Rhodopsin
From Proteopedia
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<StructureSection load='1u19' size='400' side='right' scene='Sandbox_173/Default_rhodopsin_pdb_1u19/1' caption='Rhodopsin dimer complex with retinal, palmitic acid, heptane triol, heptyl thiohexopyranoside, Zn+2 and Hg+2 ions [[1u19]]'> | <StructureSection load='1u19' size='400' side='right' scene='Sandbox_173/Default_rhodopsin_pdb_1u19/1' caption='Rhodopsin dimer complex with retinal, palmitic acid, heptane triol, heptyl thiohexopyranoside, Zn+2 and Hg+2 ions [[1u19]]'> | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{STRUCTURE_1jfp| PDB=1jfp | SIZE=400| SCENE= |right|CAPTION=Acetyl-CoA synthase with Fe4S4 center complex with glycerol and Ni+2 ion [[1jfp]].}} | ||
| + | |||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
===Rhodopsin=== | ===Rhodopsin=== | ||
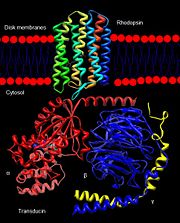
| - | Rhodopsin, a homodimeric protein, is a highly characterized [[G protein-coupled receptor]] found in membranous disks of the outer segments of rod and cone cells, though rhodopsin is more concentrated in rod cells which are sensitive to light but cannot discriminate colors. Rhodopsin is part of the superfamily of G protein-coupled receptors that mediate responses to visual, olfactory, hormonal, and neurotransmitter signals among others<ref name="Article1">PMID:20004206</ref>. Rhodopsin is involved in visual signal transduction and the visual system in classic G protein-coupled receptor mechanisms<ref name="Article12">PMID:11891118</ref>. | + | '''Rhodopsin,''' a homodimeric protein, is a highly characterized [[G protein-coupled receptor]] found in membranous disks of the outer segments of rod and cone cells, though rhodopsin is more concentrated in rod cells which are sensitive to light but cannot discriminate colors. Rhodopsin is part of the superfamily of G protein-coupled receptors that mediate responses to visual, olfactory, hormonal, and neurotransmitter signals among others<ref name="Article1">PMID:20004206</ref>. Rhodopsin is involved in visual signal transduction and the visual system in classic G protein-coupled receptor mechanisms<ref name="Article12">PMID:11891118</ref>. |
===G Protein-Coupled Receptors=== | ===G Protein-Coupled Receptors=== | ||
Revision as of 07:33, 2 January 2014
| |||||||||||
3D structures of rhodopsin
Rhodopsin (Rn)
Updated on 02-January-2014
3aym, 3ayn, 2z73, 2ziy – Rn + detergents + retinal – Flying squid
3am6 – Rn-2 + cholesterol + retinal – Acetabularia acetabulum
2x72 – bRn + detergents + retinal + guanine nucleotide-binding protein peptide – bovine
3qc9 – bRn + Mg + ADP
3oax, 3c9l, 2ped, 2i35, 2i36, 2i37, 1u19, 1gzm, 1l9h, 1hzx - bRn + detergents + retinal
3cap - bovine Rn + detergents
1jfp, 1f88 - bRn + retinal
3c9m - bRn (mutant) + detergents + retinal
2j4y, 4bez - bRn (mutant) + detergents
3dqb, 4a4m - bRn + guanine nucleotide-binding protein peptide + detergents
4bey - bRn (mutant) + guanine nucleotide-binding protein peptide + detergents
1vqx, 1nzs – bRn C terminal – NMR
1edx - bRn N terminal – NMR
1eds, 1edv, 1edw – bRn intradiskal loop – NMR
1fdf – bRn helix 7 - NMR
1xio – Rn - Anabaena
1gu8, 1gue, 1h68, 1jgj, 3qap, 3qdc – NpRn II – Natronomonas pharaonis
2ksy – NpRn II - NMR
1h2s, 2f93, 2f95 – NpRn II + Rn II transducer
4gyc - NpRn II (mutant) + Rn II transducer
Metarhodopsin II
3pqr – bMRn + guanine nucleotide-binding protein peptide + detergents + retinal
3pxo - bMRn + detergents + retinal
1ln6 - bMRn + retinal
Bathorhodopsin
2g87 - bBRn + detergents + retinal
Lumirhodopsin
2hpy - bLRn + detergents + retinal
Halorhodopsin
1e12, 2jaf - HRn + detergents + retinal – Halobacterium salinarium
2jag - HRn (mutant) + detergents + retinal
3a7k, 3abw, 3qbg, 3qbi, 3qbk, 3qbl, 3vvk – NpRn + detergents + retinal
Archaerhodopsin
1uaz – HRn-1 + retinal – Halobacterium
1vgo, 2z55 - HRn-2 + retinal
2ei4 - HRn-2 + retinal + bacterioruberin
Proteorhodopsin
2l6x - GpPRn + detergents + retinal – Gamma proteobacterium
4kly, 4knf - GpPRn + retinal
4jq6 – PRn + retinal + lipid
Xanthorhodopsin
3ddl - XRn + detergents + retinal – Salinibacter ruber
Deltarhodopsin
4fbz - Rn + bacterioruberin + retinal – Haloterrigena thermotolerans
References
- ↑ Hornak V, Ahuja S, Eilers M, Goncalves JA, Sheves M, Reeves PJ, Smith SO. Light activation of rhodopsin: insights from molecular dynamics simulations guided by solid-state NMR distance restraints. J Mol Biol. 2010 Feb 26;396(3):510-27. Epub 2009 Dec 11. PMID:20004206 doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2009.12.003
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 Sakmar TP. Structure of rhodopsin and the superfamily of seven-helical receptors: the same and not the same. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2002 Apr;14(2):189-95. PMID:11891118
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 Kristiansen K. Molecular mechanisms of ligand binding, signaling, and regulation within the superfamily of G-protein-coupled receptors: molecular modeling and mutagenesis approaches to receptor structure and function. Pharmacol Ther. 2004 Jul;103(1):21-80. PMID:15251227 doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2004.05.002
- ↑ Millar RP, Newton CL. The year in G protein-coupled receptor research. Mol Endocrinol. 2010 Jan;24(1):261-74. Epub 2009 Dec 17. PMID:20019124 doi:10.1210/me.2009-0473
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Meng EC, Bourne HR. Receptor activation: what does the rhodopsin structure tell us? Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2001 Nov;22(11):587-93. PMID:11698103
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Shieh T, Han M, Sakmar TP, Smith SO. The steric trigger in rhodopsin activation. J Mol Biol. 1997 Jun 13;269(3):373-84. PMID:9199406 doi:10.1006/jmbi.1997.1035
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 7.4 7.5 7.6 7.7 7.8 Okada T, Ernst OP, Palczewski K, Hofmann KP. Activation of rhodopsin: new insights from structural and biochemical studies. Trends Biochem Sci. 2001 May;26(5):318-24. PMID:11343925
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Okada T, Sugihara M, Bondar AN, Elstner M, Entel P, Buss V. The retinal conformation and its environment in rhodopsin in light of a new 2.2 A crystal structure. J Mol Biol. 2004 Sep 10;342(2):571-83. PMID:15327956 doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2004.07.044
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Janz JM, Farrens DL. Assessing structural elements that influence Schiff base stability: mutants E113Q and D190N destabilize rhodopsin through different mechanisms. Vision Res. 2003 Dec;43(28):2991-3002. PMID:14611935
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 Kisselev OG. Focus on molecules: rhodopsin. Exp Eye Res. 2005 Oct;81(4):366-7. PMID:16051215 doi:10.1016/j.exer.2005.06.018
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 11.2 Verhoeven MA, Bovee-Geurts PH, de Groot HJ, Lugtenburg J, DeGrip WJ. Methyl substituents at the 11 or 12 position of retinal profoundly and differentially affect photochemistry and signalling activity of rhodopsin. J Mol Biol. 2006 Oct 13;363(1):98-113. Epub 2006 Jul 28. PMID:16962138 doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2006.07.039
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 12.2 12.3 Morris MB, Dastmalchi S, Church WB. Rhodopsin: structure, signal transduction and oligomerisation. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2009 Apr;41(4):721-4. Epub 2008 Aug 3. PMID:18692154 doi:10.1016/j.biocel.2008.04.025
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 13.2 13.3 13.4 Nelson, D., and Cox, M. Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry. 2008. 5th edition. W. H. Freeman and Company, New York, New York, USA. pp. 462-465.
- ↑ Hurley JB, Spencer M, Niemi GA. Rhodopsin phosphorylation and its role in photoreceptor function. Vision Res. 1998 May;38(10):1341-52. PMID:9667002
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 15.2 Park JH, Scheerer P, Hofmann KP, Choe HW, Ernst OP. Crystal structure of the ligand-free G-protein-coupled receptor opsin. Nature. 2008 Jul 10;454(7201):183-7. Epub 2008 Jun 18. PMID:18563085 doi:10.1038/nature07063
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 Surya A, Knox BE. Enhancement of opsin activity by all-trans-retinal. Exp Eye Res. 1998 May;66(5):599-603. PMID:9628807 doi:10.1006/exer.1997.0453
See Also
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, Wayne Decatur, Jaime Prilusky, Joel L. Sussman, Cinting Lim