This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Sandbox Reserved 820
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 45: | Line 45: | ||
=== Binding sites === | === Binding sites === | ||
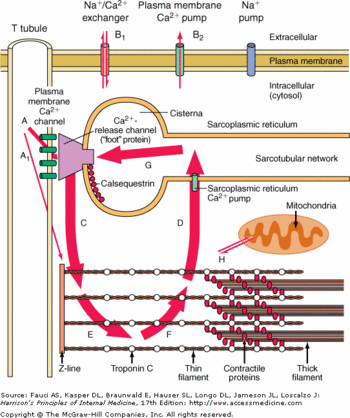
| - | CASQ2 is anchored into the membrane of SR thanks to two integral proteins: the triadin and the junctin.<ref name="Regulation of Ryanodine Receptors by Calsequestrin: Effect of High Luminal Ca2+ and Phosphorylation (Beard et Al., 2005)"> | + | CASQ2 is anchored into the membrane of SR thanks to two integral proteins: the triadin and the junctin.<ref name="Regulation of Ryanodine Receptors by Calsequestrin: Effect of High Luminal Ca2+ and Phosphorylation (Beard et Al., 2005)">PMID:15731387</ref> Triadin as well as Juctin can bind to CASQ2 because of its KEKE motif between the amino acids 210 and 224 for the triadin.<ref name="Regulation of Ryanodine Receptors by Calsequestrin: Effect of High Luminal Ca2+ and Phosphorylation (Beard et Al., 2005)">http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15731387</ref> The binding site of CASQ2 for the both protein is the Asp-rich region of the C-terminal region.<ref name="Regulation of Ryanodine Receptors by Calsequestrin: Effect of High Luminal Ca2+ and Phosphorylation (Beard et Al., 2005)">http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15731387</ref> |
Triadin and Junctin interact with Ryanodin Receptor (RyR).<ref name="Regulation of Ryanodine Receptors by Calsequestrin: Effect of High Luminal Ca2+ and Phosphorylation (Beard et Al., 2005)">http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15731387</ref> | Triadin and Junctin interact with Ryanodin Receptor (RyR).<ref name="Regulation of Ryanodine Receptors by Calsequestrin: Effect of High Luminal Ca2+ and Phosphorylation (Beard et Al., 2005)">http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15731387</ref> | ||
The binding site of CASQ2 to RyR is unknow.<ref name="Regulation of Ryanodine Receptors by Calsequestrin: Effect of High Luminal Ca2+ and Phosphorylation (Beard et Al., 2005)">http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15731387</ref> | The binding site of CASQ2 to RyR is unknow.<ref name="Regulation of Ryanodine Receptors by Calsequestrin: Effect of High Luminal Ca2+ and Phosphorylation (Beard et Al., 2005)">http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15731387</ref> | ||
Revision as of 16:35, 2 January 2014
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 06/12/2018, through 30/06/2019 for use in the course "Structural Biology" taught by Bruno Kieffer at the University of Strasbourg, ESBS. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1480 through Sandbox Reserved 1543. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Cerrone M, Napolitano C, Priori SG. Catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia: A paradigm to understand mechanisms of arrhythmias associated to impaired Ca(2+) regulation. Heart Rhythm. 2009 Nov;6(11):1652-9. doi: 10.1016/j.hrthm.2009.06.033. Epub 2009 , Jun 30. PMID:19879546 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.hrthm.2009.06.033
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 http://www.nature.com/nsmb/journal/v5/n6/abs/nsb0698-476.html
- ↑ http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0014579300022468
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 4.6 4.7 Beard NA, Laver DR, Dulhunty AF. Calsequestrin and the calcium release channel of skeletal and cardiac muscle. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2004 May;85(1):33-69. PMID:15050380 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2003.07.001
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 Beard NA, Casarotto MG, Wei L, Varsanyi M, Laver DR, Dulhunty AF. Regulation of ryanodine receptors by calsequestrin: effect of high luminal Ca2+ and phosphorylation. Biophys J. 2005 May;88(5):3444-54. Epub 2005 Feb 24. PMID:15731387 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1529/biophysj.104.051441