Diversity/Importance
Serine hydroxymethyltransferase (SHMT) is a ubiquitous enzyme that is found in all prokaryotes and eukaryotes. SHMT has a total molecular weight of ~46kD. Each monomeric unit of SHMT has a molecular weight of ~23kD. There are multiple isoforms of the SHMT enzyme. Serine hydroxymethyltransferase isoforms have namely been identified from Escherichia coli and Bacillus stearothermophilus. The diverse presence of serine hydroxymethyltransferase is in part because of the importance of 5,10-methylene tetrahydrofolate. This intermediate is important for the synthesis of the essential biomolecules purine, thymidine, choline, and methionine. Serine hydroxymethyltransferase deficiencies have been linked to Smith-Magneis syndrome (SMS). Also, SHMT inhibitors are being evaluated as potential anti-cancer and anti-microbial drugs.
Function
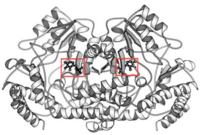
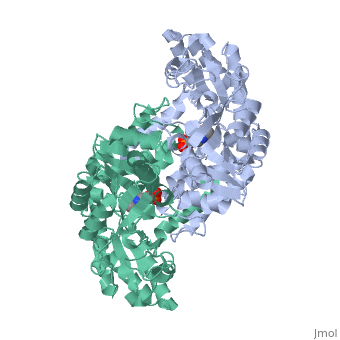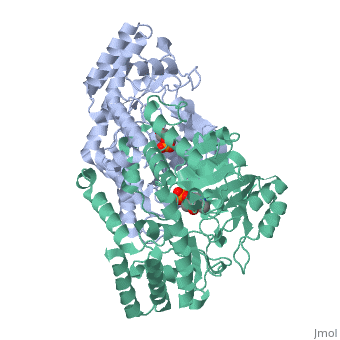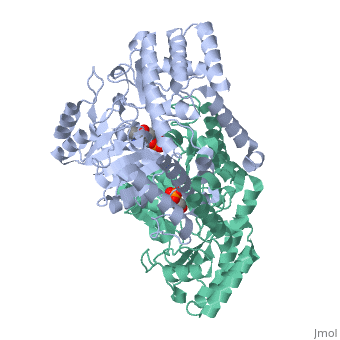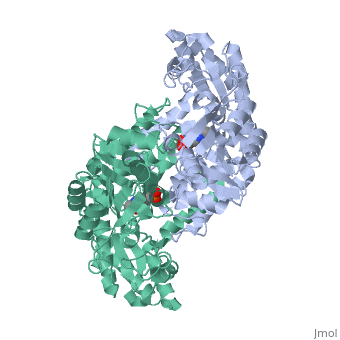
Ribbon Diagram of bsSHMT with bound PLP
This enzyme is part of the pyridoxal phosphate (PLP)-dependent enzymes. The enzyme is broadly classified as a transferase enzyme. Transferase enzymes primarily work by catalyzing the transfer of a specific functional group from one molecule to another. This enzyme is utilized mainly for two functions. First, the enzyme catalyzes the reversible conversion of L-serine to L-glycine. Second, the enzyme catalyzes the reversible conversion of tetrahydrofolate to 5,10-methylene tetrahydrofolate. Although the enzyme's purpose is the interconversion of these molecules, the reactions occur within the same chemical mechanism. The interconversion of both molecules is diagrammed below in Enzymatic Function of SHMT. The ribbon diagram shows the dimeric form of "Bacillus stearothermophilus", which is the the native state of the enzyme. The two red box annotations show the ligand binding sites within each monomer. Within each monomer, the pyridoxal-5'-phosphate (PLP) binds within a divot between the two domains. PLP is covalently bound to serine hydroxymethyltransferase.
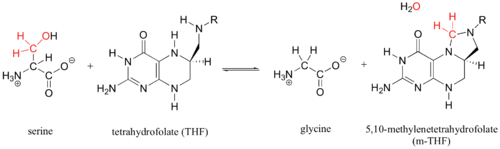
Enzymatic Function of SHMT
Structure and Folding
General Structure
Serine Hydroxymethyltransferase exists in different forms. In "Bacillus Stearthermophilus", SHMT exists as a dimer with two monomeric folds comprised of two separate domains. The enzyme monomer fold is comprised of the C-terminal domain and the N-Terminal Domain. The C-terminal domain folds into an αβ sandwich. The N-terminal domain is comprised of two further sub-domains. The first N-terminal sub-domain is a smaller domain composed of only 3 α-helices and 1 β-strand. The second N-terminal subdomain is the PLP binding domain. This sub-domain folds into an αβα structure that has a seven-stranded mixed β sheet surrounded by α-helices on both sides, hence αβα. Thus far, only X-Ray crystallography has been utilized in the determination of SHMT structure. Successful X-Ray crystals have been developed for the protein alone and for protein in the presence of substrate. These crystal structures, however, mostly consist of SHMT parts pieced together through various studies. A whole 3D structure for one specific organism has yet to be crystallized. As a result of the lack of a pure 3D structure, forming a SHMT crystal structure with inhibitor present has been unsuccessful.The following links allow for the viewing of secondary structural features and specific residues of the protein.
1)
2)
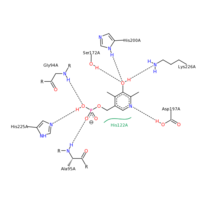
SHMT residue interactions with PLP
SHMT and PLP
The figure on the right shows the PLP binding interactions with specific residues on SHMT. The PLP molecule binds to different residues based upon its orientation in the SHMT PLP binding pocket. Residues G94, H225, and A95 all interact with the phosphate group on PLP. Both G94 and A95 utilize hydrogen bonding between the amide hydrogen and and the oxygen on the phosphate group. In this case, these two residues are proton donors. H225 is an proton acceptor and utilizes the double bonded nitrogen on the Histidine ring to accept a proton from the only hydroxyl group on the phosphate portion of PLP. Residues S172, H200, K226, and D197 all hydrogen bond with the aromatic portion of PLP. S172, H200, and K226 all interact with the hydroxyl group on the aromatic portion of PLP. S172 is a proton donor, H200 is a proton donor, but K226 is a proton acceptor. D197 interacts with the nitrogen within the aromatic ring of PLP. D197 is the proton donor in this case. All of these residues interacting with PLP are polar. PLP has many polar entities including the phosphate, the hydroxyl group on the aromatic ring, and the nitrogen embedded within the aromatic ring. It is no surprise that PLP binds within a polar binding pocket in SHMT. The polar-polar interactions help stabilize the ligand within the binding pocket.
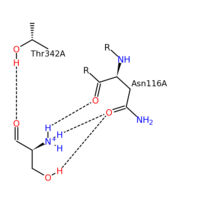
SHMT residue interactions with serine substrate
SHMT and Serine
The figure on the left represents the substrate binding interactions with specific residues of the SHMT enzyme. T342 and N116 are very important residues for substrate binding within PLP. Once again the polar residues of SHMT bind to the polar serine substrate. A key factor for both the PLP and substrate binding is the specific hydrogen donating/accepting by the respective parts. One possible hypothesis to inhibition of SHMT comes from the differences in hydrogen bonding between substrate and inhibitor. In the substrates case, the serine substrate is primarily proton donating. In the case of inhibition through the use of antifolates, there are more hydrogen accepting atoms than hydrogen donating atoms. In fact, the binding portion of tetrahydrofolate (substrate) compared to methotrexate (inhibitor) makes it clear. THF substrate contains three proton donating atoms within the binding portion while methotrexate contains three proton accepting atoms within the binding portion. As we know, hydrogen bonding stabilizes the secondary structure of a protein. When methotrexate is introduced, hydrogen bonding shifts and destabilizes the protein.
Mechanism
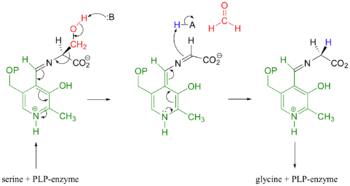
Mechanistic Conversion of Serine to Glycine catalyzed by SHMT
The most widely accepted mechanism of action is through the process of modified retro-aldol cleavage. In this case, the mechanism starts with the serine/PLP-enzyme complex. The base represented by 'B' attacks the hydrogen of the hydroxyl group on serine. Resonance allows the process of tautomerization to occur. This end results of tautomerization results in the formation of a formaldehyde, and acidic 'H-A' compound, and an imine attached to the serine-PLP complex. The double bond of the imine then reacts with the acidic 'H-A' compound. Resonance then allows the new complex to form glycine and the PLP-enzyme.
In the case of serine hydroxymethyltransferase, the pyridoxal-5'-phosphate is the cofactor. The SHMT enzyme has no enzymatic activity without the presence of this cofactor. On the large C-terminal domain, PLP is covalently bound to the N-terminus of an alpha helix following a beta strand. The K226 residue specifically is important for the binding. The amino group on this lysine residue helps bind PLP. The phosphate group of PLP is bound to the N-terminus of the next alpha helix. The PLP will pack against the B strands present. The binding of PLP to SHMT supports conformation of the active site which is located in a space between the two monomeric domains at the border between the two monomeric units of the SHMT dimer. For now, serine and tetrahydrofolate (THF) are the only known biological substrates of SHMT. The end products are of course glycine and 5,10-methylene tetrahydrofolate. If the reaction is flipped, the substrates and products are also flipped. An important point of the SHMT mechanism is that fact that the reaction can start with either serine or glycine as the substrate. As far as inhibitors, antifolates are known to reduce and/or eliminate the enzymatic activity of SHMT. This is not surprising because of the fact that folate compounds are substrates of SHMT.
Applications
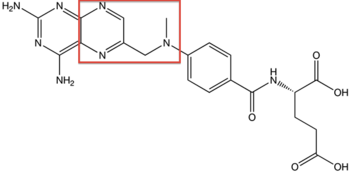
Structure of Methotrexate
Therapeutics
One potential application for SHMT is in cancer-therapeutics. As stated in previous sections, one of the substrates of SHMT is tetrahydrofolate (THF). Anti-folates have been a hot topic of research because of their application to cancer. Methotrexate, the first chemotherapy drug discovered, has been used since the 1950s as a treatment for a variety of autoimmune disorders and as a treatment for cancer. Methotrexate is classified as an anti-folate. Anti-folates are effective because they inhibit the enzymatic activity of a specific proteins. Since SHMT specifically uses THF as a substrate, anti-folates have an even greater potential to become a therapeutic agent by inhibiting the function of SHMT. It has been shown that reductions in SHMT activity directly decrease cancer cell proliferation. It is hypothesized that glycine plays the biggest role. One of the key factors in cancer metastasis is the ability of cancer to establish its own blood supply. To establish its own blood supply and survive as its own entity, cancer must produce heme to oxygenate the system. It is known that Glycine powers the biosynthesis of heme. Since SHMT catalyzes the conversion of Serine to Glycine, the metastasis of cancer is be facilitated by the presence of SHMT. Furthermore, over-expression of SHMT via mutated genes would cause the further proliferation of cancer. Indeed, discoveries of SHMT inhibitors are key in stopping the proliferation and metastasis of cancer.
Smith-Magneis Syndrome (SMS)
This enzyme has important implications in disease and medicine. Smith-Magneis syndrome (SMS) is a genetic disorder that contains a mutation of the cSHMT gene on chromosome 17. The defect causes up to a 50% loss of cytosolic-SHMT. Unlike cancer, which is attributed to the over-expression of SHMT, Smith-Magneis Syndrome results from the under-expression of SHMT. Once again, the glycine product plays an important role. In the case of SMS, glycine production is lacking. NMDA receptors are associated with learning and memory. Glycine must be bound to the NMDA receptor for the efficient opening of ion channels and the subsequent transfer of neurotransmitters. In SMS, since glycine is lacking, there would be less transfer of neurotransmitters to NMDA receptors and thus the progression of SMS symptoms. The diagnosis of Smith-Magneis Syndrome often comes after the diagnosis of psychiatric problems. Many of the symptoms associated with SMS are mental and the physical symptoms can vary from person to person. Currently there is no cure for SMS. Management of symptoms through psychological counseling and medication are currently the only methods used in the treatment of SMS.
References
Citations