]]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
[[Reverse transcriptase]] (RT) or RNA-dependent DNA polymerase transcribes single-stranded RNA into double-stranded [[DNA]]. HIV-1 RT is from the human immunodeficiency virus and is a heterodimer of P66 and P51 subchains. The images at the left and at the right correspond to one representative RT structure, ''i.e.'' crystal structure of HIV-1 Reverse transcriptase ([[1hmv]]). There are more details on HIV-1 RT in [[Phl p 2]]. P15 is its RNAse H domain. There are two types of inhibitors for RT: NNRTIs are the non-nucleoside inhibitors, and NRTIs are the nucleoide inhibitors. Being the protein that gives their name to Retroviruses, Reverse Transcriptase is, along with [[Hiv protease|Protease]] and Integrase, the most important part of the protein system involved in the process of infection and reproduction for viruses like HIV, MuLV and AMV. RT has the unusual property of transcribing ssRNA into dsDNA going against the Central Dogma of Molecular Biology. | [[Reverse transcriptase]] (RT) or RNA-dependent DNA polymerase transcribes single-stranded RNA into double-stranded [[DNA]]. HIV-1 RT is from the human immunodeficiency virus and is a heterodimer of P66 and P51 subchains. The images at the left and at the right correspond to one representative RT structure, ''i.e.'' crystal structure of HIV-1 Reverse transcriptase ([[1hmv]]). There are more details on HIV-1 RT in [[Phl p 2]]. P15 is its RNAse H domain. There are two types of inhibitors for RT: NNRTIs are the non-nucleoside inhibitors, and NRTIs are the nucleoide inhibitors. Being the protein that gives their name to Retroviruses, Reverse Transcriptase is, along with [[Hiv protease|Protease]] and Integrase, the most important part of the protein system involved in the process of infection and reproduction for viruses like HIV, MuLV and AMV. RT has the unusual property of transcribing ssRNA into dsDNA going against the Central Dogma of Molecular Biology. | ||
Since its discovery in 1970, the study of its properties and mechanisms of action have been of high interest among the scientific community due to the unique properties that makes it an important medical target enzyme and important tool for genetic engineering applications like RT-PCR in the construction of cDNA libraries. See also <br /> | Since its discovery in 1970, the study of its properties and mechanisms of action have been of high interest among the scientific community due to the unique properties that makes it an important medical target enzyme and important tool for genetic engineering applications like RT-PCR in the construction of cDNA libraries. See also <br /> | ||
Revision as of 12:22, 1 January 2014
| |||||||||||
3D Structures of Reverse transcriptase
Updated on 01-January-2014
HIV-1 RT P66/P51
3dlk, 1hmv - P66/P51
1mu2, 1jle, 1hpz, 1hqu, 1qe1, 1dlo, 2wom, 2won, 3tam, 4dg1 - P66/P51 (mutant)
1har - P66 N-terminal
3qip - P66/P51+NNRTI nevirapine + RNase H inhibitor
3lp0, 3lp1, 3lp2, 1vrt, 3hvt - P66/P51+NNRTI nevirapine
4i7f - P66/P51 + NNRTI nevirapine analog
2hnd, 2hny, 1s1u, 1s1x, 1lw0, 1lwc, 1lwe, 1lwf, 1jlb, 1jlf, 1fkp - P66/P51 (mutant)+NNRTI nevirapine
3m8p, 3mec - P66/P51+NNRTI etravirine
3med - P66/P51 (mutant)+NNRTI etravirine
3mee, 2zd1, 3qlh - P66/P51+NNRTI rilpivirine
3meg, 2ze2, 3bgr, 4g1q, 4icl, 4id5, 4idk, 4ify, 4ig0, 4ig3, 4kfb - P66/P51 (mutant)+NNRTI rilpivirine
1ikw, 1fk9 - P66/P51 +NNRTI efavirenz
1jkh, 1ikv, 1fko - P66/P51 (mutant)+NNRTI efavirenz
3dya, 3e01, 3drp - P66/P51+NNRTI pyrazole
3drr, 3drs - P66/P51 (mutant)+NNRTI pyrazole
3irx, 3is9, 3lak, 3lal, 3lam, 3lan, 3ffi, 3di6, 3dle, 3dlg, 2rki, 3c6t, 3c6u, 2rf2, 2vg5, 2vg6, 2vg7, 2opp, 1jlq, 1ep4, 1c0t, 1c0u, 1dtt, 1dtq, 1bqm, 1rt1, 1rt2, 1rev, 1rtj, 1vru, 1hnv, 1hni, 3t19 - P66/P51+NNRTI
1s1t, 1s1v, 1s1w, 1s6p, 1s6q, 1s9e, 1s9g, 1suq, 1sv5, 3dm2, 3dmj, 3dok, 3dol, 2opq, 2opr, 2ops, 2ic3, 2hnz, 1jlg, 1bqn, 1uwb, 1tvr, 3qo9, 3t1a - P66/P51 (mutant)+NNRTI
3kk1, 1c1b, 1rti, 4kv8 - P66/P51+ inhibitor
2ynf, 2yng, 2ynf, 2yng - P66/P51 (mutant) + NNRTI
1jla - P66/P51 (mutant)+ NRTI
3ig1 - P66/P51+ inhibitor beta-thujaplicinol
3i0r, 3i0s, 3m8q, 3isn, 3ith, 1c1c, 3nbp - P66/P51+ pyrimidine derivative
1ikx - P66/P51 (mutant)+ pyrimidine derivative
1tv6 - P66/P51+ pyridine derivative
1jlc, 1iky, 1eet - P66/P51(mutant)+ pyridine derivative
2b5j, 2ban, 2be2, 1rth, 1hvt - P66/P51+ pyridone derivative
1lw2, 1rt3 - P66/P51 (mutant)+ NRTI
1tkt, 1tkx, 1tkz, 1tl1, 1tl3 - P66/P51+ quinoline derivative
2b6a - P66/P51+ THR-50
2i5j - P66/P51 (mutant)+hydrazone derivative
1rt4, 1rt5, 1rt6, 1rt7 - P66/P51+ carboxanilide derivative
1klm - P66/P51+piperazine derivative
2jle – P66+NNRTI
3kjv, 3kk3, 1r0a, 1n5y, 1n6q, 1hys - P66/P51+DNA
1j5o, 1rtd, 3klf, 3v4i, 3v6d - P66/P51 (mutant)+DNA
3v81 - P66/P51 (mutant)+DNA + NNRTI
1hvu - P66/P51+RNA
4b3o, 4b3p, 4b3q - P66/P51 + RNA + DNA
1t03, 1t05 - P66/P51+DNA+Fab+NRTI
3jsm - P66/P51 (mutant)+DNA+NRTI
2hmi - P66/P51 (mutant)+DNA+Fab
2iaj - P66/P51 (mutant)+NRTI
3kk2 - P66/P51+DNA+NRTI
3jyt - P66/P51 (mutant)+DNA+NRTI
HIV-1 AZT-resistant RT P66/P51
3kli - P66/P51 (mutant)
3kle, 3klg, 3klh – P66/P51 (mutant) + DNA
HIV-1 RT P66
2jle – P66+NNRTI
1har - P66 N-terminal
HIV-1 RT P15
1rdh, 1hrh – P15
3lp3 – P15+inhibitor MK3
3k2p – P15+inhibitor beta-thujaplicinol
3hyf – P15+pyrimidine derivative
1o1w – P15+Mg - NMR
HIV-2 RT
1mu2 - RT (mutant)
Leukemia virus RT
2hb5, 1mml - catalytic fragment
2r2r, 2r2t, 2fjv, 2fjw, 2fjx, 1ztw, 2fvs, 2fvr, 2fvq, 2fvp, 1n4l – catalytic fragment+DNA
2r2s, 2r2u - catalytic fragment+DNA+Co Bleomycin
1ztt - catalytic fragment+DNA+netropsin
1rw3, 1nnd – fragment (mutant)
1i6j, 1d0e, 1d1u, 1qaj, 1qai – N-terminal+DNA
3fsi - catalytic fragment+DNA+trypanocidal
XMRV RT
3v1o, 3v1q – RNAse H domain
3v1r – RNAse H domain + inhibitor
4hkq – RT residues 658-1328 (mutant) + DNA + RNA
2lsn – RT – Simian foamy virus - NMR
RT from telomerase
2b2a - RT telomerase catalytic subunit (mutant) - Tetrahymena thermophila
2r4g - RT telomerase RNA-binding domain
3du6, 3du5 - TcRT telomerase catalytic subunit - Tribolium castaneum
3kyl - TcRT telomerase catalytic subunit + DNA
See Also
- Reverse Transcriptase at Wikipedia
- Molecule of the Month (09/2002) at RCSB Protein Data Bank
- List of Reverse Transcriptase articles at Proteopedia and at RCSB Protein Data Bank
- Model of Reverse Transcriptase as one of the CBI Molecules on the Molecular Playground
- See Transcription for additional Proteopedia articles on the subject.
- For additional information, see: Human Immunodeficiency Virus
- For additional information, see: Transcription and RNA Processing
References
- ↑ Kohlstaedt LA, Wang J, Friedman JM, Rice PA, Steitz TA. Crystal structure at 3.5 A resolution of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase complexed with an inhibitor. Science. 1992 Jun 26;256(5065):1783-90. PMID:1377403 doi:[http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.1377403 http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.1377403
- [2] Consurf Server Data Base. Evolutionary conservation profile for Reverse Transcriptase PDB file 1JLB
- [3] Abbondanzieri, E.A. et al. Nature 453, 184-189 (2008) | doi:10.1038/nature06941
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Daniel Moyano-Marino, Joel L. Sussman, Alexander Berchansky, David Canner, Amol Kapoor, Jaime Prilusky, Brian Foley, Lynmarie K Thompson, Eric Martz