Sandbox Reserved 764
From Proteopedia
(→'''5-Enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase''') |
(→'''5-Enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase''') |
||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
'''Length''': __ residues | '''Length''': __ residues | ||
| - | '''Domains''': | + | '''Domains''': 2 |
The monomeric enzyme '''5-Enolpyruvlyshikimate-3-phosphate synthase (EPSPS)''' is an enzyme involved in the shikimate pathway found only in plants and microorganisms. The shikimate pathway is essential for the biosynthesis of chorismate, a precursor to majority of the aromatic compounds produced in the cell, including the aromatic amino acids (L-tyrosine, L-phenylalanine, L-tryptophan),that are needed for protein synthesis. Studies suggest that the compounds produced in this pathway constitute as much as or more than 35% of the dry mass of plants. | The monomeric enzyme '''5-Enolpyruvlyshikimate-3-phosphate synthase (EPSPS)''' is an enzyme involved in the shikimate pathway found only in plants and microorganisms. The shikimate pathway is essential for the biosynthesis of chorismate, a precursor to majority of the aromatic compounds produced in the cell, including the aromatic amino acids (L-tyrosine, L-phenylalanine, L-tryptophan),that are needed for protein synthesis. Studies suggest that the compounds produced in this pathway constitute as much as or more than 35% of the dry mass of plants. | ||
Revision as of 23:42, 1 December 2013
| This Sandbox is Reserved from Sep 25, 2013, through Mar 31, 2014 for use in the course "BCH455/555 Proteins and Molecular Mechanisms" taught by Michael B. Goshe at the North Carolina State University. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 299, Sandbox Reserved 300 and Sandbox Reserved 760 through Sandbox Reserved 779. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
|
Contents |
5-Enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase
Formula weight:
Classification: transferase
Length: __ residues
Domains: 2
The monomeric enzyme 5-Enolpyruvlyshikimate-3-phosphate synthase (EPSPS) is an enzyme involved in the shikimate pathway found only in plants and microorganisms. The shikimate pathway is essential for the biosynthesis of chorismate, a precursor to majority of the aromatic compounds produced in the cell, including the aromatic amino acids (L-tyrosine, L-phenylalanine, L-tryptophan),that are needed for protein synthesis. Studies suggest that the compounds produced in this pathway constitute as much as or more than 35% of the dry mass of plants.
EPSP Synthase Structure
three-dimensional backbone of EPSP synthase elucidated through X-ray crystallography in 1991 by W. C. Stallings et al. (14). This provided a basis for more in-depth studies of structure and function, and it was followed by further X-ray chrystallographic analysis by Ernst Schönbrunn and coworkers who resolved in atomic detail the structure and active site of EPSP synthase bound to S3P and EPSP synthase binding S3P and glyphosate (1). NMR was used to further detail the interactions of S3P with the N-terminal domain of EPSP synthase and the conformational changes that take place upon substrate binding (15).
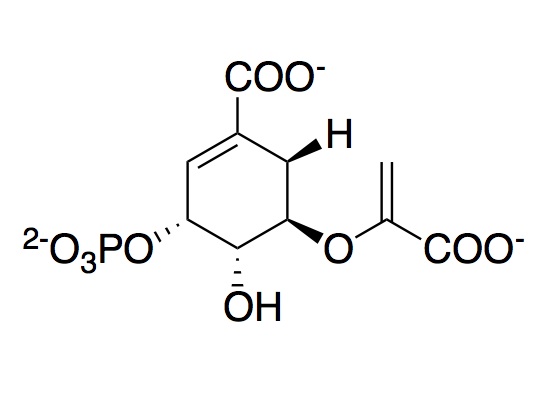
EPSP Synthase Mechanism
Implicatons
The implications in studying EPSP synthase involve the fact that this enzyme is not present in humans but is essential for bacteria and apicomplexan parasites. This makes EPSP synthase a selective target for antimicrobial drugs and decreases possible negative impacts of drugs in humans.