Overview
The Ku protein binds to the ends of double-strand breaks CAN I EDIT? and it is required in DNA-repair for non-homologous end joining. The eukaryotic Ku protein is a
composed of a
and a
. This contributes to genomic integrity through its ability to bind DNA double-strand breaks and facilitate repair by the non-homologous end-joining pathway. The crystal structure of the human Ku heterodimer was determined both alone and
element at 2.7 and 2.5 A resolution, respectively. Ku70 and Ku80 share a common topology and form a dyad-symmetrical molecule with a preformed ring that encircles duplex DNA. The binding site can cradle two full turns of DNA while encircling only the central 3-4 base pairs (bp). Ku makes no contacts with DNA bases and few with the sugar-phosphate backbone, but it fits sterically to major and minor groove contours so as to position the DNA helix in a defined path through the protein ring. These features seem well designed to structurally support broken DNA ends and to bring the DNA helix into phase across the junction during end processing and ligation. [1]
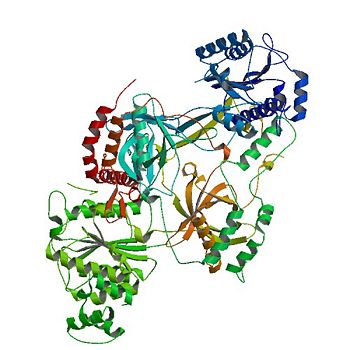
Crystal structure of Ku Heterodimer unbound to DNA
[1]
Structure
Ku Ring
The is composed of a broad base of beta barrels that cradle the DNA, and a narrow bridge that serves to protect the double strand break from base pairing with other DNA base pairs and degradation [1]. There is little interaction between the ring and the backbone or base pairs of DNA; instead, the ring associates with DNA by the cradle fitting into the major grooves of the helix [1]. The positive electrostatic charge caused by polarization of the ring also allows the negatively charged backbone of DNA to be guided into the correct position [1] NEED SCENE OF POS CHARGE OR POLARIZATION. The Ku protein also has a high affinity to DNA due to its form being preset for the helix. As a result of the asymmetric ring, there is a strong preference (Kd value of 1.5 to 4 X 10^-10 M[1]) for the Ku ring to slide onto the ends of DNA [1]. In addition, other asymmetric features, such as a abundance of Asp residues on the N terminus of the Ku Ring NEED SCENE OF ASP ON N-TERMINUS OR MAYBE JUST ASP IN GENERAL, prevent the Ku protein from sliding further on the DNA helix. While wrapping over the entire helix, the Ku ring is thin over the bridge, allowing ligases and polymerases to efficiently interact in non-homologous end joining (NHEJ). [1]
Domains
Consisting of (α/β-Domain, β-barrel, C-terminal arm, DNA-binding ring), the Ku70 subunit dimerizes with the Ku80 subunit to form the protein.[1]
Unlike other DNA binding proteins, the Ku protein is asymmetrical from the differences between the Ku70 and Ku80 subunits.
This asymmetry leads to different favorable locations for DNA based on major and minor grooves.[1]
The Ku70 subunit is to DNA at the double strand break, providing protectiion and interaction with its domains.[2]
In contrast, the Ku80 subunit DNA away from the free end.[1] Once a homodimer, the protein has diverged into two domains that are now 15% similar in residues. [3]
α/β-Domain
Contained inside the is a Rossman fold at the N terminus that is used to bind nucleotides in DNA.[1]
In terms of protein structure, the α/β-Domain contributes little to the dimer interface between the subunits.
The C terminus of the domain can be bound to other repair molecules, using the α/β-Domain as a scaffold.[1]
β-barrel
The is the main source of interactions of the Ku heterodimer itself and DNA helix, with each β-barrel being composed of seven β strands with the majority in antiparallel arrangement.[1]
The quantity of the strands lends the structures to be symmetrical. Both β-barrel in the dimer form the base of the cradle by fitting in the grooves of DNA.
C-terminal arm
The is an α-helical domain that associates with the β-barrel of the opposite subunit, with the arm stretching across the DNA helix.[1]
As a result, the C-terminal arm strengthens the cradle composed of the two β-barrels.
DNA binding ring
The on the open end of DNA is associated with the Ku70 subunit.
By binding DNA, Ku realigns the the strands and protects the molecule from degradation and unwanted bonds while NHEJ occurs.[1]
The regulation of the DNA binding ring of Ku is still under research, with data supporting oxidative stress and redox reactions decreasing the association of the Ku heterodimer with bound DNA through alterations in cysteine residues on the Ku70 subunit NEED SCENE OF CYSTEINES. [3] [4]
Function
The serves to assist in non-homologous end joining (NHEJ), and also in telomere synthesis and protection. These functions are separate interactions based on key residues that are being identified through current research. Recent research also links the Ku protein with heterochromatin formation through interaction with Rif and Sir proteins. [3][4]

